Role of Autophagy in Viral Infection
A topical collection in Cells (ISSN 2073-4409). This collection belongs to the section "Autophagy".
Viewed by 50708Editor
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
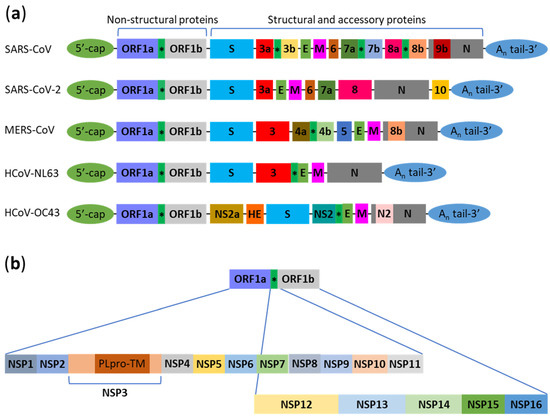
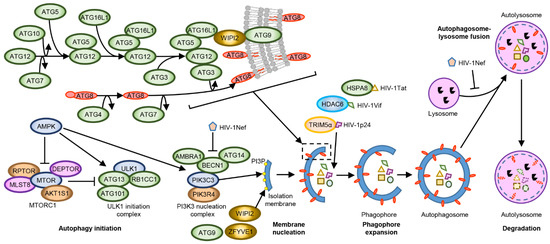
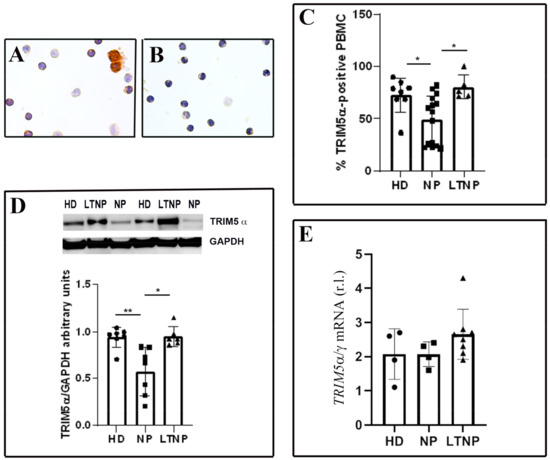
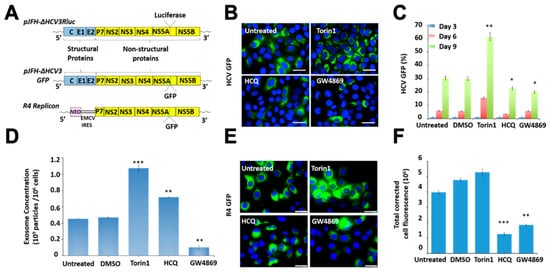
Macroautophagy (hereafter referred to as autophagy) is a degradation pathway whereby cytosolic double-membrane-bound compartments termed autophagosomes engulf cytoplasmic constituents such as sub-cellular organelles and microbial pathogens, and target them for lysosomal degradation. Autophagy is thus an autonomous innate immune defense through which cells can eliminate viruses by capture into autophagosomes with subsequent killing through autophagy. Autophagy can also restrict viral infection by promoting the survival or death of infected cells, control inflammation by cooperating with pattern recognition receptor signaling to induce pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, and coordinate adaptive immunity by delivering virus-derived antigens for presentation to CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. However, viruses can also usurp autophagy to promote their propagation. Examples of the latter include membrane rearrangements, direct antagonism of autophagy proteins, and the prevention of autolysosome maturation.
In this Collection of Cells, I invite you to contribute papers in the form of original research articles, reviews, or shorter perspective articles, on all aspects related to the theme of “Role of Autophagy in Viral Infections”. Expert articles describing mechanistic, functional, cellular, biochemical, or general aspects of the interplay between autophagy and specific viruses (or viruses within a single family) of medical and veterinary importance, as well as future therapeutics using autophagy to control viral infections, are highly welcome.
Dr. Grant R. Campbell
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Cells is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- animal viruses
- autophagy
- human viruses
- immunity
- inflammation
- non-lytic release
- secretory autophagy
- translational medicine
- viral evasion
- viral pathogenesis
- virophagy
- virus
- virus–host interactions
- xenophagy