Functions of Nuclear Receptors
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Prof. Hiroshi Miyamoto
Prof. Hiroshi Miyamoto
 Prof. Hiroshi Miyamoto
Prof. Hiroshi Miyamoto
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Director of Genitourinary Pathology, University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, NY, USA
Interests: nuclear hormone receptors; androgen receptor; glucocorticoid receptor; antiandrogens; glucocorticoids; urothelial cancer; prostate cancer; genitourinary pathology
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Nuclear receptors are a class of proteins classified as transcription factors that regulate the expression of specific genes, including those involving critical biological functions such as development, homeostasis, and metabolism, via binding of their cognate ligands. Nearly 50 nuclear receptor family members encoded in the human/mouse/rat genome have been identified. Recently, a large body of evidence has emerged suggesting that nuclear receptors play an important role in pathological conditions such as the development and progression of neoplasms. However, exact functions of nuclear receptors remain far from being fully understood. The aim of this Topical Collection is to provide an overview of previous and novel findings indicating the functional role of nuclear receptors in physiological conditions as well as a variety of disorders. Original research or review articles on signaling related to any nuclear receptors are most welcome.
Dr. Hiroshi Miyamoto
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Cells is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- nuclear receptors
- steroid hormone receptors
- retinoid receptors
- orphan receptors
- transactivation
- transrepression
- non-genomic effects
- coactivators
- corepressors
- agonists
- antagonists
Published Papers (35 papers)
Open AccessReview
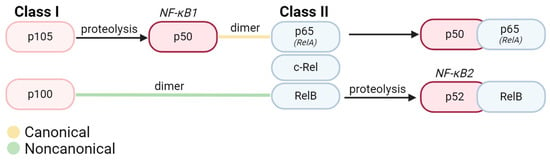
NF-κB as an Inducible Regulator of Inflammation in the Central Nervous System
by
Sudha Anilkumar and Elizabeth Wright-Jin
Viewed by 820
Abstract
The NF-κB (nuclear factor K-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells) transcription factor family is critical for modulating the immune proinflammatory response throughout the body. During the resting state, inactive NF-κB is sequestered by IκB in the cytoplasm. The proteasomal degradation of IκB activates NF-κB,
[...] Read more.
The NF-κB (nuclear factor K-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells) transcription factor family is critical for modulating the immune proinflammatory response throughout the body. During the resting state, inactive NF-κB is sequestered by IκB in the cytoplasm. The proteasomal degradation of IκB activates NF-κB, mediating its translocation into the nucleus to act as a nuclear transcription factor in the upregulation of proinflammatory genes. Stimuli that initiate NF-κB activation are diverse but are canonically attributed to proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines. Downstream effects of NF-κB are cell type-specific and, in the majority of cases, result in the activation of pro-inflammatory cascades. Acting as the primary immune responders of the central nervous system, microglia exhibit upregulation of NF-κB upon activation in response to pathological conditions. Under such circumstances, microglial crosstalk with other cell types in the central nervous system can induce cell death, further exacerbating the disease pathology. In this review, we will emphasize the role of NF-κB in triggering neuroinflammation mediated by microglia.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
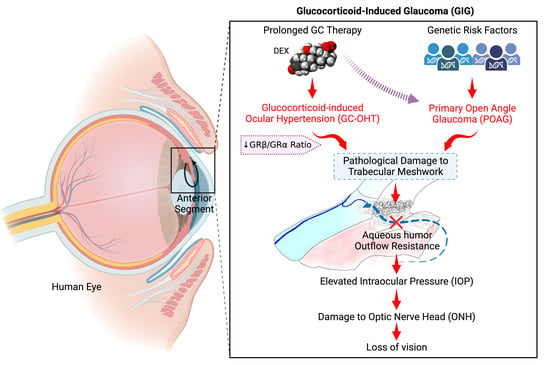
Role of Glucocorticoids and Glucocorticoid Receptors in Glaucoma Pathogenesis
by
Pinkal D. Patel, Bindu Kodati and Abbot F. Clark
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2287
Abstract
The glucocorticoid receptor (GR), including both alternative spliced isoforms (GRα and GRβ), has been implicated in the development of primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) and iatrogenic glucocorticoid-induced glaucoma (GIG). POAG is the most common form of glaucoma, which is the leading cause of irreversible
[...] Read more.
The glucocorticoid receptor (GR), including both alternative spliced isoforms (GRα and GRβ), has been implicated in the development of primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) and iatrogenic glucocorticoid-induced glaucoma (GIG). POAG is the most common form of glaucoma, which is the leading cause of irreversible vision loss and blindness in the world. Glucocorticoids (GCs) are commonly used therapeutically for ocular and numerous other diseases/conditions. One serious side effect of prolonged GC therapy is the development of iatrogenic secondary ocular hypertension (OHT) and OAG (i.e., GC-induced glaucoma (GIG)) that clinically and pathologically mimics POAG. GC-induced OHT is caused by pathogenic damage to the trabecular meshwork (TM), a tissue involved in regulating aqueous humor outflow and intraocular pressure. TM cells derived from POAG eyes (GTM cells) have a lower expression of GRβ, a dominant negative regulator of GC activity, compared to TM cells from age-matched control eyes. Therefore, GTM cells have a greater pathogenic response to GCs. Almost all POAG patients develop GC-OHT when treated with GCs, in contrast to a GC responder rate of 40% in the normal population. An increased expression of GRβ can block GC-induced pathogenic changes in TM cells and reverse GC-OHT in mice. The endogenous expression of GRβ in the TM may relate to differences in the development of GC-OHT in the normal population. A number of studies have suggested increased levels of endogenous cortisol in POAG patients as well as differences in cortisol metabolism, suggesting that GCs may be involved in the development of POAG. Additional studies are warranted to better understand the molecular mechanisms involved in POAG and GIG in order to develop new disease-modifying therapies to better treat these two sight threatening forms of glaucoma. The purpose of this timely review is to highlight the pathological and clinical features of GC-OHT and GIG, mechanisms responsible for GC responsiveness, potential therapeutic options, as well as to compare the similar features of GIG with POAG.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Glucocorticoid Receptor Regulates and Interacts with LEDGF/p75 to Promote Docetaxel Resistance in Prostate Cancer Cells
by
Evelyn S. Sanchez-Hernandez, Pedro T. Ochoa, Tise Suzuki, Greisha L. Ortiz-Hernandez, Juli J. Unternaehrer, Hossam R. Alkashgari, Carlos J. Diaz Osterman, Shannalee R. Martinez, Zhong Chen, Isaac Kremsky, Charles Wang and Carlos A. Casiano
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1462
Abstract
Patients with advanced prostate cancer (PCa) invariably develop resistance to anti-androgen therapy and taxane-based chemotherapy. Glucocorticoid receptor (GR) has been implicated in PCa therapy resistance; however, the mechanisms underlying GR-mediated chemoresistance remain unclear. Lens epithelium-derived growth factor p75 (LEDGF/p75, also known as PSIP1
[...] Read more.
Patients with advanced prostate cancer (PCa) invariably develop resistance to anti-androgen therapy and taxane-based chemotherapy. Glucocorticoid receptor (GR) has been implicated in PCa therapy resistance; however, the mechanisms underlying GR-mediated chemoresistance remain unclear. Lens epithelium-derived growth factor p75 (LEDGF/p75, also known as PSIP1 and DFS70) is a glucocorticoid-induced transcription co-activator implicated in cancer chemoresistance. We investigated the contribution of the GR–LEDGF/p75 axis to docetaxel (DTX)-resistance in PCa cells. GR silencing in DTX-sensitive and -resistant PCa cells decreased LEDGF/p75 expression, and GR upregulation in enzalutamide-resistant cells correlated with increased LEDGF/p75 expression. ChIP-sequencing revealed GR binding sites in the LEDGF/p75 promoter. STRING protein–protein interaction analysis indicated that GR and LEDGF/p75 belong to the same transcriptional network, and immunochemical studies demonstrated their co-immunoprecipitation and co-localization in DTX-resistant cells. The GR modulators exicorilant and relacorilant increased the sensitivity of chemoresistant PCa cells to DTX-induced cell death, and this effect was more pronounced upon LEDGF/p75 silencing. RNA-sequencing of DTX-resistant cells with GR or LEDGF/p75 knockdown revealed a transcriptomic overlap targeting signaling pathways associated with cell survival and proliferation, cancer, and therapy resistance. These studies implicate the GR–LEDGF/p75 axis in PCa therapy resistance and provide a pre-clinical rationale for developing novel therapeutic strategies for advanced PCa.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
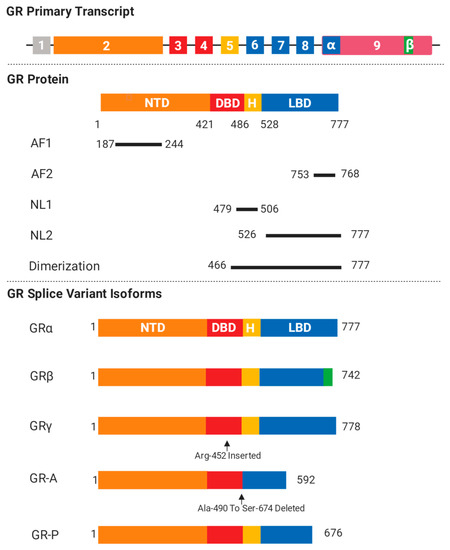
The Biologist’s Guide to the Glucocorticoid Receptor’s Structure
by
Nick Deploey, Laura Van Moortel, Inez Rogatsky, Frank Peelman and Karolien De Bosscher
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2928
Abstract
The glucocorticoid receptor α (GRα) is a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily and functions as a glucocorticoid (GC)-responsive transcription factor. GR can halt inflammation and kill off cancer cells, thus explaining the widespread use of glucocorticoids in the clinic. However, side effects
[...] Read more.
The glucocorticoid receptor α (GRα) is a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily and functions as a glucocorticoid (GC)-responsive transcription factor. GR can halt inflammation and kill off cancer cells, thus explaining the widespread use of glucocorticoids in the clinic. However, side effects and therapy resistance limit GR’s therapeutic potential, emphasizing the importance of resolving all of GR’s context-specific action mechanisms. Fortunately, the understanding of GR structure, conformation, and stoichiometry in the different GR-controlled biological pathways is now gradually increasing. This information will be crucial to close knowledge gaps on GR function. In this review, we focus on the various domains and mechanisms of action of GR, all from a structural perspective.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
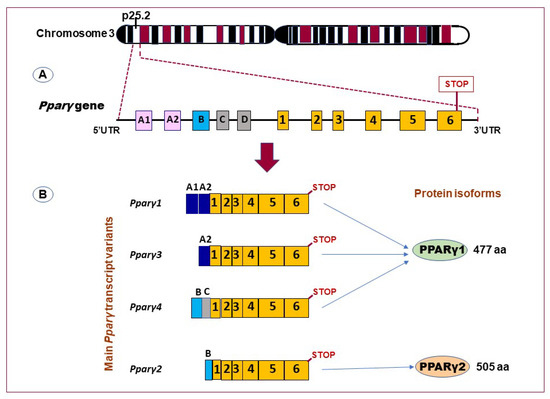
Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-γ as a Target and Regulator of Epigenetic Mechanisms in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
by
Mohamed Zaiou
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 2043
Abstract
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ) belongs to the superfamily of nuclear receptors that control the transcription of multiple genes. Although it is found in many cells and tissues, PPARγ is mostly expressed in the liver and adipose tissue. Preclinical and clinical studies show that
[...] Read more.
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ) belongs to the superfamily of nuclear receptors that control the transcription of multiple genes. Although it is found in many cells and tissues, PPARγ is mostly expressed in the liver and adipose tissue. Preclinical and clinical studies show that PPARγ targets several genes implicated in various forms of chronic liver disease, including nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Clinical trials are currently underway to investigate the beneficial effects of PPARγ agonists on NAFLD/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Understanding PPARγ regulators may therefore aid in unraveling the mechanisms governing the development and progression of NAFLD. Recent advances in high-throughput biology and genome sequencing have greatly facilitated the identification of epigenetic modifiers, including DNA methylation, histone modifiers, and non-coding RNAs as key factors that regulate PPARγ in NAFLD. In contrast, little is still known about the particular molecular mechanisms underlying the intricate relationships between these events. The paper that follows outlines our current understanding of the crosstalk between PPARγ and epigenetic regulators in NAFLD. Advances in this field are likely to aid in the development of early noninvasive diagnostics and future NAFLD treatment strategies based on PPARγ epigenetic circuit modification.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
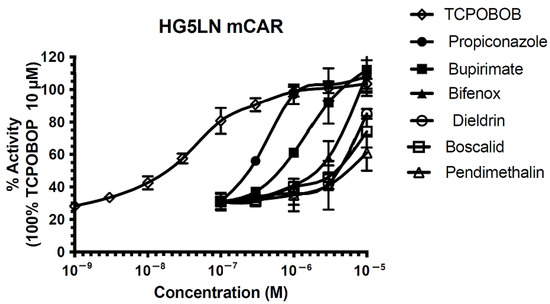
Steatosis and Metabolic Disorders Associated with Synergistic Activation of the CAR/RXR Heterodimer by Pesticides
by
Yannick Dauwe, Lucile Mary, Fabiana Oliviero, Marina Grimaldi, Patrick Balaguer, Véronique Gayrard and Laïla Mselli-Lakhal
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1634
Abstract
The nuclear receptor, constitutive androstane receptor (CAR), which forms a heterodimer with the retinoid X receptor (RXR), was initially reported as a transcription factor that regulates hepatic genes involved in detoxication and energy metabolism. Different studies have shown that CAR activation results in
[...] Read more.
The nuclear receptor, constitutive androstane receptor (CAR), which forms a heterodimer with the retinoid X receptor (RXR), was initially reported as a transcription factor that regulates hepatic genes involved in detoxication and energy metabolism. Different studies have shown that CAR activation results in metabolic disorders, including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, by activating lipogenesis in the liver. Our objective was to determine whether synergistic activations of the CAR/RXR heterodimer could occur in vivo as described in vitro by other authors, and to assess the metabolic consequences. For this purpose, six pesticides, ligands of CAR, were selected, and Tri-butyl-tin (TBT) was used as an RXR agonist. In mice, CAR’s synergic activation was induced by dieldrin associated with TBT, and combined effects were induced by propiconazole, bifenox, boscalid, and bupirimate. Moreover, a steatosis, characterized by increased triglycerides, was observed when TBT was combined with dieldrin, propiconazole, bifenox, boscalid, and bupirimate. Metabolic disruption appeared in the form of increased cholesterol and lowered free fatty acid plasma levels. An in-depth analysis revealed increased expression of genes involved in lipid synthesis and lipid import. These results contribute to the growing understanding of how environmental contaminants can influence nuclear receptor activity and associated health risks.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
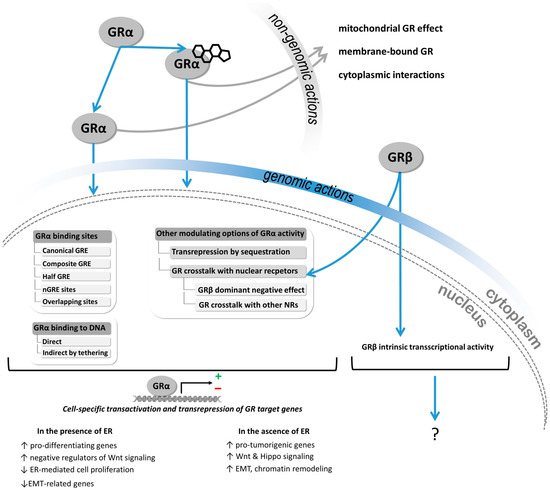
Context-Dependent Role of Glucocorticoid Receptor Alpha and Beta in Breast Cancer Cell Behaviour
by
Henriett Butz, Éva Saskői, Lilla Krokker, Viktória Vereczki, Alán Alpár, István Likó, Erika Tóth, Erika Szőcs, Mihály Cserepes, Katalin Nagy, Imre Kacskovics and Attila Patócs
Viewed by 1865
Abstract
Background. The dual role of GCs has been observed in breast cancer; however, due to many concomitant factors, GR action in cancer biology is still ambiguous. In this study, we aimed to unravel the context-dependent action of GR in breast cancer.
Methods
[...] Read more.
Background. The dual role of GCs has been observed in breast cancer; however, due to many concomitant factors, GR action in cancer biology is still ambiguous. In this study, we aimed to unravel the context-dependent action of GR in breast cancer.
Methods. GR expression was characterized in multiple cohorts: (1) 24,256 breast cancer specimens on the RNA level, 220 samples on the protein level and correlated with clinicopathological data; (2) oestrogen receptor (ER)-positive and -negative cell lines were used to test for the presence of ER and ligand, and the effect of the GRβ isoform following GRα and GRβ overexpression on GR action, by in vitro functional assays.
Results. We found that GR expression was higher in ER− breast cancer cells compared to ER+ ones, and GR-transactivated genes were implicated mainly in cell migration. Immunohistochemistry showed mostly cytoplasmic but heterogenous staining irrespective of ER status. GRα increased cell proliferation, viability, and the migration of ER− cells. GRβ had a similar effect on breast cancer cell viability, proliferation, and migration. However, the GRβ isoform had the opposite effect depending on the presence of ER: an increased dead cell ratio was found in ER+ breast cancer cells compared to ER− ones. Interestingly, GRα and GRβ action did not depend on the presence of the ligand, suggesting the role of the “intrinsic”, ligand-independent action of GR in breast cancer.
Conclusions. Staining differences using different GR antibodies may be the reason behind controversial findings in the literature regarding the expression of GR protein and clinicopathological data. Therefore, caution in the interpretation of immunohistochemistry should be applied. By dissecting the effects of GRα and GRβ, we found that the presence of the GR in the context of ER had a different effect on cancer cell behaviour, but independently of ligand availability. Additionally, GR-transactivated genes are mostly involved in cell migration, which raises GR’s importance in disease progression.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
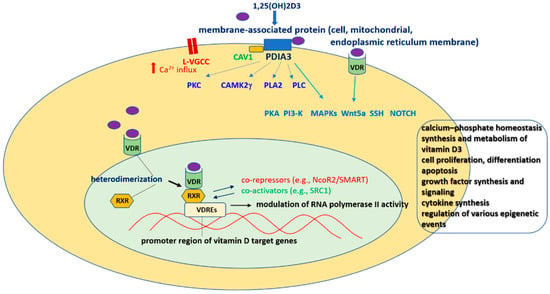
The Vitamin D Receptor as a Potential Target for the Treatment of Age-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases Such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases: A Narrative Review
by
Władysław Lasoń, Danuta Jantas, Monika Leśkiewicz, Magdalena Regulska and Agnieszka Basta-Kaim
Cited by 22 | Viewed by 3932
Abstract
The vitamin D receptor (VDR) belongs to the nuclear receptor superfamily of transcription factors. The VDR is expressed in diverse brain regions and has been implicated in the neuroprotective, antiaging, prosurvival, and anti-inflammatory action of vitamin D. Accordingly, a relationship between vitamin D
[...] Read more.
The vitamin D receptor (VDR) belongs to the nuclear receptor superfamily of transcription factors. The VDR is expressed in diverse brain regions and has been implicated in the neuroprotective, antiaging, prosurvival, and anti-inflammatory action of vitamin D. Accordingly, a relationship between vitamin D insufficiency and susceptibility to neurodegenerative diseases has been suggested. However, due to the multitargeted mechanisms of vitamin D and its often overlapping genomic and nongenomic effects, the role of the VDR in brain pathologies remains obscure. In this narrative review, we present progress in deciphering the molecular mechanism of nuclear VDR-mediated vitamin D effects on prosurvival and anti-inflammatory signaling pathway activity within the central nervous system. In line with the concept of the neurovascular unit in pathomechanisms of neurodegenerative diseases, a discussion of the role of the VDR in regulating the immune and vascular brain systems is also included. Next, we discuss the results of preclinical and clinical studies evaluating the significance of vitamin D status and the efficacy of vitamin D supplementation in the treatment of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases, emphasizing the possible role of the VDR in these phenomena. Finally, the associations of some VDR polymorphisms with higher risks and severity of these neurodegenerative disorders are briefly summarized.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
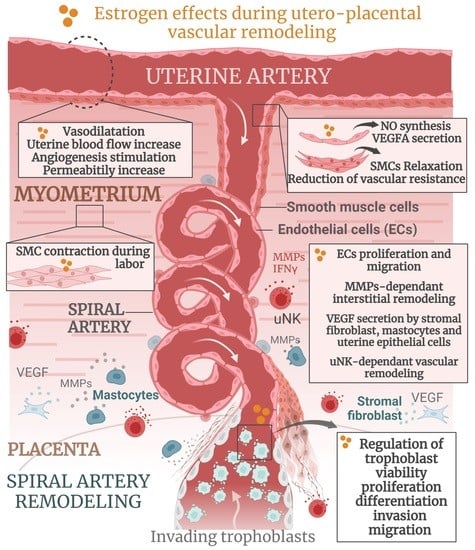
Estrogen Actions in Placental Vascular Morphogenesis and Spiral Artery Remodeling: A Comparative View between Humans and Mice
by
Mariam Rusidzé, Adrien Gargaros, Chanaëlle Fébrissy, Charlotte Dubucs, Ariane Weyl, Jessie Ousselin, Jacqueline Aziza, Jean-François Arnal and Françoise Lenfant
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 4022
Abstract
Estrogens, mainly 17β-estradiol (E2), play a critical role in reproductive organogenesis, ovulation, and fertility via estrogen receptors. E2 is also a well-known regulator of utero-placental vascular development and blood-flow dynamics throughout gestation. Mouse and human placentas possess strikingly different morphological configurations that confer
[...] Read more.
Estrogens, mainly 17β-estradiol (E2), play a critical role in reproductive organogenesis, ovulation, and fertility via estrogen receptors. E2 is also a well-known regulator of utero-placental vascular development and blood-flow dynamics throughout gestation. Mouse and human placentas possess strikingly different morphological configurations that confer important reproductive advantages. However, the functional interplay between fetal and maternal vasculature remains similar in both species. In this review, we briefly describe the structural and functional characteristics, as well as the development, of mouse and human placentas. In addition, we summarize the current knowledge regarding estrogen actions during utero-placental vascular morphogenesis, which includes uterine angiogenesis, the control of trophoblast behavior, spiral artery remodeling, and hemodynamic adaptation throughout pregnancy, in both mice and humans. Finally, the estrogens that are present in abnormal placentation are also mentioned. Overall, this review highlights the importance of the actions of estrogens in the physiology and pathophysiology of placental vascular development.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
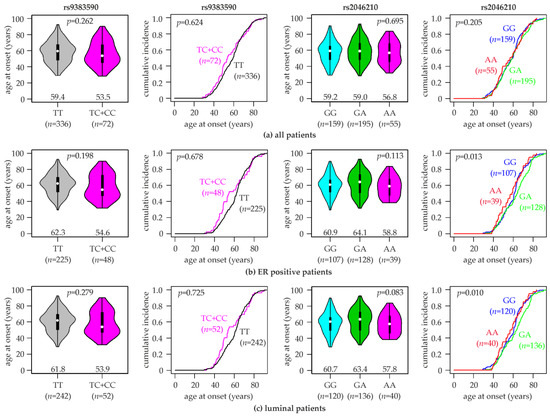
Association of the Estrogen Receptor 1 Polymorphisms rs2046210 and rs9383590 with the Risk, Age at Onset and Prognosis of Breast Cancer
by
Heidi Miedl, Denise Oswald, Isabella Haslinger, Manuela Gstoettner, René Wenzl, Katharina Proestling, Christian Schneeberger, Iveta Yotova and Martin Schreiber
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 1585
Abstract
Estrogen receptor α (ERα), encoded by the
ESR1 gene, is a key prognostic and predictive biomarker firmly established in routine diagnostics and as a therapeutic target of breast cancer, and it has a central function in breast cancer biology. Genetic variants at 6q25.1,
[...] Read more.
Estrogen receptor α (ERα), encoded by the
ESR1 gene, is a key prognostic and predictive biomarker firmly established in routine diagnostics and as a therapeutic target of breast cancer, and it has a central function in breast cancer biology. Genetic variants at 6q25.1, containing the
ESR1 gene, were found to be associated with breast cancer susceptibility. The rs2046210 and rs9383590 single nucleotide variants (SNVs) are located in the same putative enhancer region upstream of
ESR1 and were separately identified as candidate causal variants responsible for these associations. Here, both SNVs were genotyped in a hospital-based case-control study of 409 female breast cancer patients and 422 female controls of a Central European (Austrian) study population. We analyzed the association of both SNVs with the risk, age at onset, clinically and molecularly relevant characteristics and prognosis of breast cancer. We also assessed the concordances between both SNVs and the associations of each SNV conditional on the other SNV. The minor alleles of both SNVs were found to be non-significantly associated with an increased breast cancer risk. Significant associations were found in specific subpopulations, particularly in patients with an age younger than 55 years. The minor homozygotes of rs2046210 and the minor homozygotes plus heterozygotes of rs9383590 exhibited a several-years-younger age at onset than the common homozygotes, which was more pronounced in ER-positive and luminal patients. Importantly, the observed associations of each SNV were not consistently nullified upon correction for the other SNV nor upon analyses in common homozygotes for the other SNV. We conclude that both SNVs remain independent candidate causal variants.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Vitamin D Receptor Expression Limits the Angiogenic and Inflammatory Properties of Retinal Endothelial Cells
by
Yong-Seok Song, Nasim Jamali, Christine M. Sorenson and Nader Sheibani
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2316
Abstract
The integrity of retinal endothelial cell (EC) is essential for establishing and maintaining the retinal blood barrier to ensure proper vision. Vitamin D is a hormone with known protective roles in EC function. The majority of vitamin D action is mediated through the
[...] Read more.
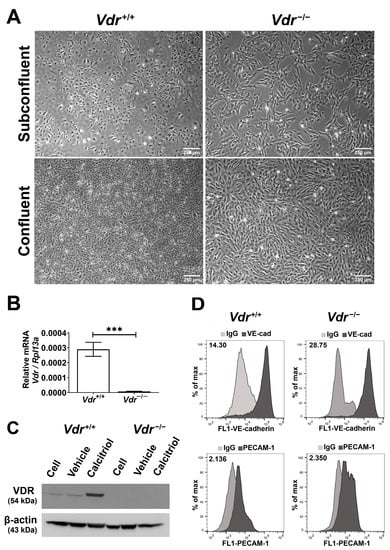
The integrity of retinal endothelial cell (EC) is essential for establishing and maintaining the retinal blood barrier to ensure proper vision. Vitamin D is a hormone with known protective roles in EC function. The majority of vitamin D action is mediated through the vitamin D receptor (VDR). VDR is a nuclear receptor whose engagement by vitamin D impacts the expression of many genes with important roles in regulation of angiogenesis and inflammation. Although many studies have investigated vitamin D-VDR action in cardiovascular protection and tumor angiogenesis, its impact on retinal EC function and regulation of ocular angiogenesis and inflammation is exceedingly limited. We previously showed calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D, is a potent inhibitor of retinal neovascularization in vivo and retinal EC capillary morphogenesis in vitro. Here, using retinal EC prepared from wild-type (
Vdr+/+) and VDR-deficient (
Vdr−/−) mice, we show that retinal EC express VDR and its expression is induced by calcitriol. The lack of VDR expression had a significant impact on endothelial cell–cell and cell–matrix interactions.
Vdr−/− retinal EC proliferated at a slower rate and were more adherent and less migratory. They also exhibited increased expression levels of inflammatory markers driven in part by sustained activation of STAT1 and NF-κB pathways and were more sensitive to oxidative challenge. These changes were attributed, in part, to down-regulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthetase, enhanced hepcidin expression, and increased intracellular iron levels. Taken together, our results indicate that VDR expression plays a fundamental role in maintaining the proper angiogenic and inflammatory state of retinal EC.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Retinoic Acid Signalling in the Pineal Gland Is Conserved across Mammalian Species and Its Transcriptional Activity Is Inhibited by Melatonin
by
Anna Ashton, Jason Clark, Julia Fedo, Angelo Sementilli, Yara D. Fragoso and Peter McCaffery
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 1580
Abstract
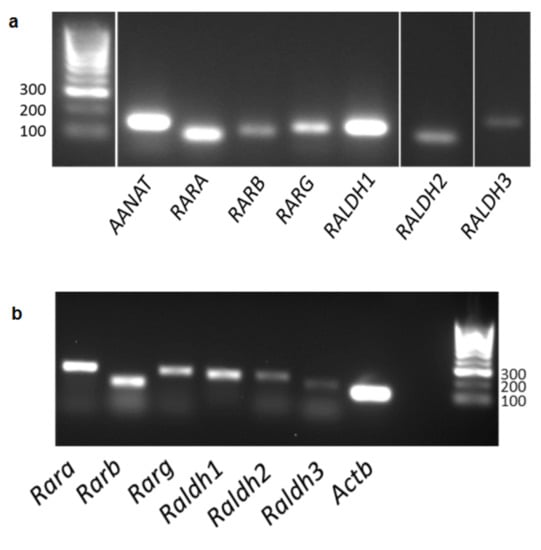
The pineal gland is integral to the circadian timing system due to its role in nightly melatonin production. Retinoic acid (RA) is a potent regulator of gene transcription and has previously been found to exhibit diurnal changes in synthesis and signalling in the
[...] Read more.
The pineal gland is integral to the circadian timing system due to its role in nightly melatonin production. Retinoic acid (RA) is a potent regulator of gene transcription and has previously been found to exhibit diurnal changes in synthesis and signalling in the rat pineal gland. This study investigated the potential for the interaction of these two systems. PCR was used to study gene expression in mouse and human pineal glands, ex-vivo organotypic cultured rat pineal gland and cell lines. The mouse and human pineal glands were both found to express the necessary components required for RA signalling. RA influences the circadian clock in the brain, therefore the short-term effect of RA on clock gene expression was determined in ex vivo rat pineal glands but was not found to rapidly regulate
Per1,
Per2,
Bmal1, or
Cry1. The interaction between RA and melatonin was also investigated and, unexpectedly, melatonin was found to suppress the induction of gene transcription by RA. This study demonstrates that pineal expression of the RA signalling system is conserved across mammalian species. There is no short-term regulation of the circadian clock but an inhibitory effect of melatonin on RA transcriptional activity was demonstrated, suggesting that there may be functional cross-talk between these systems.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Structure-Based Study to Overcome Cross-Reactivity of Novel Androgen Receptor Inhibitors
by
Mariia Radaeva, Huifang Li, Eric LeBlanc, Kush Dalal, Fuqiang Ban, Fabrice Ciesielski, Bonny Chow, Helene Morin, Shannon Awrey, Kriti Singh, Paul S. Rennie, Nada Lallous and Artem Cherkasov
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2203
Abstract
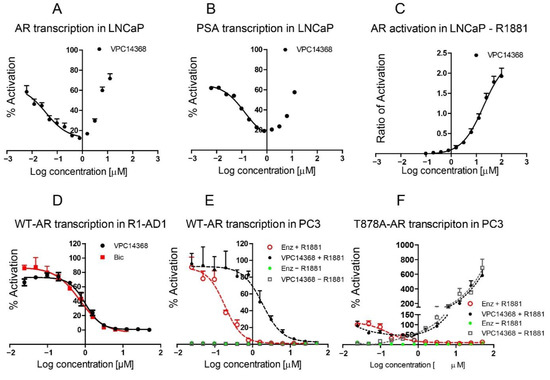
The mutation-driven transformation of clinical anti-androgen drugs into agonists of the human androgen receptor (AR) represents a major challenge for the treatment of prostate cancer patients. To address this challenge, we have developed a novel class of inhibitors targeting the DNA-binding domain (DBD)
[...] Read more.
The mutation-driven transformation of clinical anti-androgen drugs into agonists of the human androgen receptor (AR) represents a major challenge for the treatment of prostate cancer patients. To address this challenge, we have developed a novel class of inhibitors targeting the DNA-binding domain (DBD) of the receptor, which is distanced from the androgen binding site (ABS) targeted by all conventional anti-AR drugs and prone to resistant mutations. While many members of the developed 4-(4-phenylthiazol-2-yl)morpholine series of AR-DBD inhibitors demonstrated the effective suppression of wild-type AR, a few represented by 4-(4-(3-fluoro-2-methoxyphenyl)thiazol-2-yl)morpholine (VPC14368) exhibited a partial agonistic effect toward the mutated T878A form of the receptor, implying their cross-interaction with the AR ABS. To study the molecular basis of the observed cross-reactivity, we co-crystallized the T878A mutated form of the AR ligand binding domain (LBD) with a bound VPC14368 molecule. Computational modelling revealed that helix 12 of AR undergoes a characteristic shift upon VPC14368 binding causing the agonistic behaviour. Based on the obtained structural data we then designed derivatives of VPC14368 to successfully eliminate the cross-reactivity towards the AR ABS, while maintaining significant anti-AR DBD potency.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals, Hormone Receptors, and Acne Vulgaris: A Connecting Hypothesis
by
Akshatha Rao, Sotonye C. Douglas and Julianne M. Hall
Cited by 27 | Viewed by 11583
Abstract
The relationship between endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and the pathogenesis of acne vulgaris has yet to be explored in the literature. Acne vulgaris is a chronic inflammatory skin disease of the pilosebaceous unit. The pathogenesis of acne involves several hormonal pathways, including androgens,
[...] Read more.
The relationship between endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and the pathogenesis of acne vulgaris has yet to be explored in the literature. Acne vulgaris is a chronic inflammatory skin disease of the pilosebaceous unit. The pathogenesis of acne involves several hormonal pathways, including androgens, insulin-like growth factor 1(IGF-1), estrogens, and corticosteroids. EDCs influence these pathways primarily through two mechanisms: altering endogenous hormone levels and interfering with hormone receptor function. This review article describes the mechanistic links between EDCs and the development of acne lesions. Highlighted is the contributory role of androgen receptor ligands, such as bisphenol A (BPA) and mono-2-ethylhexyl Phthalate (MEHP), via upregulation of lipogenic genes and resultant exacerbation of cholesterol synthesis. Additionally discussed is the protective role of phytoestrogen EDCs in counteracting androgen-induced sebocyte maturation through attenuation of PPARy transcriptional activity (i.e., resveratrol) and restoration of estrogen-regulated TGF-B expression in skin cells (i.e., genistein). Examination of the relationship between EDCs and acne vulgaris may inform adjunctive avenues of treatment such as limiting environmental exposures, and increasing low-glycemic, plant-rich foods in the diet. With a better understanding of the cumulative role that EDCs play in acne, clinicians can be better equipped to treat and ultimately improve the lives of their patients.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
Sex Hormone Receptor Signaling in Bladder Cancer: A Potential Target for Enhancing the Efficacy of Conventional Non-Surgical Therapy
by
Hiroki Ide and Hiroshi Miyamoto
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 3477
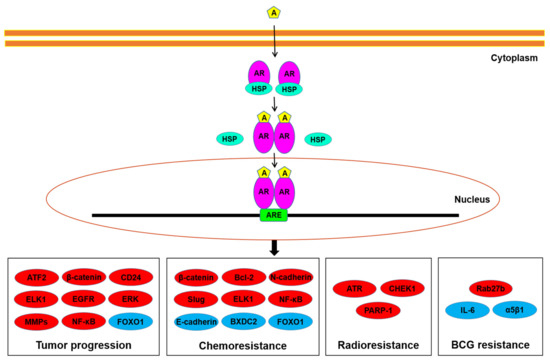
Abstract
There have been critical problems in the non-surgical treatment for bladder cancer, especially residence to intravesical pharmacotherapy, including BCG immunotherapy, cisplatin-based chemotherapy, and radiotherapy. Recent preclinical and clinical evidence has suggested a vital role of sex steroid hormone-mediated signaling in the progression of
[...] Read more.
There have been critical problems in the non-surgical treatment for bladder cancer, especially residence to intravesical pharmacotherapy, including BCG immunotherapy, cisplatin-based chemotherapy, and radiotherapy. Recent preclinical and clinical evidence has suggested a vital role of sex steroid hormone-mediated signaling in the progression of urothelial cancer. Moreover, activation of the androgen receptor and estrogen receptor pathways has been implicated in modulating sensitivity to conventional non-surgical therapy for bladder cancer. This may indicate the possibility of anti-androgenic and anti-estrogenic drugs, apart from their direct anti-tumor activity, to function as sensitizers of such conventional treatment. This article summarizes available data suggesting the involvement of sex hormone receptors, such as androgen receptor, estrogen receptor-α, and estrogen receptor-β, in the progression of urothelial cancer, focusing on their modulation for the efficacy of conventional therapy, and discusses their potential of overcoming therapeutic resistance.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
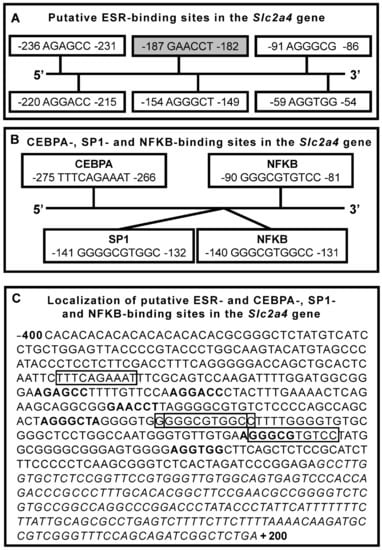
Estrogen and Glycemic Homeostasis: The Fundamental Role of Nuclear Estrogen Receptors ESR1/ESR2 in Glucose Transporter GLUT4 Regulation
by
Karen Cristina Rego Gregorio, Caroline Pancera Laurindo and Ubiratan Fabres Machado
Cited by 35 | Viewed by 4355
Abstract
Impaired circulating estrogen levels have been related to impaired glycemic homeostasis and diabetes mellitus (DM), both in females and males. However, for the last twenty years, the relationship between estrogen, glycemic homeostasis and the mechanisms involved has remained unclear. The characterization of estrogen
[...] Read more.
Impaired circulating estrogen levels have been related to impaired glycemic homeostasis and diabetes mellitus (DM), both in females and males. However, for the last twenty years, the relationship between estrogen, glycemic homeostasis and the mechanisms involved has remained unclear. The characterization of estrogen receptors 1 and 2 (ESR1 and ESR2) and of insulin-sensitive glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4) finally offered a great opportunity to shed some light on estrogen regulation of glycemic homeostasis. In this manuscript, we review the relationship between estrogen and DM, focusing on glycemic homeostasis, estrogen, ESR1/ESR2 and GLUT4. We review glycemic homeostasis and GLUT4 expression (muscle and adipose tissues) in
Esr1−/− and
Esr2−/− transgenic mice. We specifically address estradiol-induced and ESR1/ESR2-mediated regulation of the
solute carrier family 2 member 4 (
Slc2a4) gene, examining ESR1/ESR2-mediated genomic mechanisms that regulate
Slc2a4 transcription, especially those occurring in cooperation with other transcription factors. In addition, we address the estradiol-induced translocation of ESR1 and GLUT4 to the plasma membrane. Studies make it clear that ESR1-mediated effects are beneficial, whereas ESR2-mediated effects are detrimental to glycemic homeostasis. Thus, imbalance of the ESR1/ESR2 ratio may have important consequences in metabolism, highlighting that ESR2 hyperactivity assumes a diabetogenic role.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
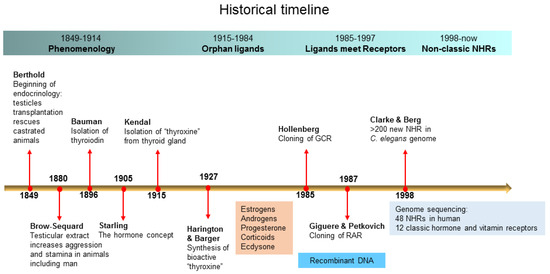
Open AccessReview
Nuclear Hormone Receptors and Their Ligands: Metabolites in Control of Transcription
by
Lian Jing Tao, Dong Eun Seo, Benjamin Jackson, Natalia B. Ivanova and Fabio Rinaldo Santori
Cited by 17 | Viewed by 4403
Abstract
Nuclear hormone receptors are a family of transcription factors regulated by small molecules derived from the endogenous metabolism or diet. There are forty-eight nuclear hormone receptors in the human genome, twenty of which are still orphans. In this review, we make a brief
[...] Read more.
Nuclear hormone receptors are a family of transcription factors regulated by small molecules derived from the endogenous metabolism or diet. There are forty-eight nuclear hormone receptors in the human genome, twenty of which are still orphans. In this review, we make a brief historical journey from the first observations by Berthold in 1849 to the era of orphan receptors that began with the sequencing of the
Caenorhabditis elegans genome in 1998. We discuss the evolution of nuclear hormone receptors and the putative ancestral ligands as well as how the ligand universe has expanded over time. This leads us to define four classes of metabolites—fatty acids, terpenoids, porphyrins and amino acid derivatives—that generate all known ligands for nuclear hormone receptors. We conclude by discussing the ongoing efforts to identify new classes of ligands for orphan receptors.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
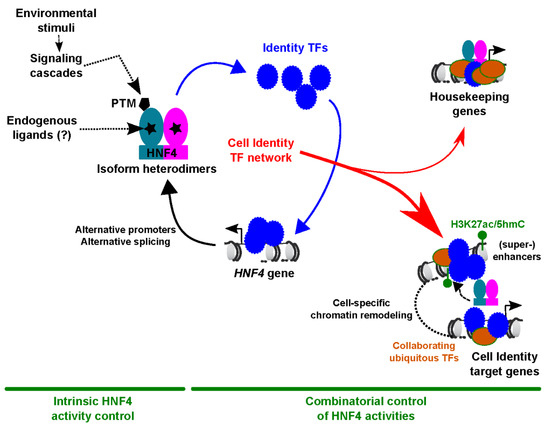
Control of Cell Identity by the Nuclear Receptor HNF4 in Organ Pathophysiology
by
Vanessa Dubois, Bart Staels, Philippe Lefebvre, Michael P. Verzi and Jérôme Eeckhoute
Cited by 34 | Viewed by 4838
Abstract
Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4 (HNF4) is a transcription factor (TF) belonging to the nuclear receptor family whose expression and activities are restricted to a limited number of organs including the liver and gastrointestinal tract. In this review, we present robust evidence pointing to
[...] Read more.
Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4 (HNF4) is a transcription factor (TF) belonging to the nuclear receptor family whose expression and activities are restricted to a limited number of organs including the liver and gastrointestinal tract. In this review, we present robust evidence pointing to HNF4 as a master regulator of cellular differentiation during development and a safekeeper of acquired cell identity in adult organs. Importantly, we discuss that transient loss of HNF4 may represent a protective mechanism upon acute organ injury, while prolonged impairment of HNF4 activities could contribute to organ dysfunction. In this context, we describe in detail mechanisms involved in the pathophysiological control of cell identity by HNF4, including how HNF4 works as part of cell-specific TF networks and how its expression/activities are disrupted in injured organs.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
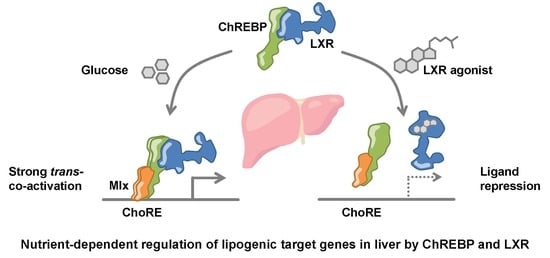
LXRα Regulates ChREBPα Transactivity in a Target Gene-Specific Manner through an Agonist-Modulated LBD-LID Interaction
by
Qiong Fan, Rikke Christine Nørgaard, Ivar Grytten, Cecilie Maria Ness, Christin Lucas, Kristin Vekterud, Helen Soedling, Jason Matthews, Roza Berhanu Lemma, Odd Stokke Gabrielsen, Christian Bindesbøll, Stine Marie Ulven, Hilde Irene Nebb, Line Mariann Grønning-Wang and Thomas Sæther
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 5901
Abstract
The cholesterol-sensing nuclear receptor liver X receptor (LXR) and the glucose-sensing transcription factor carbohydrate responsive element-binding protein (ChREBP) are central players in regulating glucose and lipid metabolism in the liver. More knowledge of their mechanistic interplay is needed to understand their role in
[...] Read more.
The cholesterol-sensing nuclear receptor liver X receptor (LXR) and the glucose-sensing transcription factor carbohydrate responsive element-binding protein (ChREBP) are central players in regulating glucose and lipid metabolism in the liver. More knowledge of their mechanistic interplay is needed to understand their role in pathological conditions like fatty liver disease and insulin resistance. In the current study, LXR and ChREBP co-occupancy was examined by analyzing ChIP-seq datasets from mice livers. LXR and ChREBP interaction was determined by Co-immunoprecipitation (CoIP) and their transactivity was assessed by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) of target genes and gene reporter assays. Chromatin binding capacity was determined by ChIP-qPCR assays. Our data show that LXRα and ChREBPα interact physically and show a high co-occupancy at regulatory regions in the mouse genome. LXRα co-activates ChREBPα and regulates ChREBP-specific target genes in vitro and in vivo. This co-activation is dependent on functional recognition elements for ChREBP but not for LXR, indicating that ChREBPα recruits LXRα to chromatin in
trans. The two factors interact via their key activation domains; the low glucose inhibitory domain (LID) of ChREBPα and the ligand-binding domain (LBD) of LXRα. While unliganded LXRα co-activates ChREBPα, ligand-bound LXRα surprisingly represses ChREBPα activity on ChREBP-specific target genes. Mechanistically, this is due to a destabilized LXRα:ChREBPα interaction, leading to reduced ChREBP-binding to chromatin and restricted activation of glycolytic and lipogenic target genes. This ligand-driven molecular switch highlights an unappreciated role of LXRα in responding to nutritional cues that was overlooked due to LXR lipogenesis-promoting function.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
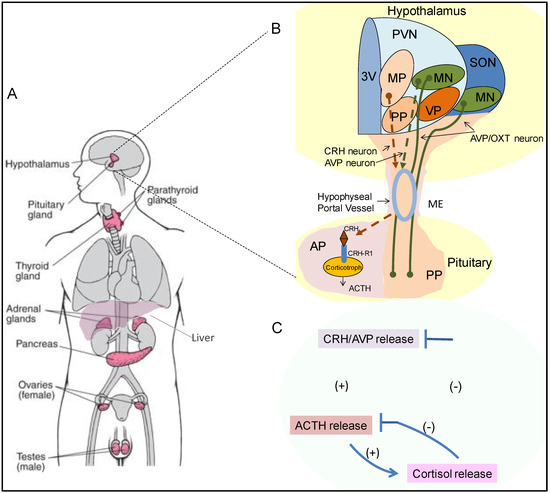
Nuclear Receptors as Regulators of Pituitary Corticotroph Pro-Opiomelanocortin Transcription
by
Dongyun Zhang and Anthony P. Heaney
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 5712
Abstract
The hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis plays a critical role in adaptive stress responses and maintaining organism homeostasis. The pituitary corticotroph is the central player in the HPA axis and is regulated by a plethora of hormonal and stress related factors that synergistically interact to
[...] Read more.
The hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis plays a critical role in adaptive stress responses and maintaining organism homeostasis. The pituitary corticotroph is the central player in the HPA axis and is regulated by a plethora of hormonal and stress related factors that synergistically interact to activate and temper pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) transcription, to either increase or decrease adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) production and secretion as needed. Nuclear receptors are a family of highly conserved transcription factors that can also be induced by various physiologic signals, and they mediate their responses via multiple targets to regulate metabolism and homeostasis. In this review, we summarize the modulatory roles of nuclear receptors on pituitary corticotroph cell POMC transcription, describe the unique and complex role these factors play in hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis (HPA) regulation and discuss potential therapeutic targets in disease states.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
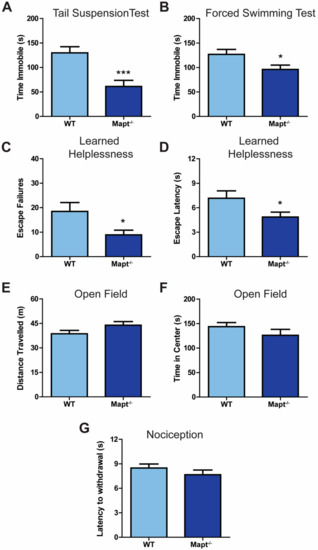
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
Hippocampal Neurogenesis Is Enhanced in Adult Tau Deficient Mice
by
Marangelie Criado-Marrero, Jonathan J. Sabbagh, Margaret R. Jones, Dale Chaput, Chad A. Dickey and Laura J. Blair
Cited by 21 | Viewed by 4941
Abstract
Tau dysfunction is common in several neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD). Affective symptoms have often been associated with aberrant tau pathology and are commonly comorbid in patients with tauopathies, indicating a connection between tau functioning and mechanisms of
[...] Read more.
Tau dysfunction is common in several neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD). Affective symptoms have often been associated with aberrant tau pathology and are commonly comorbid in patients with tauopathies, indicating a connection between tau functioning and mechanisms of depression. The current study investigated depression-like behavior in
Mapt−/− mice, which contain a targeted deletion of the gene coding for tau. We show that 6-month
Mapt−/− mice are resistant to depressive behaviors, as evidenced by decreased immobility time in the forced swim and tail suspension tests, as well as increased escape behavior in a learned helplessness task. Since depression has also been linked to deficient adult neurogenesis, we measured neurogenesis in the hippocampal dentate gyrus and subventricular zone using 5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine (BrdU) labeling. We found that neurogenesis is increased in the dentate gyrus of 14-month-old
Mapt−/− brains compared to wild type, providing a potential mechanism for their behavioral phenotypes. In addition to the hippocampus, an upregulation of proteins involved in neurogenesis was observed in the frontal cortex and amygdala of the
Mapt−/− mice using proteomic mass spectrometry. All together, these findings suggest that tau may have a role in the depressive symptoms observed in many neurodegenerative diseases and identify tau as a potential molecular target for treating depression.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
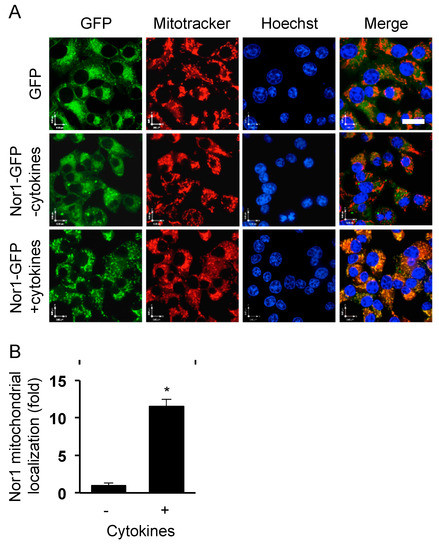
Open AccessArticle
Disruption of Beta-Cell Mitochondrial Networks by the Orphan Nuclear Receptor Nor1/Nr4a3
by
Anne-Françoise Close, Nidheesh Dadheech, Hélène Lemieux, Qian Wang and Jean Buteau
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 4136
Abstract
Nor1, the third member of the Nr4a subfamily of nuclear receptor, is garnering increased interest in view of its role in the regulation of glucose homeostasis. Our previous study highlighted a proapoptotic role of Nor1 in pancreatic beta cells and showed that Nor1
[...] Read more.
Nor1, the third member of the Nr4a subfamily of nuclear receptor, is garnering increased interest in view of its role in the regulation of glucose homeostasis. Our previous study highlighted a proapoptotic role of Nor1 in pancreatic beta cells and showed that Nor1 expression was increased in islets isolated from type 2 diabetic individuals, suggesting that Nor1 could mediate the deterioration of islet function in type 2 diabetes. However, the mechanism remains incompletely understood. We herein investigated the subcellular localization of Nor1 in INS832/13 cells and dispersed human beta cells. We also examined the consequences of Nor1 overexpression on mitochondrial function and morphology. Our results show that, surprisingly, Nor1 is mostly cytoplasmic in beta cells and undergoes mitochondrial translocation upon activation by proinflammatory cytokines. Mitochondrial localization of Nor1 reduced glucose oxidation, lowered ATP production rates, and inhibited glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Western blot and microscopy images revealed that Nor1 could provoke mitochondrial fragmentation via mitophagy. Our study unveils a new mode of action for Nor1, which affects beta-cell viability and function by disrupting mitochondrial networks.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
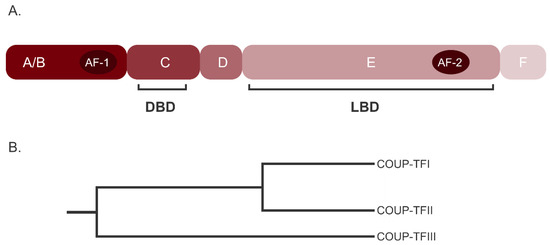
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
COUP-TFII in Health and Disease
by
Simone Polvani, Sara Pepe, Stefano Milani and Andrea Galli
Cited by 35 | Viewed by 5168
Abstract
The nuclear receptors (NRs) belong to a vast family of evolutionary conserved proteins acting as ligand-activated transcription factors. Functionally, NRs are essential in embryogenesis and organogenesis and in adulthood they are involved in almost every physiological and pathological process. Our knowledge of NRs
[...] Read more.
The nuclear receptors (NRs) belong to a vast family of evolutionary conserved proteins acting as ligand-activated transcription factors. Functionally, NRs are essential in embryogenesis and organogenesis and in adulthood they are involved in almost every physiological and pathological process. Our knowledge of NRs action has greatly improved in recent years, demonstrating that both their expression and activity are tightly regulated by a network of signaling pathways, miRNA and reciprocal interactions. The Chicken Ovalbumin Upstream Promoter Transcription Factor II (COUP-TFII, NR2F2) is a NR classified as an orphan due to the lack of a known natural ligand. Although its expression peaks during development, and then decreases considerably, in adult tissues, COUP-TFII is an important regulator of differentiation and it is variably implicated in tissues homeostasis. As such, alterations of its expression or its transcriptional activity have been studied and linked to a spectrum of diseases in organs and tissues of different origins. Indeed, an altered COUP-TFII expression and activity may cause infertility, abnormality in the vascular system and metabolic diseases like diabetes. Moreover, COUP-TFII is actively investigated in cancer research but its role in tumor progression is yet to be fully understood. In this review, we summarize the current understanding of COUP-TFII in healthy and pathological conditions, proposing an updated and critical view of the many functions of this NR.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Perturbation of Nuclear Hormone Receptors by Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals: Mechanisms and Pathological Consequences of Exposure
by
Julie M. Hall and Callie W. Greco
Cited by 31 | Viewed by 5358
Abstract
Much of the early work on Nuclear Hormone Receptors (NHRs) focused on their essential roles as mediators of sex steroid hormone signaling in reproductive development and function, and thyroid hormone-dependent formation of the central nervous system. However, as NHRs display tissue-specific distributions and
[...] Read more.
Much of the early work on Nuclear Hormone Receptors (NHRs) focused on their essential roles as mediators of sex steroid hormone signaling in reproductive development and function, and thyroid hormone-dependent formation of the central nervous system. However, as NHRs display tissue-specific distributions and activities, it is not surprising that they are involved and vital in numerous aspects of human development and essential for homeostasis of all organ systems. Much attention has recently been focused on the role of NHRs in energy balance, metabolism, and lipid homeostasis. Dysregulation of NHR function has been implicated in numerous pathologies including cancers, metabolic obesity and syndrome, Type II diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, hyperlipidemia, male and female infertility and other reproductive disorders. This review will discuss the dysregulation of NHR function by environmental endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs), and the associated pathological consequences of exposure in numerous tissues and organ systems, as revealed by experimental, clinical, and epidemiological studies.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
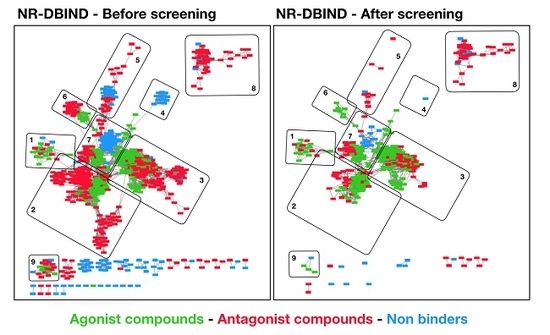
Hits Discovery on the Androgen Receptor: In Silico Approaches to Identify Agonist Compounds
by
Manon Réau, Nathalie Lagarde, Jean-François Zagury and Matthieu Montes
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2677
Abstract
The androgen receptor (AR) is a transcription factor that plays a key role in sexual phenotype and neuromuscular development. AR can be modulated by exogenous compounds such as pharmaceuticals or chemicals present in the environment, and particularly by AR agonist compounds that mimic
[...] Read more.
The androgen receptor (AR) is a transcription factor that plays a key role in sexual phenotype and neuromuscular development. AR can be modulated by exogenous compounds such as pharmaceuticals or chemicals present in the environment, and particularly by AR agonist compounds that mimic the action of endogenous agonist ligands and whether restore or alter the AR endocrine system functions. The activation of AR must be correctly balanced and identifying potent AR agonist compounds is of high interest to both propose treatments for certain diseases, or to predict the risk related to agonist chemicals exposure. The development of
in silico approaches and the publication of structural, affinity and activity data provide a good framework to develop rational AR hits prediction models. Herein, we present a docking and a pharmacophore modeling strategy to help identifying AR agonist compounds. All models were trained on the NR-DBIND that provides high quality binding data on AR and tested on AR-agonist activity assays from the Tox21 initiative. Both methods display high performance on the NR-DBIND set and could serve as starting point for biologists and toxicologists. Yet, the pharmacophore models still need data feeding to be used as large scope undesired effect prediction models.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
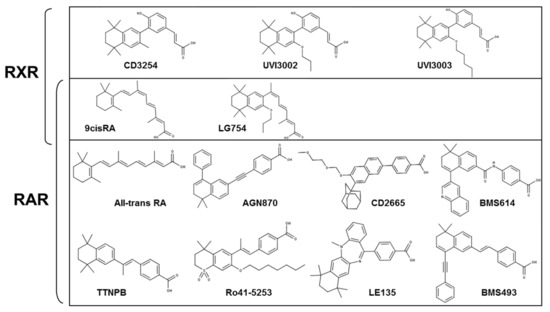
Regulation of RXR-RAR Heterodimers by RXR- and RAR-Specific Ligands and Their Combinations
by
Albane le Maire, Catherine Teyssier, Patrick Balaguer, William Bourguet and Pierre Germain
Cited by 54 | Viewed by 7013
Abstract
The three subtypes (α, β, and γ) of the retinoic acid receptor (RAR) are ligand-dependent transcription factors that mediate retinoic acid signaling by forming heterodimers with the retinoid X receptor (RXR). Heterodimers are functional units that bind ligands (retinoids), transcriptional co-regulators and DNA,
[...] Read more.
The three subtypes (α, β, and γ) of the retinoic acid receptor (RAR) are ligand-dependent transcription factors that mediate retinoic acid signaling by forming heterodimers with the retinoid X receptor (RXR). Heterodimers are functional units that bind ligands (retinoids), transcriptional co-regulators and DNA, to regulate gene networks controlling cell growth, differentiation, and death. Using biochemical, crystallographic, and cellular approaches, we have set out to explore the spectrum of possibilities to regulate RXR-RAR heterodimer-dependent transcription through various pharmacological classes of RAR- and RXR- specific ligands, alone or in combination. We reveal the molecular details by which these compounds direct specificity and functionality of RXR-RAR heterodimers. Among these ligands, we have reevaluated and improved the molecular and structural definition of compounds CD2665, Ro41-5253, LE135, or LG100754, highlighting novel functional features of these molecules. Our analysis reveals a model of RXR-RAR heterodimer action in which each subunit retains its intrinsic properties in terms of ligand and co-regulator binding. However, their interplay upon the combined action of RAR- and RXR-ligands allows for the fine tuning of heterodimer activity. It also stresses the importance of accurate ligand characterization to use synthetic selective retinoids appropriately and avoid data misinterpretations.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Function of Nr4a Orphan Nuclear Receptors in Proliferation, Apoptosis and Fuel Utilization Across Tissues
by
Jacob A. Herring, Weston S. Elison and Jeffery S. Tessem
Cited by 80 | Viewed by 5880
Abstract
The Nr4a family of nuclear hormone receptors is composed of three members—Nr4a1/Nur77, Nr4a2/Nurr1 and Nr4a3/Nor1. While currently defined as ligandless, these transcription factors have been shown to regulate varied processes across a host of tissues. Of particular interest, the Nr4a family impinge, in
[...] Read more.
The Nr4a family of nuclear hormone receptors is composed of three members—Nr4a1/Nur77, Nr4a2/Nurr1 and Nr4a3/Nor1. While currently defined as ligandless, these transcription factors have been shown to regulate varied processes across a host of tissues. Of particular interest, the Nr4a family impinge, in a tissue dependent fashion, on cellular proliferation, apoptosis and fuel utilization. The regulation of these processes occurs through both nuclear and non-genomic pathways. The purpose of this review is to provide a balanced perspective of the tissue specific and Nr4a family member specific, effects on cellular proliferation, apoptosis and fuel utilization.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
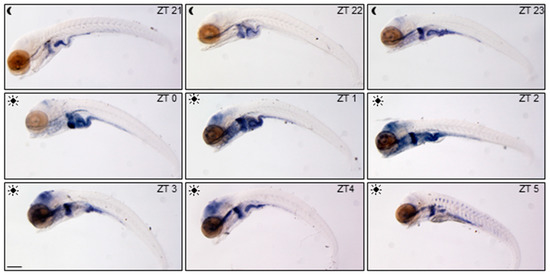
Feeding Entrainment of the Zebrafish Circadian Clock Is Regulated by the Glucocorticoid Receptor
by
Elisa Morbiato, Elena Frigato, Alberto Dinarello, Francesca Maradonna, Nicola Facchinello, Francesco Argenton, Oliana Carnevali, Luisa Dalla Valle and Cristiano Bertolucci
Cited by 21 | Viewed by 4511
Abstract
Glucocorticoids (GCs) are steroid hormones mainly acting as key regulators of body homeostasis and stress responses. Their activities are primarily based on the binding to the GC receptor (GR), a member of the nuclear receptor family, that regulates tissue-specific sets of genes. GCs
[...] Read more.
Glucocorticoids (GCs) are steroid hormones mainly acting as key regulators of body homeostasis and stress responses. Their activities are primarily based on the binding to the GC receptor (GR), a member of the nuclear receptor family, that regulates tissue-specific sets of genes. GCs secretion follows a circadian rhythmicity with a peak linked to the animal’s activity phase. In mammals, GCs are also implicated in feeding entrainment mechanisms as internal zeitgeber. Here, we investigated, by means of behavioural and molecular approaches, the circadian clock and its regulation by light and food in wild-type (WT) and null glucocorticoid receptor (
gr−/−) zebrafish larvae, juveniles and adults. In both WT and
gr−/− larvae and adults, behavioural activity and clock gene expression were entrained to the light–dark (LD) cycle and rhythmic in constant conditions. Differences in the pattern of clock genes’ expression indicated a modulatory role of GCs. A significant role of Gr was detected in the feeding entrainment which was absent or markedly dampened in mutants. Furthermore, the expression of two clock-regulated genes involved in glucidic and lipidic metabolism was altered, highlighting the participation of GCs in metabolic processes also in fish. Taken together, our results confirmed the role of GC-mediated Gr signaling in the feeding entrainment in a non-mammalian species, the zebrafish.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
Androgens and Androgen Receptor Actions on Bone Health and Disease: From Androgen Deficiency to Androgen Therapy
by
Jia-Feng Chen, Pei-Wen Lin, Yi-Ru Tsai, Yi-Chien Yang and Hong-Yo Kang
Cited by 53 | Viewed by 8299
Abstract
Androgens are not only essential for bone development but for the maintenance of bone mass. Therefore, conditions with androgen deficiency, such as male hypogonadism, androgen-insensitive syndromes, and prostate cancer with androgen deprivation therapy are strongly associated with bone loss and increased fracture risk.
[...] Read more.
Androgens are not only essential for bone development but for the maintenance of bone mass. Therefore, conditions with androgen deficiency, such as male hypogonadism, androgen-insensitive syndromes, and prostate cancer with androgen deprivation therapy are strongly associated with bone loss and increased fracture risk. Here we summarize the skeletal effects of androgens—androgen receptors (AR) actions based on in vitro and in vivo studies from animals and humans, and discuss bone loss due to androgens/AR deficiency to clarify the molecular basis for the anabolic action of androgens and AR in bone homeostasis and unravel the functions of androgen/AR signaling in healthy and disease states. Moreover, we provide evidence for the skeletal benefits of androgen therapy and elucidate why androgens are more beneficial than male sexual hormones, highlighting their therapeutic potential as osteoanabolic steroids in improving bone fracture repair. Finally, the application of selective androgen receptor modulators may provide new approaches for the treatment of osteoporosis and fractures as well as building stronger bones in diseases dependent on androgens/AR status.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
The Glucocorticoid Receptor in Cardiovascular Health and Disease
by
Bing Liu, Tie-Ning Zhang, Jessica K. Knight and Julie E. Goodwin
Cited by 75 | Viewed by 11887
Abstract
The glucocorticoid receptor is a member of the nuclear receptor family that controls many distinct gene networks, governing various aspects of development, metabolism, inflammation, and the stress response, as well as other key biological processes in the cardiovascular system. Recently, research in both
[...] Read more.
The glucocorticoid receptor is a member of the nuclear receptor family that controls many distinct gene networks, governing various aspects of development, metabolism, inflammation, and the stress response, as well as other key biological processes in the cardiovascular system. Recently, research in both animal models and humans has begun to unravel the profound complexity of glucocorticoid signaling and convincingly demonstrates that the glucocorticoid receptor has direct effects on the heart and vessels in vivo and in vitro. This research has contributed directly to improving therapeutic strategies in human disease. The glucocorticoid receptor is activated either by the endogenous steroid hormone cortisol or by exogenous glucocorticoids and acts within the cardiovascular system via both genomic and non-genomic pathways. Polymorphisms of the glucocorticoid receptor are also reported to influence the progress and prognosis of cardiovascular disease. In this review, we provide an update on glucocorticoid signaling and highlight the critical role of this signaling in both physiological and pathological conditions of the cardiovascular system. With increasing in-depth understanding of glucocorticoid signaling, the future is promising for the development of targeted glucocorticoid treatments and improved clinical outcomes.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Importance of the Androgen Receptor Signaling in Gene Transactivation and Transrepression for Pubertal Maturation of the Testis
by
Nadia Y. Edelsztein and Rodolfo A. Rey
Cited by 42 | Viewed by 6145
Abstract
Androgens are key for pubertal development of the mammalian testis, a phenomenon that is tightly linked to Sertoli cell maturation. In this review, we discuss how androgen signaling affects Sertoli cell function and morphology by concomitantly inhibiting some processes and promoting others that
[...] Read more.
Androgens are key for pubertal development of the mammalian testis, a phenomenon that is tightly linked to Sertoli cell maturation. In this review, we discuss how androgen signaling affects Sertoli cell function and morphology by concomitantly inhibiting some processes and promoting others that contribute jointly to the completion of spermatogenesis. We focus on the molecular mechanisms that underlie anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) inhibition by androgens at puberty, as well as on the role androgens have on Sertoli cell tight junction formation and maintenance and, consequently, on its effect on proper germ cell differentiation and meiotic onset during spermatogenesis.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
The Role of Nuclear Receptors in Prostate Cancer
by
Masaki Shiota, Naohiro Fujimoto, Eiji Kashiwagi and Masatoshi Eto
Cited by 26 | Viewed by 6670
Abstract
The nuclear receptor (NR) superfamily consists of 48 members that are divided into seven subfamilies. NRs are transcription factors that play an important role in a number of biological processes. The NR superfamily includes androgen receptor, which is a key player in prostate
[...] Read more.
The nuclear receptor (NR) superfamily consists of 48 members that are divided into seven subfamilies. NRs are transcription factors that play an important role in a number of biological processes. The NR superfamily includes androgen receptor, which is a key player in prostate cancer pathogenesis, suggesting the functional roles of other NRs in prostate cancer. The findings on the roles of NRs in prostate cancer thus far have shown that several NRs such as vitamin D receptor, estrogen receptor β, and mineralocorticoid receptor play antioncogenic roles, while other NRs such as peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ and estrogen receptor α as well as androgen receptor play oncogenic roles. However, the roles of other NRs in prostate cancer remain controversial or uninvestigated. Further research on the role of NRs in prostate cancer is required and may lead to the development of novel preventions and therapeutics for prostate cancer.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Transcriptomic Response to 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D in Human Fibroblasts with or without a Functional Vitamin D Receptor (VDR): Novel Target Genes and Insights into VDR Basal Transcriptional Activity
by
Pedro L. F. Costa, Monica M. França, Maria L. Katayama, Eduardo T. Carneiro, Regina M. Martin, Maria A. K. Folgueira, Ana C. Latronico and Bruno Ferraz-de-Souza
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 3237
Abstract
The vitamin D receptor (VDR) mediates vitamin D actions beyond bone health. While VDR activation by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (1,25D) leads to robust transcriptional regulation, less is known about VDR actions in the absence of 1,25D. We analyzed the transcriptomic response to 1,25D in
[...] Read more.
The vitamin D receptor (VDR) mediates vitamin D actions beyond bone health. While VDR activation by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (1,25D) leads to robust transcriptional regulation, less is known about VDR actions in the absence of 1,25D. We analyzed the transcriptomic response to 1,25D in fibroblasts bearing a severe homozygous hereditary vitamin D resistant rickets-related p.Arg30* VDR mutation (MUT) and in control fibroblasts (CO). Roughly 4.5% of the transcriptome was regulated by 1,25D in CO fibroblasts, while MUT cells without a functional VDR were insensitive to 1,25D. Novel VDR target genes identified in human fibroblasts included bone and cartilage factors
CILP,
EFNB2, and
GALNT12. Vehicle-treated CO and MUT fibroblasts had strikingly different transcriptomes, suggesting basal VDR activity. Indeed, oppositional transcriptional effects in basal conditions versus after 1,25D activation were implied for a subset of target genes mostly involved with cell cycle. Cell proliferation assays corroborated this conjectured oppositional basal VDR activity, indicating that precise 1,25D dosage in target tissues might be essential for modulating vitamin D actions in human health.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
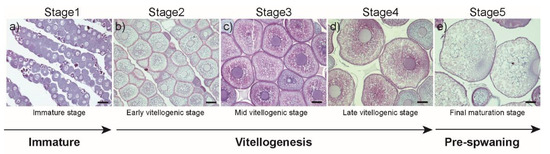
Involvement of Estrogen and Its Receptors in Morphological Changes in the Eyes of the Japanese Eel, Anguilla japonica, in the Process of Artificially-Induced Maturation
by
Ji-Yeon Hyeon, Sung-Pyo Hur, Byeong-Hoon Kim, Jun-Hwan Byun, Eun-Su Kim, Bong-Soo Lim, Bae-Ik Lee, Shin-Kwon Kim, Akihiro Takemura and Se-Jae Kim
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 3919
Abstract
During the long migration from river habitats to the spawning ground, the Japanese eel undergoes sexual maturation. This spawning migration occurs concurrently with morphological changes, such as increases in eye size; however, the mechanisms by which sex steroids and their receptors influence these
[...] Read more.
During the long migration from river habitats to the spawning ground, the Japanese eel undergoes sexual maturation. This spawning migration occurs concurrently with morphological changes, such as increases in eye size; however, the mechanisms by which sex steroids and their receptors influence these changes in peripheral tissues remain unclear. The aim of this study was to investigate changes in the eyes of female Japanese eels during sexual maturation, and our research focused on estrogen receptor (ER)α and ERβ transcripts. During ovarian development, the gonadosomatic index increased and yolk-laden oocytes developed rapidly. These changes occurred in conjunction with a steady increase in plasma levels of estradiol-17β (E
2). Concomitant increases in transcript levels of ERα and ERβ in eye, brain, pituitary, and ovary were also observed. Fluorescence in-situ hybridization analyses revealed that ERα and ERβ transcripts were present in the choriocapillary layer and photoreceptor layer of the eyes, and the analysis also revealed that their signals in these layers became stronger in mature females compared to those observed in immature females, suggesting that under the influence of gonadotropins, morphological changes in the eyes are regulated by E
2 through the activation of its receptors. In conclusion, E
2 plays a crucial role in physiological adaptations that occur in peripheral tissues during the spawning migration.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
The Role of Androgen Receptor Signaling in Ovarian Cancer
by
Taichi Mizushima and Hiroshi Miyamoto
Cited by 46 | Viewed by 7237
Abstract
Emerging evidence has suggested that androgen receptor signaling plays an important role in ovarian cancer outgrowth. Specifically, androgen receptor activation appears to be associated with increased risks of developing ovarian cancer and inducing tumor progression. However, conflicting findings have also been reported. This
[...] Read more.
Emerging evidence has suggested that androgen receptor signaling plays an important role in ovarian cancer outgrowth. Specifically, androgen receptor activation appears to be associated with increased risks of developing ovarian cancer and inducing tumor progression. However, conflicting findings have also been reported. This review summarizes and discusses the available data indicating the involvement of androgens as well as androgen receptor and related signals in ovarian carcinogenesis and cancer growth. Although the underlying molecular mechanisms for androgen receptor functions in ovarian cancer remain far from being fully understood, current observations may offer effective chemopreventive and therapeutic approaches, via modulation of androgen receptor activity, against ovarian cancer. Indeed, several clinical trials have been conducted to determine the efficacy of androgen deprivation therapy in patients with ovarian cancer.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Planned Papers
The below list represents only planned manuscripts. Some of these
manuscripts have not been received by the Editorial Office yet. Papers
submitted to MDPI journals are subject to peer-review.
Title: The Role of Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptors (PPARs) in Neuroinflammation
Authors: Celene Titus; Md. Tozammel Hoque; Reina Bendayan
Affiliation: Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Leslie Dan Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Toronto, 144 College Street, Toronto, ON M5S 3M2, Canada
Abstract: Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated receptors (PPARs) are members of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily of ligand-activated transcription factors that play a vital role in lipid and glucose homeostasis. Recent evidence suggests that PPARs, through their activation by specific ligands, may play an important role in neuroinflammation, and proposes that these receptors could be a promising novel therapeutic target for several neurological disorders. This review will focus on the pivotal function of PPARs in regulating neuroinflammation and the potential role that the various PPAR isoforms (PPARα, PPARβ/δ, PPARγ) may play in the treatment of neurological disorders. Furthermore, the role of newly developed ligands/mediators of PPARs for the treatment of brain inflammation and neuronal damage will be addressed.