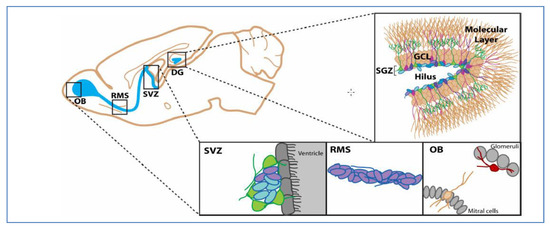
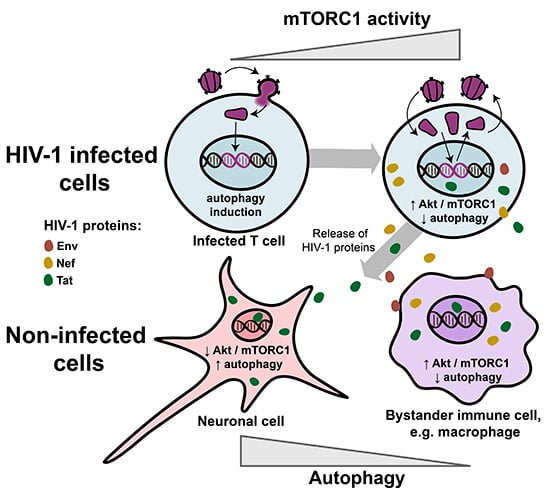
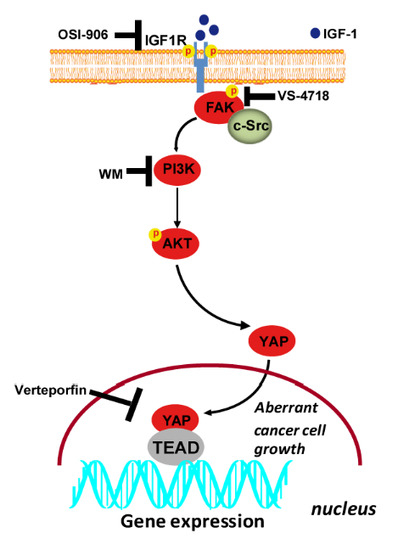
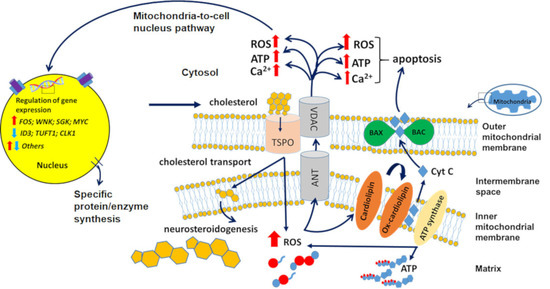
Compartmentilisation of Cellular Signaling
A topical collection in Cells (ISSN 2073-4409). This collection belongs to the section "Cell Signaling".
Viewed by 46703Editor
Interests: cell signalling; cyclic AMP; gene expression
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
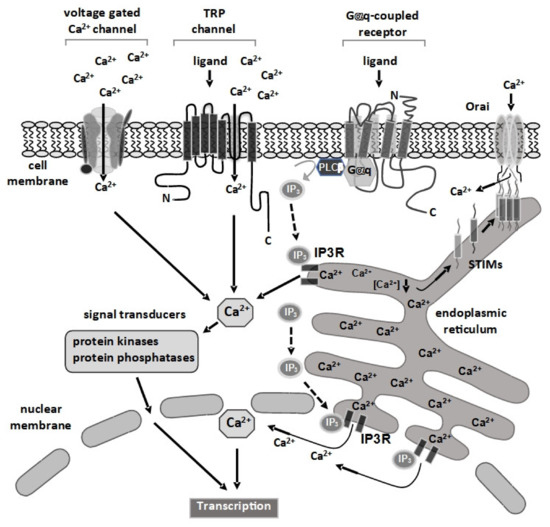
The 3 main classes of cell-surface receptors (ion channel-linked receptors, G-protein-linked receptors, and enzyme-linked receptors) mediate most of the signaling in multi-cellular organisms by controlling the activities of intracellular signal transduction pathways. It is now clear that spatial and temporal separation of signal transduction pathways often determines the specificity of cellular responses to receptor activation. Recent advances have improved our understanding of how receptor signalling is influenced by the formation of molecular complexes (signalosomes) in distinct cellular compartments and restricted protein biosynthesis, and many examples have been found where signalosome deregulation leads to disease.
For example, basic research on the cyclic nucleotide, cyclic 3’,5’-adenosine monophosphate (cyclic AMP) established the concept of second messenger molecules, which mediate the intracellular actions of a wide range of G-protein-linked cell surface receptors for hormones, neurotransmitters and growth factors, as well as sensory stimuli. Biological processes mediated by cyclic AMP include memory formation, metabolism, gene regulation, and immune function and its deregulation is associated with many pathologies, including metabolic, cardiovascular, pulmonary, and inflammatory disorders as well as certain cancers. Cyclic AMP signalling is now known to occur in discrete signalosomes, located to discrete sub-cellular compartments, or cyclic AMP nanodomains, and is now widely viewed as the paradigm for “compartmentalised” cellular signalling in biological systems. It is envisaged that future drug treatments should be developed to recover the function of cAMP nanodomains, thereby alleviating the symptoms of pulmonary and cardiovascular disease. The available drugs at best slow the progression of disease and can cause severe side effects.
The aims of this Topical Collection, therefore, are to bring together new, cutting-edge insights into the compartmentalisation of receptor signalling from the major cell surface receptors and their integration into cell responses linked to health and disease. The scope of these research highlights will encompass new technologies to probe compartmentalized signalling, including advances in imaging, pharmacology and “omics” and disruptive technologies to disease models and drug development.
Dr. Stephen Yarwood
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Cells is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- signal transduction
- cell surface receptors
- molecular pharmacology
- compartmentalization
- imaging
- omics