Advances in Multiple Myeloma Research and Treatment
A topical collection in Cancers (ISSN 2072-6694). This collection belongs to the section "Cancer Therapy".
Viewed by 55806Editor
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
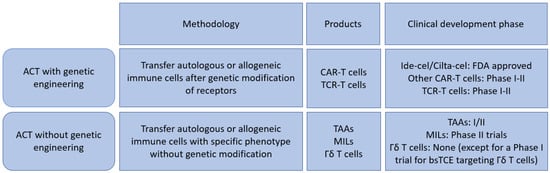
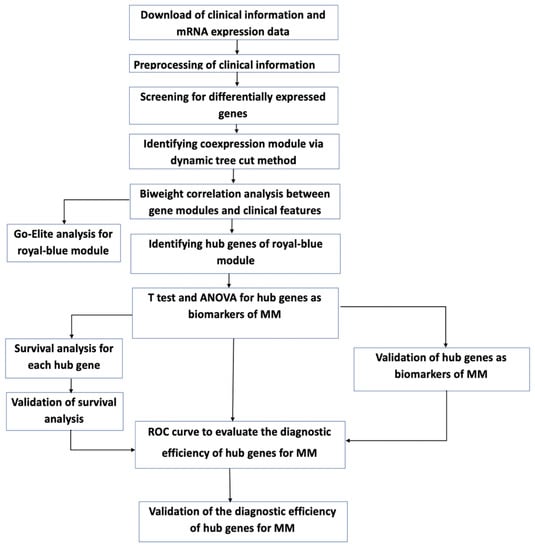
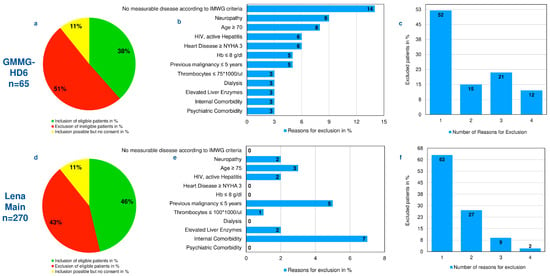
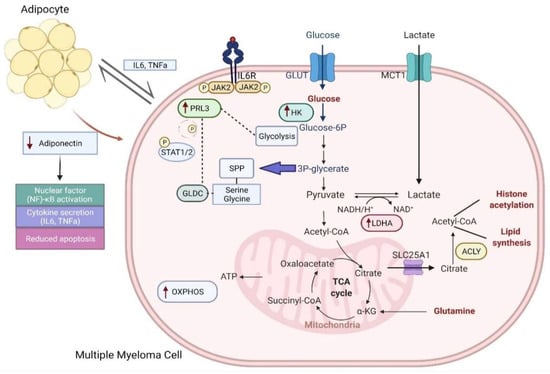
Multiple myeloma represents the second common hematologic malignancy. During the past decades, unprecedented progress was made in research with a focus on understanding myeloma biology and the development of novel drugs directly targeting the malignant cell and its surrounding microenvironment, which translated directly in a markedly improved prognosis of patients affected with this disease. Most recently, emerging cellular treatment options and novel antibody constructs are entering the treatment armentarium. However, despite all the progress made, multiple myeloma so far remains an uncurable and in the majority of patients life limiting disease with still subgroups of patients with a still impaired prognosis, e.g., with high-risk myeloma or being refractory to the established treatment options of special unmet need for novel developments. This Special Issue reflects the recent advances in research and treatment, working toward turning myeloma into a curable disease.
Prof. Dr. Katja Weisel
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Cancers is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2900 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Multiple myeloma
- bone marrow microenvironment
- treatment
- immunotherapy