The Impact of COVID-19 Infection in Cancer
A topical collection in Cancers (ISSN 2072-6694). This collection belongs to the section "Cancer Epidemiology and Prevention".
Viewed by 142158Editors
2. Department of Research, Unit of Cellular Network and Therapeutic Innovation, Regina Elena National Cancer Institute, 00144 Rome, Italy
Interests: tumor biology; molecular oncology; onco-suppressor p53; autophagy; hypoxia; oxidative stress; tumor microenvironment; glioblastoma; personalized medicine
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: herpesviruses; viral oncology; autophagy and unfolded protein response
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
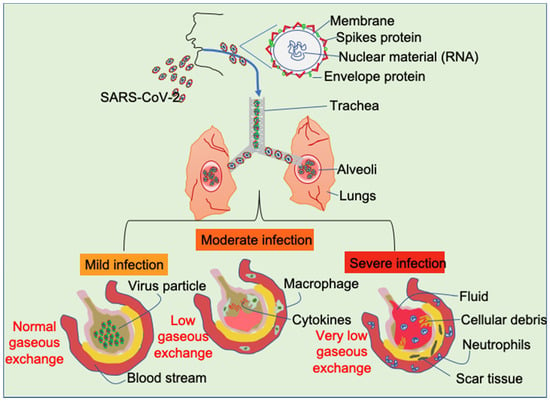
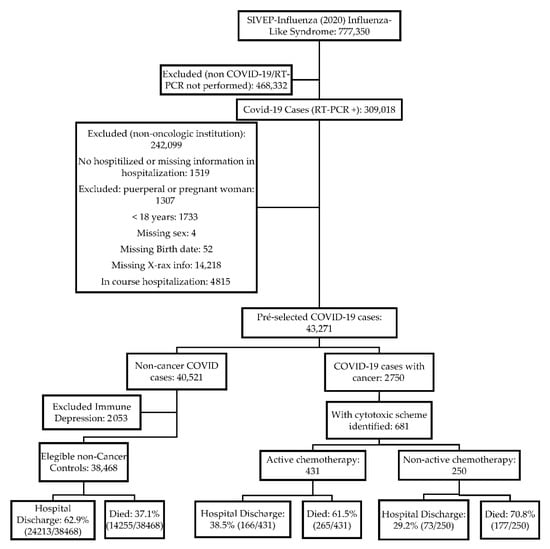
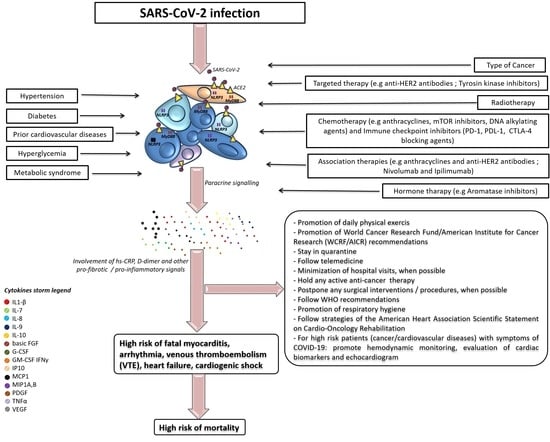
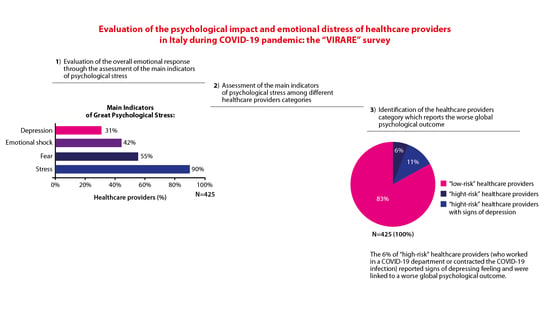
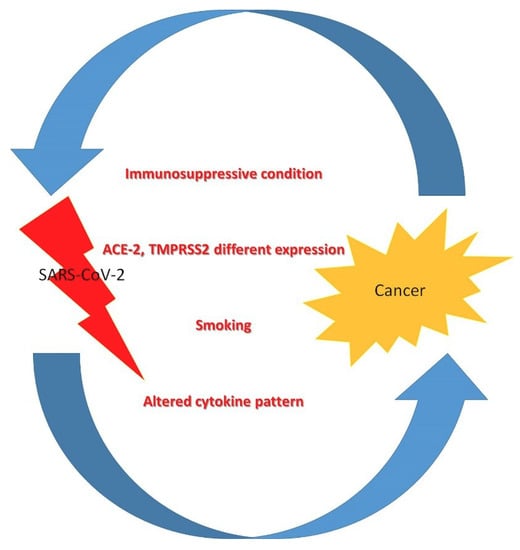
Highly pathogenic coronavirus SARS-CoV2 infection is spreading worldwide causing the COVID-19 disease. During such infection that predominantly interests the lungs, a massive release of inflammatory cytokines may contribute to the destruction of infected alveolar cells and induce fibrosis and endothelial cell damage, promoting the activation of the coagulation pathway, which worsens the local clinical picture of the disease and may also have systemic impact. Besides intense inflammation, these cytokines impair the function of the immune system. Both effects predispose to cancer onset, especially of those types associated with oncogenic herpesviruses reactivation, and may worsen the course of established cancers. In this Topical Collection, we would like to bring together articles covering different aspects of the possible impact of COVID-19 on cancer. In fact, people with cancer are among those at higher risk of complications if infected by SARS-CoV2, because their immune systems are already weakened by cancer and related treatment.
Dr. Gabriella D’Orazi
Dr. Mara Cirone
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Cancers is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2900 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- SARS-CoV2
- coronavirus
- herpesviruses
- inflammatory cytokines
- cancer treatment
- cancer progression
- immune dysfunctions