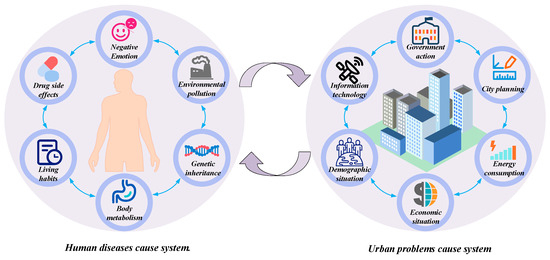
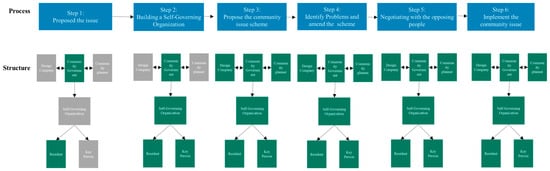
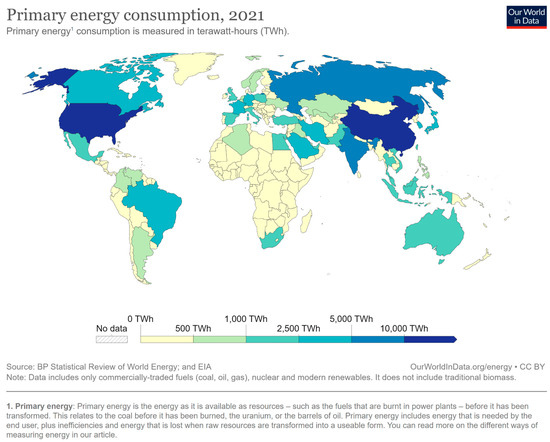
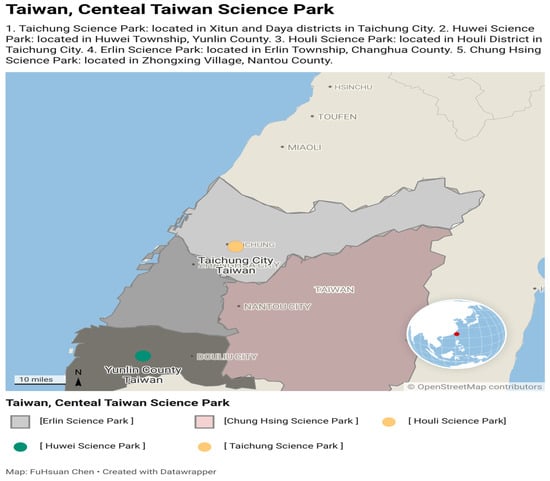
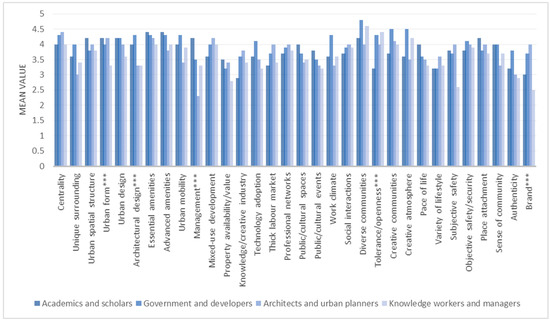
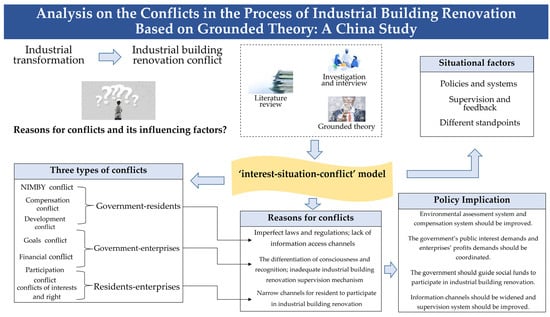
Strategies for Sustainable Urban Development
A topical collection in Buildings (ISSN 2075-5309). This collection belongs to the section "Architectural Design, Urban Science, and Real Estate".
Viewed by 67621Editors
2. School of Management Science and Real Estate, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400045, China
3. Department of Real Estate and Construction, University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Interests: green building; sustainable urbanization; low carbon city; city carrying capacity
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: sustainable construction; sustainable urbanisation; smart construction; smart cities
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: sustainable urban planning; sustainable urban land use; resilient cities; land policies
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Buildings invites research papers related to the above theme for inclusion in a Special Issue arranged to be published in 2022.
The aim of this Special Issue is to present the latest research findings and ideas with respect to the theme of strategies for sustainable urban development to readers globally.
The pursuance of sustainable urban development is a dynamic and long term mission as new challenges against the mission continuosly appear. The development of new technologies in the digital era presents opportunities for discovering strategies that are more capable in addressing these challenges. These strategies cross a wide range of dimensions, including governance, economic measures, technical methods, management mechanism, and other aspects.
The inclusion of these research studies on this specific theme in the journal will provide valuable theories and technologies for designating effective methods for promoting sustainable urban development.
This Special Issue is edited by Liyin Shen, Jorge Ochoa, and Haijun Bao.
This collection belongs to the Architectural Design, Urban Science, and Real Estate Section.
Prof. Dr. Liyin Shen
Dr. Jorge Ochoa
Prof. Dr. Haijun Bao
Guest Editors
Yitian Ren, PhD Researcher
Guest Editor Assistant
Department of Planning and Environmental Management, The University of Manchester, Manchester, UK
Email: yitian.ren@manchester.ac.uk
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Buildings is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- sustainable urbanization
- sustainable urban planning and design
- sustainable urban land use
- digital technologies
- sustainability measures
- urban policy and governance
- sustainable development goals
- circular economy
- response to COVID-19