Digital Transformations within Circular Built Environment Research and Innovation
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Prof. Dr. David J. Edwards
Prof. Dr. David J. Edwards
 Prof. Dr. David J. Edwards
Prof. Dr. David J. Edwards
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
1. Department of the Built Environment, Birmingham City University, Birmingham B4 7XG, UK
2. CIDB Centre of Excellence, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg 2092, South Africa
Interests: construction management; plant and machinery management; digital technologies; health and safety; pedagogical research in higher education; business management
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
 Prof. Dr. Clinton Aigbavboa
Prof. Dr. Clinton Aigbavboa
 Prof. Dr. Clinton Aigbavboa
Prof. Dr. Clinton Aigbavboa
E-Mail
Website
Co-Collection Editor
Department of Construction Management and Quantity Surveying, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg 2006, South Africa
Interests: sustainable construction; digitalization of the construction industry; construction industry development; construction and engineering management; post-occupancy evaluation
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
 Dr. Obuks Ejohwomu
Dr. Obuks Ejohwomu
 Dr. Obuks Ejohwomu
Dr. Obuks Ejohwomu
E-Mail
Website
Co-Collection Editor
Department of Mechanical, Aerospace & Civil Engineering (MACE), Infrastructure and Resilience, Thomas Ashton Institute, and Manchester Environmental Research Institute (MERI), The University of Manchester, Manchester, UK
Interests: built environment sustainability; digital; health and safety; productivity; project management; procurement; carbon neutrality in buildings
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
 Dr. Chris Roberts
Dr. Chris Roberts
 Dr. Chris Roberts
Dr. Chris Roberts
E-Mail
Website
Co-Collection Editor
Planning, Environment and Development, Birmingham City University, Birmingham B5 5JU, UK
Interests: management and process efficiencies, as well as wider societal and particularly environmental implications of construction management and the wider built environment
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
An increasing global population, scarce natural resources and environmental degradation (caused by unsustainable anthropometric activities) have created an ecological imbalance that has lurched humanity to the precipice of a global catastrophe. Yet, despite this dystopian vision, digital technologies and innovations offer an important opportunity to engender impactful environmental governance that mitigates the impact of humanity but also promotes greater harmonisation between the built and the natural environment. This Special Issue showcases the latest international research and development in the field of digitising the built environment within a circular economy and will serve to stimulate future digital adoption and innovation. All phases of the physical built environment’s life cycle may be considered (e.g. design, construction, end use and demolition) together with occupant comfort, health and wellbeing. The overarching ambition is to establish a benchmark for inspirational contemporary developments in the field not only as a means of engendering wider polemic debate, but also to hasten the pace of implementation in both government policy and industry practice.
Prof. Dr. David J. Edwards
Prof. Dr. Clinton Aigbavboa
Dr. Obuks Ejohwomu
Dr. Chris Roberts
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Buildings is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Building information modelling
- Circular economy
- Cyber physical systems
- Environmental governance
- Energy efficiency
- Industry 4.0
- Occupant health and wellbeing
- Sustainable development
Published Papers (12 papers)
Open AccessReview
Architectural Design Criteria Considering the Circular Economy and Buildability for Smart Disaster Relief Shelter Prototyping
by
Reyhaneh Karimi, Sara Shirowzhan and Samad M. E. Sepasgozar
Viewed by 1923
Abstract
The frequency of natural disasters is exacerbated by the escalating impacts of climate change with the need for effective relief shelters for victims and displaced individuals. Providing accessible and easy-to-assemble relief shelters is essential in addressing these needs. Due to climate-related challenges and
[...] Read more.
The frequency of natural disasters is exacerbated by the escalating impacts of climate change with the need for effective relief shelters for victims and displaced individuals. Providing accessible and easy-to-assemble relief shelters is essential in addressing these needs. Due to climate-related challenges and the need for sustainable solutions, the integration of circularity principles in shelter design has become imperative. Circular economy principles promote the efficient use of resources, minimising waste generation and the cost of shelters. Moreover, a considerable number of people usually suffer from homelessness, and an increasing number of families live in slums in every part of the globe. All such people are entitled to be housed in affordable, safe, and appropriate shelters for at least several months after a disaster until they can either rebuild their former houses or find somewhere decent to settle after recovering from the hardship. With the aim of investigating the immediate housing needs of people after a disaster, this paper identifies the essential factors that must be taken into account during shelter design. The paper also presents the prototype developed on the basis of theoretical criteria and the identified factors. The paper’s main objectives were to design an easy-to-assemble emergency shelter on circular economy principles, identify critical factors for the circularity and buildability of the shelter, and present a proposed smart shelter acceptance model. The methodology behind the research involves conducting an intensive literature review and creating a novel prototype of a smart disaster relief shelter on the basis of long-run laboratory work and various prototype iterations. The paper presents the details of the novel prototype and shows materials that enhance the circularity of the shelter, according to a unique architectural design strategy of ‘reusing’ materials to enhance circularity practice in the design and construction sectors. The prototype was developed in a workshop after 6 months of reiterations using plastic water bottles, basic pipes, and other reusable materials. Then, by incorporating the essential factors, a set of criteria was designed that can be used as a guide for the architectural design of shelters. The criteria offered in this paper are useful to evaluate each factor’s importance in shelter design. In total, 51 effective factors in designing and constructing such accommodation are presented, clustered into five design strategy groups: social–cultural, physical–technical, environmental, economic, and organisational.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Developing a Reference Framework for Claim Management Office: A Multi-Method Approach of an International Construction Firm
by
Ali Mohammad Mirzaee, David Edwards and Wellington Didibhuku Thwala
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1122
Abstract
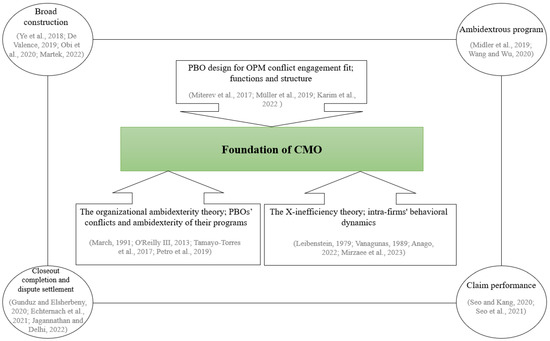
A claim management office (CMO) is a new intra-organisation fit based on an organisational project management (OPM) approach and deals specifically with improving claim performance. However, CMOs are either misunderstood or often overlooked in construction companies, mainly due to ignorance of the OPM
[...] Read more.
A claim management office (CMO) is a new intra-organisation fit based on an organisational project management (OPM) approach and deals specifically with improving claim performance. However, CMOs are either misunderstood or often overlooked in construction companies, mainly due to ignorance of the OPM context but further exacerbated by a lack of real case study research on how to adopt CMOs in these organisations. To address this knowledge gap, this present study integrates organisational ambidexterity with X-inefficiency theory (due to organisation intra-firm irrational decisions when managing such claims) to generate a reference framework for the CMO by probing its implementation within an international construction firm. A multi-method approach, including a single case study (a firm which adopted a CMO) and internal and external expert panels, was used for sampling, data collection, analysis and validation of the framework. The reference framework provides new perspectives on how construction-related companies and practitioners can adopt a CMO structure, which enables them to improve claims performance by planning in three interrelated activities, viz. function-, process- and performance-based. Theoretically, findings also contribute to the X-inefficiency and organisational ambidexterity theories, specifically, how different influences among the reference framework’s elements lead to better organisational claim performance as a plausible roadmap for future work.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Fostering Digitalization of Construction Projects through Integration: A Conceptual Project Governance Model
by
Zhixue Liu, Ronggui Ding, Zheng Gong and Obuks Ejohwomu
Viewed by 3963
Abstract
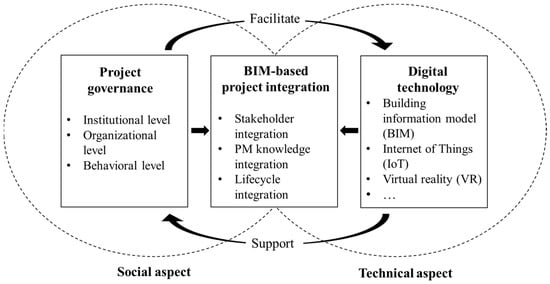
The construction industry has fared poorly in the process of digital transformation, while the main challenge is the digitalization of construction projects. Changes in project management approaches are urgently required in construction organizations to better align digital technology and organizational conditions. However, little
[...] Read more.
The construction industry has fared poorly in the process of digital transformation, while the main challenge is the digitalization of construction projects. Changes in project management approaches are urgently required in construction organizations to better align digital technology and organizational conditions. However, little literature has explored the pivotal role of the project management approach from an organizational perspective. To fill this gap, this research investigates ways of using a project governance model for integration to promote the digitalization of construction projects through a case study. The three integration dimensions, namely stakeholder integration, lifecycle integration, and project management knowledge integration, are identified, and governance elements under each dimension are displayed—and further stratified—based on the three levels of the governance model, including institutional level, organizational level, and behavioral level. The logical relationship between elements and their roles in project digitization is finally summarized. The developed conceptual model will provide an approach for construction enterprises to promote project digitalization.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Intelligent Risk Prognosis and Control of Foundation Pit Excavation Based on Digital Twin
by
Zhe Sun, Haoyang Li, Yan Bao, Xiaolin Meng and Dongliang Zhang
Cited by 6 | Viewed by 2039
Abstract
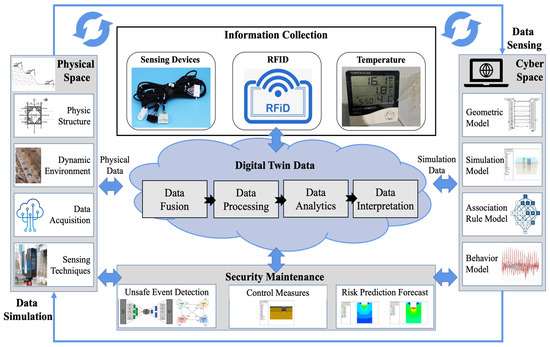
Timely risk information acquisition and diagnosis during foundation pit excavation (FPE) processes are vital for ensuring the safe and effective construction of underground urban infrastructures. Unfortunately, diverse geological and hydrogeological conditions and complex shapes of the foundation pit create barriers for reliable FPE
[...] Read more.
Timely risk information acquisition and diagnosis during foundation pit excavation (FPE) processes are vital for ensuring the safe and effective construction of underground urban infrastructures. Unfortunately, diverse geological and hydrogeological conditions and complex shapes of the foundation pit create barriers for reliable FPE risk prognosis and control. Furthermore, typical support systems during FPE use temporary measures, which have limited capacity to confront excessive loads, large deformations, and seepage. This study aims to establish an intelligent risk prognosis and control framework based on digital twin (DT) for ensuring safe and effective FPE processes. Previous studies have conducted extensive experimental and numerical analyses for examining unsafe conditions during FPE. How to enable intelligent risk prognosis and control of tedious FPE processes by integrating physics-based models and sensory data collected in the field is still challenging. DT could help to establish the interaction and feedback mechanisms between the physical and virtual space. In this study, the authors have established a DT model that consists of a physical space model and a high-fidelity physics-based model of a foundation pit in virtual space. As a result, a mechanism for effective acquisition and fusion of heterogeneous information from both physical and virtual space is established. Then, the authors proposed an integrated model and data-driven approach for examining safety risks during FPE. In the end, the authors have validated the proposed method through a case study of the FPE of the Wuhan Metro Line. The results show that the proposed method could provide theoretical and practical support for future intelligent FPE.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Integrating BIM in Construction Dispute Resolution: Development of a Contractual Framework
by
Rabiah Muhammad and Abdur Rehman Nasir
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 2946
Abstract
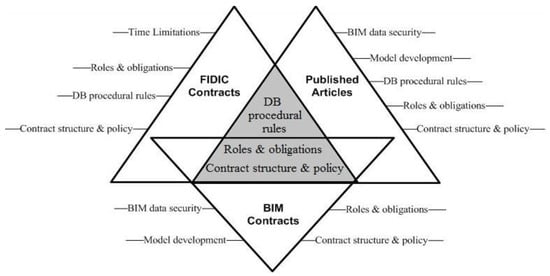
Building information modeling (BIM), through its data-rich digital representation of building elements, has revolutionized the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry. Facilitating the process of its implementation, several legal aspects of BIM have been discussed and standardized in the published contract systems, but
[...] Read more.
Building information modeling (BIM), through its data-rich digital representation of building elements, has revolutionized the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry. Facilitating the process of its implementation, several legal aspects of BIM have been discussed and standardized in the published contract systems, but legal provisions for dispute resolution through BIM are yet to be established. With more enhanced use of BIM, there is a need for a dedicated protocol for utilizing BIM in construction dispute resolution. This study aims to identify, analyze, and classify the potential legal aspects for integrating BIM into the construction dispute resolution process and thereby determine the corresponding provisions required in BIM-enabled contracts. Potential legal aspects were extracted through an analysis of published literature, including research papers, FIDIC contracts, and standard BIM contract documents. A questionnaire survey involving 140 respondents was conducted from which the 24 identified legal aspects were validated to be incorporated in BIM contracts as contract provisions. The proposed BIM-DRes framework maps the legal aspects and finalized contractual provisions with the phases of a construction project and highlights the main stakeholders associated with or affected by these aspects. The developed framework was further validated by three experts from the construction industry. This research explores this overlooked area and expands the body of knowledge on BIM-based dispute resolution, setting the ground for the extension of BIM-enabled contracts.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Selection of Circular Proposals in Building Projects: An MCDM Model for Lifecycle Circularity Assessments Using AHP
by
Mohamed Abadi and David R. Moore
Cited by 7 | Viewed by 2504
Abstract
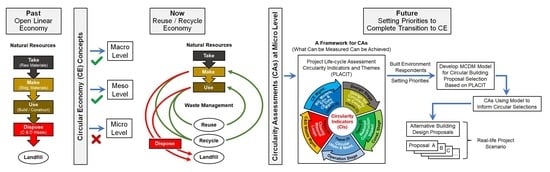
The circular economy (CE) in construction literature engages with individual CE concepts, mostly at the ‘macro’/‘meso’ levels, and lacks holistic frameworks of indicators for circularity assessments (CAs) to inform decision-making at the ‘micro’ (project) level. This article presents a model using the Analytic
[...] Read more.
The circular economy (CE) in construction literature engages with individual CE concepts, mostly at the ‘macro’/‘meso’ levels, and lacks holistic frameworks of indicators for circularity assessments (CAs) to inform decision-making at the ‘micro’ (project) level. This article presents a model using the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) for circular proposal selection in building projects based on a previously validated conceptual framework. The model involves twelve circularity indicators (CIs) classed under five themes relevant to building lifecycle stages. A questionnaire survey was used to establish the final weight vector of CIs. Participants acknowledged the immediate and prolonged effects of design on circularity and viewed waste as ‘design flaws’ but focused on aspirational design indicators relevant to achieving future circularity and missed opportunities for embedding circular materials in design. Moreover, UK participants showed distinctive behaviours towards CAs (proactive/reactive) based on work experience. ‘UK-Experts’ focused on ‘front-end’ design indicators, while ‘UK-Non-experts’ focused on ‘back-end’ waste management indicators. The findings indicate a partial transition to CE better described as a ‘recycle/reuse economy’. CAs and multiple-criteria decision-making (MCDM) techniques facilitate automated decision-making, which provides a new pathway to digital transformation within built environment. Future research will develop a decision-making tool and apply the proposed model in real-life projects.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
Governance, Standards and Regulation: What Construction and Mining Need to Commit to Industry 4.0
by
Kai Smith and Samad Sepasgozar
Cited by 14 | Viewed by 2638
Abstract
Digital transformation has become a pressing concern for the Australian government in the wake of COVID-19. While a thriving construction industry is key to Australia’s economic recovery, the promised land of Industry 4.0 continues to elude the sector. Unlike the mining industry, which
[...] Read more.
Digital transformation has become a pressing concern for the Australian government in the wake of COVID-19. While a thriving construction industry is key to Australia’s economic recovery, the promised land of Industry 4.0 continues to elude the sector. Unlike the mining industry, which has obtained government funding to future-proof its workforce, the building industry remains at risk of being left behind because it has failed to prosecute the case for its own planned Fourth Industrial Revolution. A consistent approach to both sectors is needed to mitigate against asymmetries in the workforce and assist those transitioning from sectors devastated by COVID-19 by providing them with the high-tech skills which fortify the link between wages and employment. SMEs given their limited resources are also vulnerable, and the sector has been rocked by waves of insolvencies in recent times. Achieving Industry 4.0 success has long been a goal among industry academics yet hardly any attention is paid to the institution or its failures. This study subjected 59 authoritative articles to bibliometric analysis and systematic literature review and identified a dearth of research on how best to regulate Industry 4.0 and deliver the standards on which construction and mining businesses will depend when making the choice to commit to Industry 4.0. Nevertheless, there are valuable lessons to be learnt when it comes to supporting SMEs and workers embarking the risky business of Digital Transformation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Digital Twin-Based Assessment Framework for Energy Savings in University Classroom Lighting
by
Hyuncheol Seo and Woo-Seung Yun
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 2888
Abstract
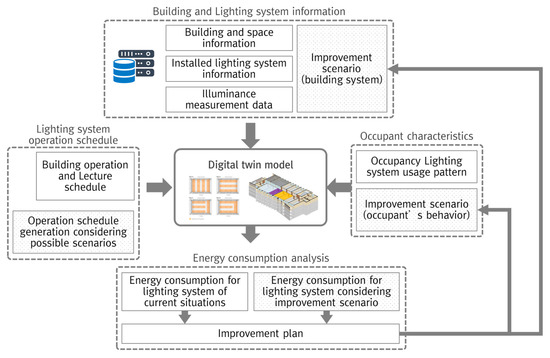
In this paper, a digital twin-based assessment framework is proposed to determine which energy-saving technologies and strategies will work best in existing buildings. The proposed framework is based on a digital twin that integrates the existing building’s hardware system, the building’s operational schedule
[...] Read more.
In this paper, a digital twin-based assessment framework is proposed to determine which energy-saving technologies and strategies will work best in existing buildings. The proposed framework is based on a digital twin that integrates the existing building’s hardware system, the building’s operational schedule database, and a probabilistic model of occupant behavior. A digital model was constructed based on field measurements and database integration for a case study involving nine university buildings and 55 classrooms. As a result, in the classrooms involved in the case study, the lighting was turned on in the absence of occupants for an average of 10.7 h a day. The results indicate that it is very important to turn off the lights after the last hour of use in university classrooms in South Korea and that it is possible to reduce power consumption by more than 60% by employing an off strategy involving a passive infrared sensor or manager. Additionally, LED lighting in most classrooms is over-designed, which indicates that 46% of the energy consumed can be saved by adjusting the luminance level to an appropriate range.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Modelling and Forecasting Temporal PM2.5 Concentration Using Ensemble Machine Learning Methods
by
Obuks Augustine Ejohwomu, Olakekan Shamsideen Oshodi, Majeed Oladokun, Oyegoke Teslim Bukoye, Nwabueze Emekwuru, Adegboyega Sotunbo and Olumide Adenuga
Cited by 23 | Viewed by 3291
Abstract
Exposure of humans to high concentrations of PM
2.5 has adverse effects on their health. Researchers estimate that exposure to particulate matter from fossil fuel emissions accounted for 18% of deaths in 2018—a challenge policymakers argue is being exacerbated by the increase in
[...] Read more.
Exposure of humans to high concentrations of PM
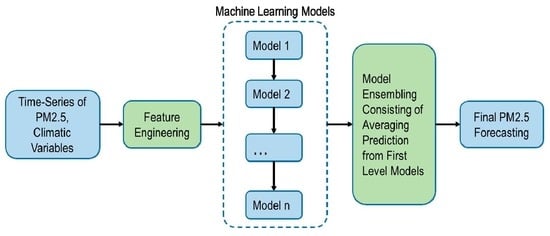
2.5 has adverse effects on their health. Researchers estimate that exposure to particulate matter from fossil fuel emissions accounted for 18% of deaths in 2018—a challenge policymakers argue is being exacerbated by the increase in the number of extreme weather events and rapid urbanization as they tinker with strategies for reducing air pollutants. Drawing on a number of ensemble machine learning methods that have emerged as a result of advancements in data science, this study examines the effectiveness of using ensemble models for forecasting the concentrations of air pollutants, using PM
2.5 as a representative case. A comprehensive evaluation of the ensemble methods was carried out by comparing their predictive performance with that of other standalone algorithms. The findings suggest that hybrid models provide useful tools for PM
2.5 concentration forecasting. The developed models show that machine learning models are efficient in predicting air particulate concentrations, and can be used for air pollution forecasting. This study also provides insights into how climatic factors influence the concentrations of pollutants found in the air.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Incremental Digital Twin Conceptualisations Targeting Data-Driven Circular Construction
by
Pedro Mêda, Diego Calvetti, Eilif Hjelseth and Hipólito Sousa
Cited by 36 | Viewed by 7288
Abstract
The construction industry faces multiple challenges, where transition to circular production is key. Digitalisation is a strategy to increase the sector’s productivity, competitiveness, and efficiency. However, digitalisation also impacts environmental goals, such as those concerning more eco-friendly solutions, energy efficiency, products recycling, and
[...] Read more.
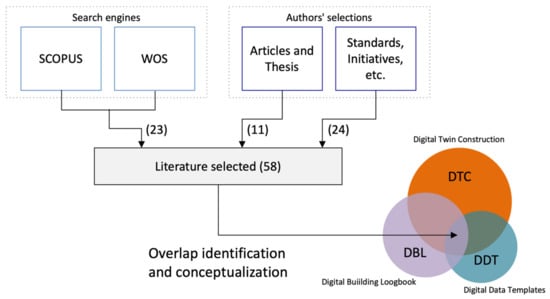
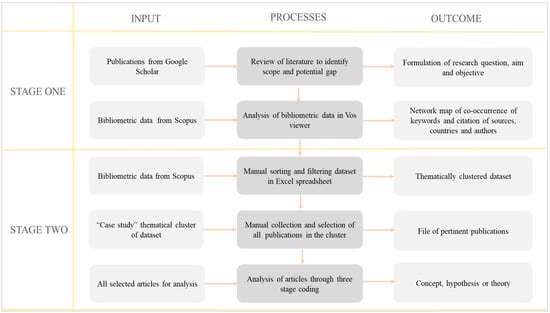
The construction industry faces multiple challenges, where transition to circular production is key. Digitalisation is a strategy to increase the sector’s productivity, competitiveness, and efficiency. However, digitalisation also impacts environmental goals, such as those concerning more eco-friendly solutions, energy efficiency, products recycling, and sustainability certifications. These strategies rely on data, understood as digital, interoperable, incremental and traceable. Data related concepts, such as digital data templates (DDT) and digital building logbooks (DBL), contribute to “good data”. Despite some research focused on each one, little importance has yet been given to their combination. Relevant relationships and overlaps exist, as they partially share the exact same data through the built environment life cycle. This research aims to provide improved understanding on the role of these concepts and their contribution to a more circular industry. The review develops conceptualisations where DDT and DBL are complementary and framed within an incremental digital twin construction (DTC). Misconceptions or confrontations between these three solutions can therefore stand down, for the benefit of a data-driven priority. To increase understanding and reduce misconceptions, our study developed the “Digital data-driven concept” (D3c). This concept contribution is the ability to structure, store, and trace data, opening way to streamlined digital transformation impacting circular built environment concerns.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
The Role of Blockchain Technology in Augmenting Supply Chain Resilience to Cybercrime
by
Aya Bayramova, David J. Edwards and Chris Roberts
Cited by 64 | Viewed by 10189
Abstract
Using a systematic review of literature, this study identifies the potential impact of blockchain solutions for augmenting supply chain resilience (SCR) to cybercrime. This rich literature synthesis forms the basis of a novel theoretical framework that provides guidance and insight for blockchain adopters
[...] Read more.
Using a systematic review of literature, this study identifies the potential impact of blockchain solutions for augmenting supply chain resilience (SCR) to cybercrime. This rich literature synthesis forms the basis of a novel theoretical framework that provides guidance and insight for blockchain adopters and vendors as well as delineate palpable benefits of this novel technology. An interpretivist philosophical design and inductive reasoning are adopted to conduct the systematic review of literature. A total of 867 papers were retrieved from Scopus database between the years of 2016 and 2020 and subsequently analysed via abductive reasoning, grounded theory and a thematic meta-analysis; where the latter was achieved using a scientometric approach and software tools such as VOS viewer and NVivo. Scientometric analysis revealed the most prolific countries, sources, publications and authors who reside at the vanguard of blockchain developments and adoption. Subsequent grounded theory analysis identified six main clusters of research endeavour viz: “case study”, “challenges and opportunity”, “traceability”, “smart contract” “blockchain and IoT” and “data security”. From 28 SCR metrics identified within literature, five were found to have been positively impacted by blockchain technology solutions, namely: “visibility”, “collaboration”, “integration”, “risk management” and “information sharing.” Prominent applications of blockchain technology in practice were “traceability systems” and “smart contracts” which are often implemented separately or in combination and primarily in food supply chains. This research constitutes the first study to critically synthesise extant literature for evaluation of blockchain solutions’ implication on SCR metrics. New perspectives obtained provided a basis for the novel theoretical framework for implementation that will be valued by software developers and adopting organizations, whilst creating new direction for researchers interested in blockchain technology.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Innovative Use of Low-Cost Digitisation for Smart Information Systems in Construction Projects
by
Mostafa Babaeian Jelodar and Feiya Shu
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 3151
Abstract
The low-level application of digital tools and information systems in construction implies that many projects cannot meet modern requirements and standard of work of advanced industries. This study adopts a practical and diagnostic approach to identify key attributes and implementation processes of information
[...] Read more.
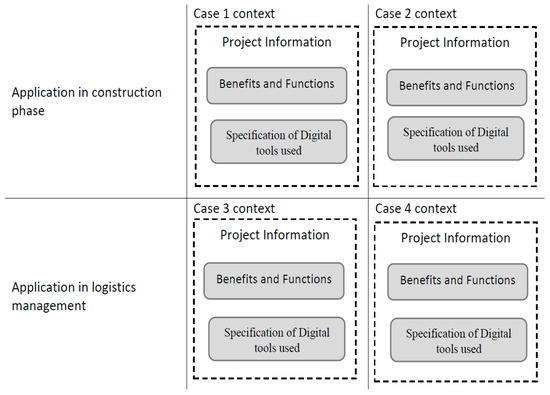
The low-level application of digital tools and information systems in construction implies that many projects cannot meet modern requirements and standard of work of advanced industries. This study adopts a practical and diagnostic approach to identify key attributes and implementation processes of information systems in construction and logistics. To have triangulation of knowledge, a three-step methodology is adopted. Initially an exploratory analysis of previous literature is performed. Secondly a diagnostic analysis of IS applications in construction is achieved by case studies. Finally, expert interviews are performed to examine and consolidate the findings. The study illustrated practical and innovative applications of low-cost digital tools in IS development and created a framework for documentation of these discrete and mostly unshared practices. It is recommended that the construction sector should embrace more advance technologies to minimise human intervention and enhance real-time capabilities. The practicality of how different low-cost and off-the-shelf tools and digital platforms can be combined is discussed and demonstrated. The study provides a clear distinction for practitioners and academics as to what is being practiced in comparison to the dominant theories.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures