Feature Papers in Molecular Biophysics Section
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Prof. Dr. Peter Pohl
Prof. Dr. Peter Pohl
 Prof. Dr. Peter Pohl
Prof. Dr. Peter Pohl
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Institute of Biophysics, Johannes Kepler University Linz, Gruberstraße 40, 4020 Linz, Austria
Interests: membrane transport; interfacial protons; water channels; protein–membrane translocation; membrane domains
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
This Topical Collection, “Feature Papers in Molecular Biophysics Section”, will bring together high-quality research articles, review articles, and communications on all aspects of Molecular Biophysics. It is dedicated to diverse recent advances in Molecular Biophysics research, as highlighted in the topics below, and comprises a selection of exclusive papers from the Editorial Board Members (EBMs) of the Molecular Biophysics Section as well as invited papers from relevant experts. We also welcome established experts in the field to make contributions to this Topical Collection. Please note that all invited papers will be published online once accepted. We aim to represent our Section as an attractive open access publishing platform for Molecular Biophysics research.
Topics include, without being limited to:
- Molecular forces in biological structures
- Conformational transitions of macromolecules
- Molecular associations
- Kinetics of molecular events
- Molecular mechanisms of membrane transport
- Single molecule biophysics
Prof. Dr. Peter Pohl
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Biomolecules is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Published Papers (7 papers)
Open AccessArticle
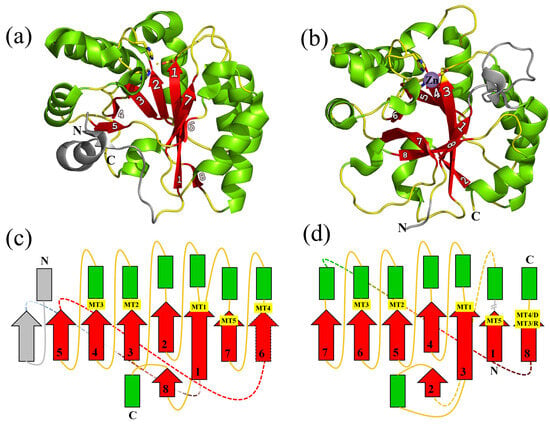
Variations of the NodB Architecture Are Attuned to Functional Specificities into and beyond the Carbohydrate Esterase Family 4
by
Alexis S. Molfetas, Nikiforos Boutris, Anastasia Tomatsidou, Michael Kokkinidis and Vasiliki E. Fadouloglou
Viewed by 588
Abstract
Enzymes of the carbohydrate esterase family 4 (CE4) deacetylate a broad range of substrates, including linear, branched and mesh-like polysaccharides. Although they are enzymes of variable amino acid sequence length, they all comprise the conserved catalytic domain NodB. NodB carries the metal binding
[...] Read more.
Enzymes of the carbohydrate esterase family 4 (CE4) deacetylate a broad range of substrates, including linear, branched and mesh-like polysaccharides. Although they are enzymes of variable amino acid sequence length, they all comprise the conserved catalytic domain NodB. NodB carries the metal binding and active site residues and is characterized by a set of conserved sequence motifs, which are linked to the deacetylation activity. Besides a non-structured, flexible peptide of variable length that precedes NodB, several members of the CE4 family contain additional domains whose function or contribution to substrate specificity are not efficiently characterized. Evidence suggests that CE4 family members comprising solely the NodB domain have developed features linked to a variety of substrate specificities. To understand the NodB-based substrate diversity within the CE4 family, we perform a comparative analysis of all NodB domains structurally characterized so far. We show that amino acid sequence variations, topology diversities and excursions away from the framework structure give rise to different NodB domain classes associated with different substrate specificities and particular functions within and beyond the CE4 family. Our work reveals a link between specific NodB domain characteristics and substrate recognition. Thus, the details of the fold are clarified, and the structural basis of its variations is deciphered and associated with function. The conclusions of this work are also used to make predictions and propose specific functions for biochemically/enzymatically uncharacterized NodB-containing proteins, which have generally been considered as putative CE4 deacetylases. We show that some of them probably belong to different enzymatic families.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
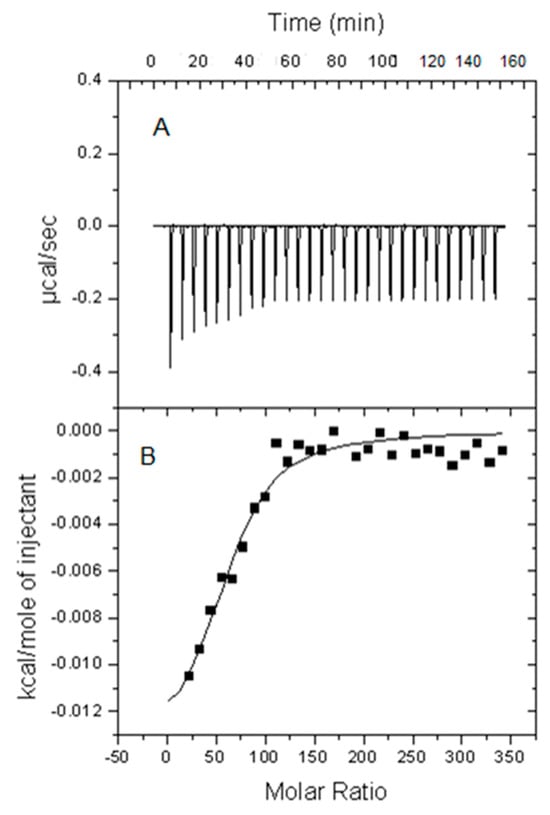
The Influence of Lipid Electric Charge on the Binding of Aβ(1–42) Amyloid Peptide to Bilayers in the Liquid-Ordered State
by
Hasna Ahyayauch, Massimo E. Masserini, Félix M. Goñi and Alicia Alonso
Viewed by 765
Abstract
The amyloidogenic Aβ peptides are widely considered as a pathogenic agent in Alzheimer’s disease. Aβ(1-42) would form aggregates of amyloid fibrils on the neuron plasma membranes, thus perturbing neuronal functionality. Conflicting data are available on the influence of bilayer order on Aβ(1-42) binding
[...] Read more.
The amyloidogenic Aβ peptides are widely considered as a pathogenic agent in Alzheimer’s disease. Aβ(1-42) would form aggregates of amyloid fibrils on the neuron plasma membranes, thus perturbing neuronal functionality. Conflicting data are available on the influence of bilayer order on Aβ(1-42) binding to membranes. In the present study, a biophysical approach was used in which isothermal calorimetry and surface pressure measurements were applied to explore the interaction of Aβ(1-42) in either monomeric, oligomeric, or fibrillar form with model membranes (bilayers or monolayers) in the liquid-ordered state that were either electrically neutral or negatively charged. In the latter case, this contained phosphatidic acid, cardiolipin, or ganglioside. The calorimetric studies showed that Aβ(1-42) fibrils, oligomers, and monomers could bind and/or be inserted into bilayers, irrespective of electric charge, in the liquid-ordered state, except that monomers could not interact with electrically neutral bilayers. The monolayer studies in the Langmuir balance demonstrated that Aβ(1-42) aggregation hindered peptide insertion into the monolayer, hindered insertion in the decreasing order of monomer > oligomer > fibril, and that lipid composition did not cause large differences in insertion, apart from a slight facilitation of monomer and oligomer insertion by gangliosides.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
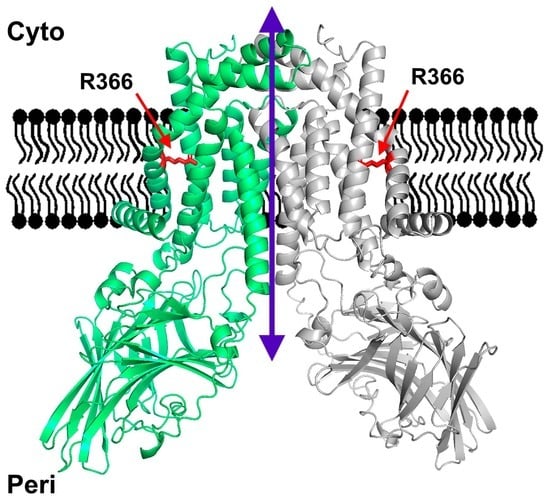
YidC from Escherichia coli Forms an Ion-Conducting Pore upon Activation by Ribosomes
by
Denis G. Knyazev, Lukas Winter, Andreas Vogt, Sandra Posch, Yavuz Öztürk, Christine Siligan, Nikolaus Goessweiner-Mohr, Nora Hagleitner-Ertugrul, Hans-Georg Koch and Peter Pohl
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1018
Abstract
The universally conserved protein YidC aids in the insertion and folding of transmembrane polypeptides. Supposedly, a charged arginine faces its hydrophobic lipid core, facilitating polypeptide sliding along YidC’s surface. How the membrane barrier to other molecules may be maintained is unclear. Here, we
[...] Read more.
The universally conserved protein YidC aids in the insertion and folding of transmembrane polypeptides. Supposedly, a charged arginine faces its hydrophobic lipid core, facilitating polypeptide sliding along YidC’s surface. How the membrane barrier to other molecules may be maintained is unclear. Here, we show that the purified and reconstituted
E. coli YidC forms an ion-conducting transmembrane pore upon ribosome or ribosome-nascent chain complex (RNC) binding. In contrast to monomeric YidC structures, an AlphaFold parallel YidC dimer model harbors a pore. Experimental evidence for a dimeric assembly comes from our BN-PAGE analysis of native vesicles, fluorescence correlation spectroscopy studies, single-molecule fluorescence photobleaching observations, and crosslinking experiments. In the dimeric model, the conserved arginine and other residues interacting with nascent chains point into the putative pore. This result suggests the possibility of a YidC-assisted insertion mode alternative to the insertase mechanism.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
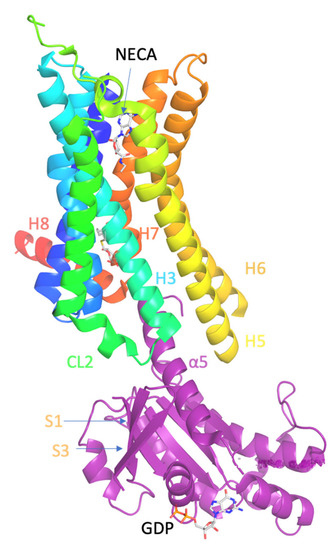
Molecular Biophysics of Class A G Protein Coupled Receptors–Lipids Interactome at a Glance—Highlights from the A2A Adenosine Receptor
by
Efpraxia Tzortzini and Antonios Kolocouris
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 1656
Abstract
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are embedded in phospholipid membrane bilayers with cholesterol representing 34% of the total lipid content in mammalian plasma membranes. Membrane lipids interact with GPCRs structures and modulate their function and drug-stimulated signaling through conformational selection. It has been shown
[...] Read more.
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are embedded in phospholipid membrane bilayers with cholesterol representing 34% of the total lipid content in mammalian plasma membranes. Membrane lipids interact with GPCRs structures and modulate their function and drug-stimulated signaling through conformational selection. It has been shown that anionic phospholipids form strong interactions between positively charged residues in the G protein and the TM5-TM6-TM 7 cytoplasmic interface of class A GPCRs stabilizing the signaling GPCR-G complex. Cholesterol with a high content in plasma membranes can be identified in more specific sites in the transmembrane region of GPCRs, such as the Cholesterol Consensus Motif (CCM) and Cholesterol Recognition Amino Acid Consensus (CRAC) motifs and other receptor dependent and receptor state dependent sites. Experimental biophysical methods, atomistic (AA) MD simulations and coarse-grained (CG) molecular dynamics simulations have been applied to investigate these interactions. We emphasized here the impact of phosphatidyl inositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P
2 or PIP
2), a minor phospholipid component and of cholesterol on the function-related conformational equilibria of the human A
2A adenosine receptor (A
2AR), a representative receptor in class A GPCR. Several GPCRs of class A interacted with PIP
2 and cholesterol and in many cases the mechanism of the modulation of their function remains unknown. This review provides a helpful comprehensive overview for biophysics that enter the field of GPCRs-lipid systems.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Tutorial for Stopped-Flow Water Flux Measurements: Why a Report about “Ultrafast Water Permeation through Nanochannels with a Densely Fluorous Interior Surface” Is Flawed
by
Juergen Pfeffermann and Peter Pohl
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1832
Abstract
Millions of years of evolution have produced proteinaceous water channels (aquaporins) that combine perfect selectivity with a transport rate at the edge of the diffusion limit. However, Itoh et al. recently claimed in
Science that artificial channels are 100 times faster and almost
[...] Read more.
Millions of years of evolution have produced proteinaceous water channels (aquaporins) that combine perfect selectivity with a transport rate at the edge of the diffusion limit. However, Itoh et al. recently claimed in
Science that artificial channels are 100 times faster and almost as selective. The published deflation kinetics of vesicles containing channels or channel elements indicate otherwise, since they do not demonstrate the facilitation of water transport. In an illustrated tutorial on the experimental basis of stopped-flow measurements, we point out flaws in data processing. In contrast to the assumption voiced in
Science, individual vesicles cannot simultaneously shrink with two different kinetics. Moreover, vesicle deflation within the dead time of the instrument cannot be detected. Since flawed reports of ultrafast water channels in
Science are not a one-hit-wonder as evidenced by a 2018 commentary by Horner and Pohl in
Science, we further discuss the achievable limits of single-channel water permeability. After analyzing (i) diffusion limits for permeation through narrow channels and (ii) hydrodynamics in the surrounding reservoirs, we conclude that it is unlikely to fundamentally exceed the evolutionarily optimized water-channeling performance of the fastest aquaporins while maintaining near-perfect selectivity.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Self-Assembly of Amyloid Fibrils into 3D Gel Clusters versus 2D Sheets
by
Kanchana Karunarathne, Nabila Bushra, Olivia Williams, Imad Raza, Laura Tirado, Diane Fakhre, Fadia Fakhre and Martin Muschol
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1437
Abstract
The deposition of dense fibril plaques represents the pathological hallmark for a multitude of human disorders, including many neurodegenerative diseases. Fibril plaques are predominately composed of amyloid fibrils, characterized by their underlying cross beta-sheet architecture. Research into the mechanisms of amyloid formation has
[...] Read more.
The deposition of dense fibril plaques represents the pathological hallmark for a multitude of human disorders, including many neurodegenerative diseases. Fibril plaques are predominately composed of amyloid fibrils, characterized by their underlying cross beta-sheet architecture. Research into the mechanisms of amyloid formation has mostly focused on characterizing and modeling the growth of individual fibrils and associated oligomers from their monomeric precursors. Much less is known about the mechanisms causing individual fibrils to assemble into ordered fibrillar suprastructures. Elucidating the mechanisms regulating this “secondary” self-assembly into distinct suprastructures is important for understanding how individual protein fibrils form the prominent macroscopic plaques observed in disease. Whether and how amyloid fibrils assemble into either 2D or 3D supramolecular structures also relates to ongoing efforts on using amyloid fibrils as substrates or scaffolds for self-assembling functional biomaterials. Here, we investigated the conditions under which preformed amyloid fibrils of a lysozyme assemble into larger superstructures as a function of charge screening or pH. Fibrils either assembled into three-dimensional gel clusters or two-dimensional fibril sheets. The latter displayed optical birefringence, diagnostic of amyloid plaques. We presume that pH and salt modulate fibril charge repulsion, which allows anisotropic fibril–fibril attraction to emerge and drive the transition from 3D to 2D fibril self-assembly.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceArticle
Sub-Millisecond Photoinduced Dynamics of Free and EL222-Bound FMN by Stimulated Raman and Visible Absorption Spectroscopies
by
Yingliang Liu, Aditya S. Chaudhari, Aditi Chatterjee, Prokopis C. Andrikopoulos, Alessandra Picchiotti, Mateusz Rebarz, Miroslav Kloz, Victor A. Lorenz-Fonfria, Bohdan Schneider and Gustavo Fuertes
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2214
Abstract
Time-resolved femtosecond-stimulated Raman spectroscopy (FSRS) provides valuable information on the structural dynamics of biomolecules. However, FSRS has been applied mainly up to the nanoseconds regime and above 700 cm
−1, which covers only part of the spectrum of biologically relevant time scales
[...] Read more.
Time-resolved femtosecond-stimulated Raman spectroscopy (FSRS) provides valuable information on the structural dynamics of biomolecules. However, FSRS has been applied mainly up to the nanoseconds regime and above 700 cm
−1, which covers only part of the spectrum of biologically relevant time scales and Raman shifts. Here we report on a broadband (~200–2200 cm
−1) dual transient visible absorption (visTA)/FSRS set-up that can accommodate time delays from a few femtoseconds to several hundreds of microseconds after illumination with an actinic pump. The extended time scale and wavenumber range allowed us to monitor the complete excited-state dynamics of the biological chromophore flavin mononucleotide (FMN), both free in solution and embedded in two variants of the bacterial light-oxygen-voltage (LOV) photoreceptor EL222. The observed lifetimes and intermediate states (singlet, triplet, and adduct) are in agreement with previous time-resolved infrared spectroscopy experiments. Importantly, we found evidence for additional dynamical events, particularly upon analysis of the low-frequency Raman region below 1000 cm
−1. We show that fs-to-sub-ms visTA/FSRS with a broad wavenumber range is a useful tool to characterize short-lived conformationally excited states in flavoproteins and potentially other light-responsive proteins.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures