Applied Physics in Cancer Cells
A topical collection in Biology (ISSN 2079-7737). This collection belongs to the section "Biophysics".
Viewed by 20605
Share This Topical Collection
Editors
 Dr. Jagoba Iturri
Dr. Jagoba Iturri
 Dr. Jagoba Iturri
Dr. Jagoba Iturri
E-Mail
Website1
Website2
Collection Editor
Department of Nanobiotechnology (DNBT), Institute for Biophysics, BOKU University for Natural Resources and Life Sciences, Muthgasse 11 (Simon Zeisel Haus), A-1190 Vienna, Austria
Interests: mechanical properties of biomaterials; scanning probe microscopy; cell adhesion; (bio)polymers; colloids and interfaces; surface analytical techniques
 Prof. Dr. José Luis Toca-Herrera
Prof. Dr. José Luis Toca-Herrera
 Prof. Dr. José Luis Toca-Herrera
Prof. Dr. José Luis Toca-Herrera
E-Mail
Website1
Website2
Collection Editor
Department of Nanobiotechnology (DNBT), Institute for Biophysics, BOKU University for Natural Resources and Life Sciences, Muthgasse 11 (Simon Zeisel Haus), A-1190 Vienna, Austria
Interests: physical chemistry; colloids and interfaces; scanning probe microscopy; spectroscopy; surface analytical techniques; mechanical properties of biomaterials; soft matter
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
This Topical Collection will focus on the state-of-the-art of applied-physics-related methodologies for investigating the behavior of cancerous cells and tissue, their measurement and characterization representing a thrilling challenge to researchers in the field.
Topics of interest might cover the characterization of cell electrical properties, mechanical, proliferation, and adhesive properties, the influence of applied magnetic fields, utilization of (nano)particles of diverse nature (i.e., magnetic), reporting of advances in ultrastructure determination, as well as surface properties, among others. These features can also be approached from a materials science or a diagnosis tool perspective, in order to discriminate between healthy and cancer cells.
Submission is open to studies with very diverse experimental techniques (optical/fluorescence microscopy, quartz crystal microbalance, electrical impedance spectroscopy, Raman/FTIR/microwave spectroscopy, reflection interference contrast microscopy, etc.), although the use of scanning probe microscopy is particularly appreciated. Manuscripts can either summarize selected areas (reviews) or be employed to discuss the latest research in the field (original articles of different length).
Dr. Jagoba Iturri
Prof. Dr. José Toca-Herrera
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Biology is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- applied physics methodologies
- cancer cell and tissue
- scanning probe microscopy
- cytomechanics and adhesive properties
- electrical properties and magnetic fields
- diagnosis tools
Published Papers (7 papers)
Open AccessArticle
Carrier-Free Cellular Transport of CRISPR/Cas9 Ribonucleoprotein for Genome Editing by Cold Atmospheric Plasma
by
Haodong Cui, Min Jiang, Wenhua Zhou, Ming Gao, Rui He, Yifan Huang, Paul K. Chu and Xue-Feng Yu
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 2436
Abstract
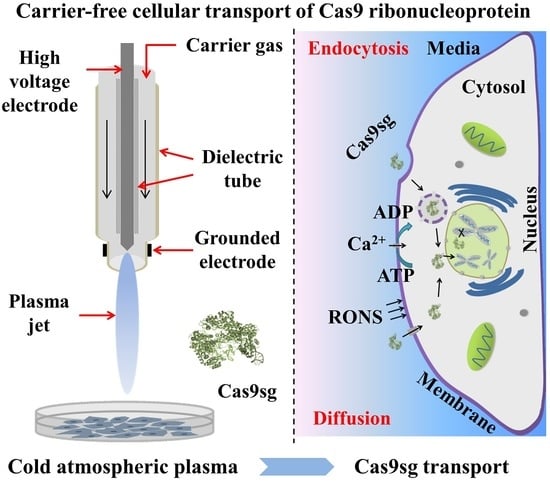
A carrier-free CRISPR/Cas9 ribonucleoprotein delivery strategy for genome editing mediated by a cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) is described. The CAP is promising in many biomedical applications due to efficient production of bioactive ionized species. The MCF-7 cancer cells after CAP exposure exhibit increased
[...] Read more.
A carrier-free CRISPR/Cas9 ribonucleoprotein delivery strategy for genome editing mediated by a cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) is described. The CAP is promising in many biomedical applications due to efficient production of bioactive ionized species. The MCF-7 cancer cells after CAP exposure exhibit increased extracellular reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RONS) and altered membrane potential and permeability. Hence, transmembrane transport of Ca
2+ into the cells increases and accelerates ATP hydrolysis, resulting in enhanced ATP-dependent endocytosis. Afterwards, the increased Ca
2+ and ATP contents promote the release of cargo into cytoplasm due to the enhanced endosomal escape. The increased membrane permeability also facilitates passive diffusion of foreign species across the membrane into the cytosol. After CAP exposure, the MCF-7 cells incubated with Cas9 ribonucleoprotein (Cas9-sgRNA complex, Cas9sg) with a size of about 15 nm show 88.9% uptake efficiency and 65.9% nuclear import efficiency via passive diffusion and ATP-dependent endocytosis pathways. The efficient transportation of active Cas9sg after the CAP treatment leads to 21.7% and 30.2% indel efficiencies in HEK293T and MCF-7 cells, respectively. This CAP-mediated transportation process provides a simple and robust alternative for the delivery of active CRISPR/Cas9 ribonucleoprotein. Additionally, the technique can be extended to other macro-biomolecules and nanomaterials to cater to different biomedical applications.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
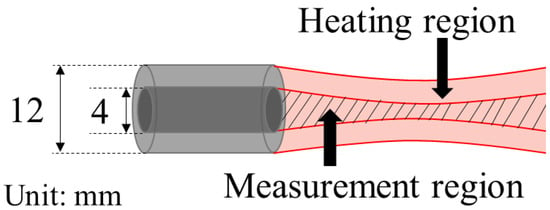
Ultrasonic Heating Detects Lipiodol Deposition within Liver Tumors after Transarterial Embolization: An In Vivo Approach
by
Natsuhiko Saito, Toshihiro Tanaka, Kiyoyuki Minamiguchi, Ryosuke Taiji, Hideyuki Nishiofuku, Takeshi Matsumoto, Toshiko Hirai, Kimihiko Kichikawa, Naoki Kawahara, Daiki Matsuda and Iwaki Akiyama
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2151
Abstract
Computed tomography (CT) is the standard method to evaluate Lipiodol deposition after transarterial embolization (TAE) for a long period. However, iodine but not Lipiodol can be observed on CT. A minimally invasive other method to detect Lipiodol has been needed to evaluate accurate
[...] Read more.
Computed tomography (CT) is the standard method to evaluate Lipiodol deposition after transarterial embolization (TAE) for a long period. However, iodine but not Lipiodol can be observed on CT. A minimally invasive other method to detect Lipiodol has been needed to evaluate accurate evaluation after procedure. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of using the rate of change in sound velocity caused by ultrasonic heating to reflect Lipiodol accumulation after TAE in a rat liver tumor model. We analyzed the association of this developed technique with CT images and histological findings. Eight rats bearing N1S1 cells were prepared. After confirmation of tumor development in a rat liver, Lipiodol was injected via the hepatic artery. Seven days after TAE, CT scan and sound velocity changes caused by ultrasonic heating were measured, and then the rats were sacrificed. An ultrasonic pulse-echo method was used to measure the sound velocity. The temperature coefficient of the sound velocity in each treated tumor was evaluated and compared with the mean CT value and the histological Lipiodol accumulation ratio. Pearson’s correlation coefficients were calculated to assess the correlation between the measured values. The correlation coefficient (r) of the mean CT value and histological Lipiodol accumulation ratio was 0.835 (
p = 0.010), which was considered statistically significant. Also, those of the temperature coefficient of the sound velocity and the histological Lipiodol accumulation ratio were statistically significant (r = 0.804;
p = 0.016). To our knowledge, this is the first study that reported the efficacy of ultrasonic heating to detect Lipiodol accumulation in rat liver tumors after TAE. Our results suggest that the rate of change in sound velocity caused by ultrasonic heating can be used to evaluate Lipiodol accumulation in liver tumors after TAE, and thus could represent an alternative to CT in this application. This new innovative technique is easy to treat and less invasive in terms of avoiding radiation compared with CT.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
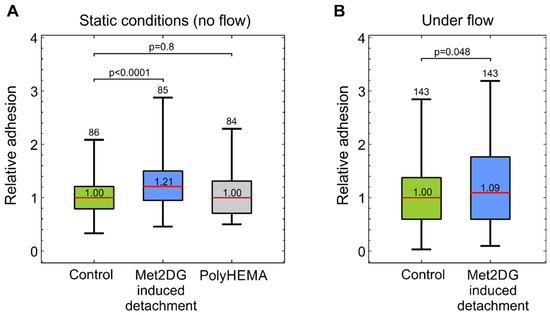
Adhesion and Stiffness of Detached Breast Cancer Cells In Vitro: Co-Treatment with Metformin and 2-Deoxy-d-glucose Induces Changes Related to Increased Metastatic Potential
by
Špela Zemljič-Jokhadar, Gašper Kokot, Mojca Pavlin and Jure Derganc
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2364
Abstract
Metastatic cancer cells can overcome detachment-induced cell death and can proliferate in anchorage-independent conditions. A recent study revealed that a co-treatment with two drugs that interfere with cell metabolism, metformin and 2-deoxy-D-glucose, promotes detachment of viable MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. In the present
[...] Read more.
Metastatic cancer cells can overcome detachment-induced cell death and can proliferate in anchorage-independent conditions. A recent study revealed that a co-treatment with two drugs that interfere with cell metabolism, metformin and 2-deoxy-D-glucose, promotes detachment of viable MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. In the present study, we analyzed if these detached viable MDA-MB-231 cells also exhibit other features related to cancer metastatic potential, i.e., if they are softer and more prone to adhere to epithelial cells. The cell mechanics of attached cells and floating cells were analyzed by optical tweezers and cell deformability cytometry, respectively. The adhesion was assessed on a confluent monolayer of HUVEC cells, with MDA-MB-231 cells either in static conditions or in a microfluidic flow. Additionally, to test if adhesion was affected by the state of the epithelial glycocalyx, HUVEC cells were treated with neuraminidase and tunicamycin. It was found that the treated MDA-MB-231 cells were more prone to adhere to HUVEC cells and that they were softer than the control, both in the floating state and after re-seeding to a substrate. The changes in the HUVEC glycocalyx, however, did not increase the adhesion potential of MDA-MB-231.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
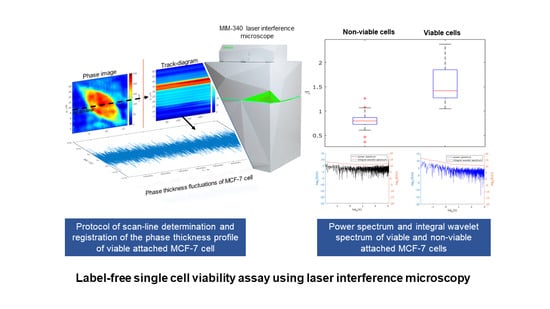
Label-Free Single Cell Viability Assay Using Laser Interference Microscopy
by
Yulia Beloglazova, Aleksandr Nikitiuk, Anna Voronina, Olga Gagarskikh, Yuriy Bayandin, Oleg Naimark and Victoria Grishko
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2976
Abstract
Laser interference microscopy (LIM) is a promising label-free method for single-cell research applicable to cell viability assessment in the studies of mammalian cells. This paper describes the development of a sensitive and reproducible method for assessing cell viability using LIM. The method, based
[...] Read more.
Laser interference microscopy (LIM) is a promising label-free method for single-cell research applicable to cell viability assessment in the studies of mammalian cells. This paper describes the development of a sensitive and reproducible method for assessing cell viability using LIM. The method, based on associated signal processing techniques, has been developed as a result of real-time investigation in phase thickness fluctuations of viable and non-viable MCF-7 cells, reflecting the presence and absence of their metabolic activity. As evinced by the values of the variable
vc, this variable determines the viability of a cell only in the attached state (
vc exceeds 20 nm
2 for viable attached cells). The critical value of the power spectrum slope
βc of the phase thickness fluctuations equals 1.00 for attached MCF-7 cells and 0.71 for suspended cells. The slope of the phase fluctuations’ power spectrum for MCF-7 cells was determined to exceed the threshold value of
βc for a living cell, otherwise the cell is dead. The results evince the power spectrum slope as the most appropriate indicator of cell viability, while the integrated evaluation criterion (
vc and
βc values) can be used to assay the viability of attached cells.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Investigation of DNA Damage and Cell-Cycle Distribution in Human Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes under Exposure to High Doses of Proton Radiotherapy
by
Justyna Miszczyk
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 2188
Abstract
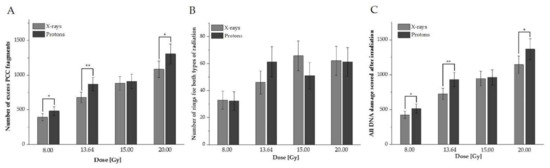
This study systematically investigates how a single high-dose therapeutic proton beam versus X-rays influences cell-cycle phase distribution and DNA damage in human peripheral blood lymphocytes (HPBLs). Blood samples from ten volunteers (both male and female) were irradiated with doses of 8.00, 13.64, 15.00,
[...] Read more.
This study systematically investigates how a single high-dose therapeutic proton beam versus X-rays influences cell-cycle phase distribution and DNA damage in human peripheral blood lymphocytes (HPBLs). Blood samples from ten volunteers (both male and female) were irradiated with doses of 8.00, 13.64, 15.00, and 20.00 Gy of 250 kV X-rays or 60 MeV protons. The dose–effect relations were calculated and distributed by plotting the frequencies of DNA damage of excess Premature Chromosome Condensation (PCC) fragments and rings in the G2/M phase, obtained via chemical induction with calyculin A. The Papworth’s
u test was used to evaluate the distribution of DNA damage. The study shows that high doses of protons induce HPBL DNA damage in the G2/M phase differently than X-rays do. The results indicate a different distribution of DNA damage following high doses of irradiation with protons versus photons between donors, types of radiation, and doses. The proliferation index confirms the impact of high doses of mitosis and the influence of radiotherapy type on the different HPBL response. The results illuminate the cellular and molecular mechanisms that underlie differences in the distribution of DNA damage and cell-cycle phases; these findings may yield an improvement in the efficacy of the radiotherapies used.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Cold Atmospheric Plasma, a Novel Approach against Bladder Cancer, with Higher Sensitivity for the High-Grade Cell Line
by
Edgar Tavares-da-Silva, Eurico Pereira, Ana S. Pires, Ana R. Neves, Catarina Braz-Guilherme, Inês A. Marques, Ana M. Abrantes, Ana C. Gonçalves, Francisco Caramelo, Rafael Silva-Teixeira, Fernando Mendes, Arnaldo Figueiredo and Maria Filomena Botelho
Cited by 18 | Viewed by 4001
Abstract
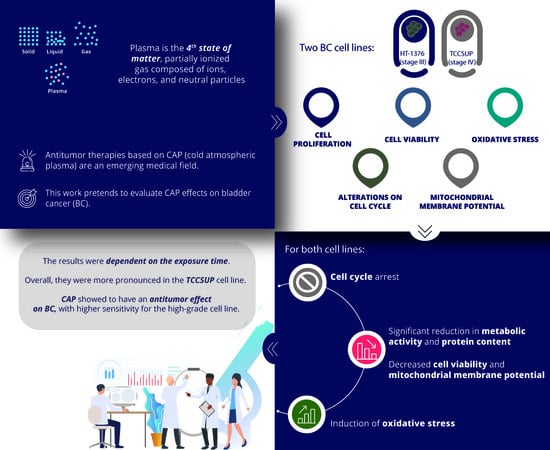
Antitumor therapies based on Cold Atmospheric Plasma (CAP) are an emerging medical field. In this work, we evaluated CAP effects on bladder cancer. Two bladder cancer cell lines were used, HT-1376 (stage III) and TCCSUP (stage IV). Cell proliferation assays were performed evaluating
[...] Read more.
Antitumor therapies based on Cold Atmospheric Plasma (CAP) are an emerging medical field. In this work, we evaluated CAP effects on bladder cancer. Two bladder cancer cell lines were used, HT-1376 (stage III) and TCCSUP (stage IV). Cell proliferation assays were performed evaluating metabolic activity (MTT assay) and protein content (SRB assay). Cell viability, cell cycle, and mitochondrial membrane potential (Δψ
m) were assessed using flow cytometry. Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RONS) and reduced glutathione (GSH) were evaluated by fluorescence. The assays were carried out with different CAP exposure times. For both cell lines, we obtained a significant reduction in metabolic activity and protein content. There was a decrease in cell viability, as well as a cell cycle arrest in S phase. The Δψ
m was significantly reduced. There was an increase in superoxide and nitric oxide and a decrease in peroxide contents, while GSH content did not change. These results were dependent on the exposure time, with small differences for both cell lines, but overall, they were more pronounced in the TCCSUP cell line. CAP showed to have a promising antitumor effect on bladder cancer, with higher sensitivity for the high-grade cell line.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Time- and Zinc-Related Changes in Biomechanical Properties of Human Colorectal Cancer Cells Examined by Atomic Force Microscopy
by
Maria Maares, Claudia Keil, Leif Löher, Andreas Weber, Amsatou Andorfer-Sarr, Hajo Haase, Jagoba Iturri and José L. Toca-Herrera
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2585
Abstract
Monitoring biomechanics of cells or tissue biopsies employing atomic force microscopy (AFM) offers great potential to identify diagnostic biomarkers for diseases, such as colorectal cancer (CRC). Data on the mechanical properties of CRC cells, however, are still scarce. There is strong evidence that
[...] Read more.
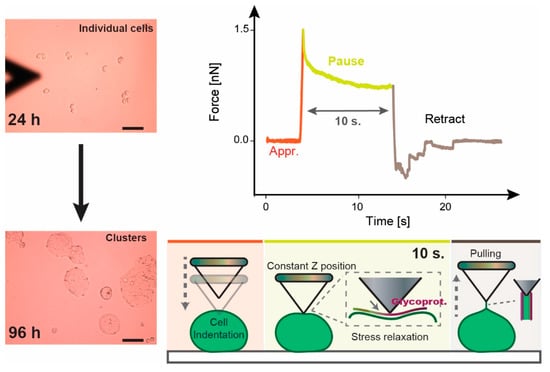
Monitoring biomechanics of cells or tissue biopsies employing atomic force microscopy (AFM) offers great potential to identify diagnostic biomarkers for diseases, such as colorectal cancer (CRC). Data on the mechanical properties of CRC cells, however, are still scarce. There is strong evidence that the individual zinc status is related to CRC risk. Thus, this study investigates the impact of differing zinc supply on the mechanical response of the in vitro CRC cell lines HT-29 and HT-29-MTX during their early proliferation (24–96 h) by measuring elastic modulus, relaxation behavior, and adhesion factors using AFM. The differing zinc supply severely altered the proliferation of these cells and markedly affected their mechanical properties. Accordingly, zinc deficiency led to softer cells, quantitatively described by 20–30% lower Young’s modulus, which was also reflected by relevant changes in adhesion and rupture event distribution compared to those measured for the respective zinc-adequate cultured cells. These results demonstrate that the nutritional zinc supply severely affects the nanomechanical response of CRC cell lines and highlights the relevance of monitoring the zinc content of cancerous cells or biopsies when studying their biomechanics with AFM in the future.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Planned Papers
The below list represents only planned manuscripts. Some of these
manuscripts have not been received by the Editorial Office yet. Papers
submitted to MDPI journals are subject to peer-review.
Title: Measurement of Temperature Dependence of Sound Velocity in Biological Tissues
Authors: Iwaki Akiyama
Affiliation: Medical Ultrasound Research Center, Doshisha University, Kyotanabe Kyoto 610-0321, Japan
Abstract: Pending...