Livestock Odor Issues and Air Quality
A topical collection in Atmosphere (ISSN 2073-4433). This collection belongs to the section "Air Quality".
Viewed by 7527
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Prof. Dr. Jacek Koziel
Prof. Dr. Jacek Koziel
 Prof. Dr. Jacek Koziel
Prof. Dr. Jacek Koziel
E-Mail
Website
Collection Editor
Livestock Nutrient Management Research Unit, U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, Bushland, TX 79012, USA
Interests: greenhouse gases; mitigation of gaseous emissions; nutrient management; livestock production systems; sustainable agriculture
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Today’s academic and industry professionals are increasingly asked to address “wicked” challenges such as those at the nexus of air quality, animal production systems, technology, environment, and sustainability. Livestock odor is an example of a “wicked”, hard-to-solve problem that is often thought to be too complex to handle and unique to every case. Response to odor is often a symptom of another problem and an opening to a larger set of underlying problems. Politics, regulations, and social and economic issues mingle with ‘hard’ engineering and science interconnected with animal production. Many promising, discovery-stage technologies for mitigation are not yet farm-scale proven. Some technologies are simply too expensive or complex. A unique opportunity lies in a paradigm shift from odor solving being a low priority, expense-only activity to being a value-adding activity. This Topical Collection aims to publish reviews, articles, and short communications that bring different perspectives on solving livestock odor issues in lab-, pilot-, and farm-proven scales. This Topical Collection ‘’Livestock Odor Issues and Air Quality’’ will encourage multidisciplinary and transdisciplinary views, comprehensive assessments, socioeconomic analyses, and case studies illustrating the current state-of-the art and informing on-going discussions on how to solve the livestock odor problem.
Prof. Dr. Jacek Koziel
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Atmosphere is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- livestock odor
- air quality
- measurements and mitigation
- dispersion modeling
- photochemistry of odor
- treatment technologies
- waste management
- environmental regulations
- socioeconomic analysis
- community odor management
- sustainable agriculture
Published Papers (2 papers)
2021
Open AccessArticle
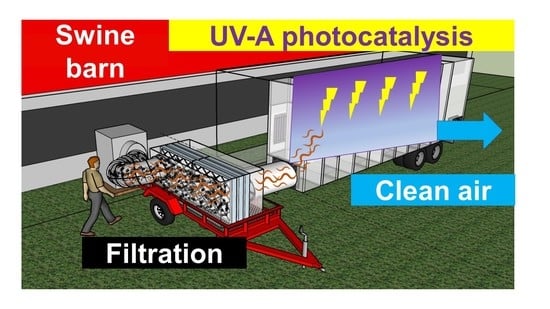
Mitigation of Odor and Gaseous Emissions from Swine Barn with UV-A and UV-C Photocatalysis
by
Myeongseong Lee, Jacek A. Koziel, Wyatt Murphy, William S. Jenks, Baitong Chen, Peiyang Li and Chumki Banik
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 3195
Abstract
UV-A (ca. 365 nm wavelength, a.k.a. ‘black light’) photocatalysis has been investigated to comprehensively mitigate odor and selected air pollutants in the livestock environment. This study was conducted to confirm the performance of UV-A photocatalysis on the swine farm. The objectives of this
[...] Read more.
UV-A (ca. 365 nm wavelength, a.k.a. ‘black light’) photocatalysis has been investigated to comprehensively mitigate odor and selected air pollutants in the livestock environment. This study was conducted to confirm the performance of UV-A photocatalysis on the swine farm. The objectives of this research were to (1) scale-up of the UV-A photocatalysis treatment, (2) evaluate the mitigation of odorous gases from swine slurry pit, (3) test different UV sources, (4) evaluate the effect of particulate matter (PM) and (5) conduct preliminary economic analyses. We tested UV-A photocatalysis at a mobile laboratory-scale capable of treating ~0.2–0.8 m
3·s
−1 of barn exhaust air. The targeted gaseous emissions of barn exhaust air were significantly mitigated (
p < 0.05) up to 40% reduction of measured odor; 63%, 44%, 32%, 40%, 66% and 49% reduction of dimethyl disulfide, isobutyric acid, butanoic acid,
p-cresol, indole and skatole, respectively; 40% reduction of H
2S; 100% reduction of O
3; and 13% reduction of N
2O. The PM mitigation effect was not significant. Formaldehyde levels did not change, and a 21% generation of CO
2 was observed. The percent reduction of targeted gases decreased as the airborne PM increased. Simultaneous chemical and sensory analysis confirmed that UV-A treatment changed the overall nuisance odor character of swine barn emissions into weaker manure odor with ‘toothpaste and ‘mint’ notes. The smell of benzoic acid generated in UV-A treatment was likely one of the compounds responsible for the less-offensive overall odor character of the UV-treated emissions. Results are needed to inform the design of a farm-scale trial, where the interior barn walls can be treated with the photocatalyst.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
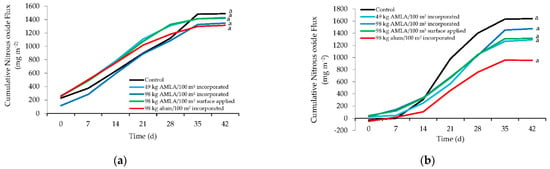
Evaluation of a Novel Poultry Litter Amendment on Greenhouse Gas Emissions
by
Kelsey Anderson, Philip A. Moore, Jr., Jerry Martin and Amanda J. Ashworth
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 2636
Abstract
Gaseous emissions from poultry litter causes production problems for producers as well as the environment, by contributing to climate change and reducing air quality. Novel methods of reducing ammonia (NH
3) and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in poultry facilities are needed. As
[...] Read more.
Gaseous emissions from poultry litter causes production problems for producers as well as the environment, by contributing to climate change and reducing air quality. Novel methods of reducing ammonia (NH
3) and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in poultry facilities are needed. As such, our research evaluated GHG emissions over a 42 d period. Three separate flocks of 1000 broilers were used for this study. The first flock was used only to produce litter needed for the experiment. The second and third flocks were allocated to 20 pens in a randomized block design with four replicated of five treatments. The management practices studied included an unamended control; a conventional practice of incorporating aluminum sulfate (referred to as alum) at 98 kg/100 m
2); a novel litter amendment made from alum mud, bauxite, and sulfuric acid (alum mud litter amendment, AMLA) applied at different rates (49 and 98 kg/100 m
2) and methods (surface applied or incorporated). Nitrous oxide emissions were low for all treatments in flocks 2 and 3 (0.40 and 0.37 mg m
2 hr
−1, respectively). The formation of caked litter (due to excessive moisture) during day 35 and 42 caused high variability in CH
4 and CO
2 emissions. Alum mud litter amendment and alum did not significantly affect GHGs emissions from litter, regardless of the amendment rate or application method. In fact, litter amendments such as alum and AMLA typically lower GHG emissions from poultry facilities by reducing ventilation requirements to maintain air quality in cooler months due to lower NH
3 levels, resulting in less propane use and concomitant reductions in CO
2 emissions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures