Journal Description
AppliedChem
AppliedChem
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on all aspects of applied chemistry published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 17.2 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 5.6 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review and reviewer names are published annually in the journal.
- AppliedChem is a companion journal of Applied Sciences.
Latest Articles
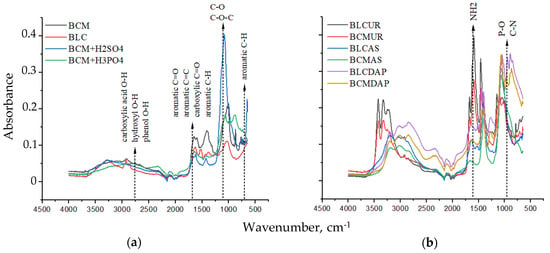
Biochar–Nitrogen Composites: Synthesis, Properties, and Use as Fertilizer for Maize
AppliedChem 2024, 4(2), 157-173; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem4020011 - 17 Apr 2024
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Nitrogen (N) is highly reactive and prone to being easily lost into the air and soil water. Biochar–N composites have proven effective in nourishing and improving maize growth. The aim of this study was to synthesize and assess the properties of composites made
[...] Read more.
Nitrogen (N) is highly reactive and prone to being easily lost into the air and soil water. Biochar–N composites have proven effective in nourishing and improving maize growth. The aim of this study was to synthesize and assess the properties of composites made from biochars (pyrolyzed at 300 °C) derived from chicken manure (N = 3.5%) and leguminous cake (N = 9%) and enriched with ammonium sulfate (AS), urea, and diammonium phosphate (DAP). The biochar pH was adjusted to approximately 6 using sulfuric and phosphoric acids prior to formulating the six tested composites. Maize was cultivated for 50 days under greenhouse conditions, with evaluations of the maize dry matter (DM) and N in the plant shoot. The biochar and composite properties underwent scrutiny for chemical and physicochemical attributes, as well as for soluble N in water and in an HCl solution. Throughout maize cultivation, the release of N as ammonium and nitrate from the composites and pure biochars in the Oxisol solution was successively assessed. Composites formulated with DAP and supplied at a dose of 270 mg kg−1 N yielded the same maize dry matter as composites in which 400 mg kg−1 N was supplied to plants. Regardless of the N source, at the end of maize cultivation, the residual N in the Oxisol was reduced and inadequate for a new cultivation, even in soils treated with urea. Notably, the biochar–N composites, particularly those formulated with DAP, were as effective as urea in nourishing and promoting robust maize growth. In contrast, the maize biomass was lower for plants fertilized with pure biochars, indicating that the N from the carbonized matrices was insufficient for optimal biomass production.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Antidiabetic Activities and GC-MS Analysis of 4-Methoxychalcone
by
Leonard D. R. Acho, Edinilze S. C. Oliveira, Simone B. Carneiro, Fernanda Paula A. Melo, Leilane de S. Mendonça, Renyer A. Costa, Rosivaldo S. Borges, Marcos B. Machado, Hector H. F. Koolen, Igor Rafael dos S. Magalhães and Emersom S. Lima
AppliedChem 2024, 4(2), 140-156; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem4020010 - 10 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disease that is mainly characterized by hyperglycemia. Chalcones and their derivatives have demonstrated promising pharmacological potential for the treatment of diabetes. The aim of the study was to evaluate antidiabetic activities and analyze 4-methoxychalcone (MPP) using GC-MS.
[...] Read more.
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disease that is mainly characterized by hyperglycemia. Chalcones and their derivatives have demonstrated promising pharmacological potential for the treatment of diabetes. The aim of the study was to evaluate antidiabetic activities and analyze 4-methoxychalcone (MPP) using GC-MS. The compound was characterized using mass spectroscopy, nuclear magnetic resonance and headspace with gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (HS-GC-MS). MPP was evaluated via the inhibition of the alpha-glucosidase enzyme, cell viability and antiglycation and hemolytic activities in vitro. The study of the interaction between the bovine serum albumin protein and MPP was investigated via molecular docking. Oral sucrose tolerance and oral glucose tolerance tests were performed in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic mice. The HS-GC-MS method was able to accurately detect and characterize the compound, and the interaction between MPP and BSA revealed the remarkable affinity for the two main binding sites of BSA. This was confirmed by the in vitro antiglycation test, since MPP showed activity through both oxidative and non-oxidative stress. MPP significantly attenuated the increase in glycemia after glucose loading in STZ-induced diabetic mice. These results confirm that MPP has antihyperglycemic activity and may be an alternative for the treatment of diabetes mellitus.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A New Simple Method for the Determination of Complex Wine Aroma Compounds Using GC-MS/MS—The Case of the Greek Variety “Agiorgitiko”
by
Ioannis Ligas, Elli Goulioti, Petros Tarantilis and Yorgos Kotseridis
AppliedChem 2024, 4(2), 122-139; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem4020009 - 10 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Wine exerts a fundamental influence on the global market, and its aroma remains a crucial attribute contributing to its commercial value. The market could benefit significantly if a simple and cheap method of analyzing a wine’s aromatic profile were developed. The purpose of
[...] Read more.
Wine exerts a fundamental influence on the global market, and its aroma remains a crucial attribute contributing to its commercial value. The market could benefit significantly if a simple and cheap method of analyzing a wine’s aromatic profile were developed. The purpose of this study is to develop such a method. A multi-analytical method for quantifying 39 volatile compounds of wine aroma was developed and validated using liquid–liquid extraction and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry (GC-MS/MS). The method was validated for its linearity, reproducibility, recovery, limit of detection, and limit of quantification and showed excellent results for almost all compounds. The method was applied to 25 commercial Protected Designation of Origin “Nemea” wines, and the results were compared and correlated with the sensory analysis results by a trained panel. The correlations among the parameters indicated that the newly developed GC-MS/MS method produces similar results to human responses.
Full article
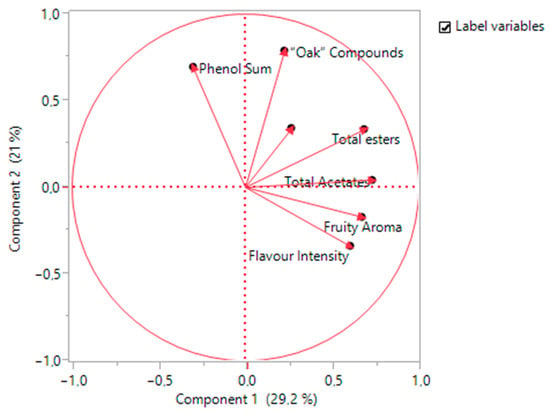
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Quantitative Analysis of NDMA in Drug Products: A Proposed High-Throughput Approach Using Headspace–SIFT-MS
by
Mark J. Perkins, Colin J. Hastie and Vaughan S. Langford
AppliedChem 2024, 4(1), 107-121; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem4010008 - 20 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Since the initial 2018 recall of angiotensin receptor blockers due to unacceptable levels of mutagenic N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) impurity, numerous drug products delivering diverse active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) have been recalled. Regulators and the industry are working together to understand and address this
[...] Read more.
Since the initial 2018 recall of angiotensin receptor blockers due to unacceptable levels of mutagenic N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) impurity, numerous drug products delivering diverse active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) have been recalled. Regulators and the industry are working together to understand and address this widescale problem. Conventional analysis of NDMA utilizes liquid or gas chromatography-based procedures that can involve complicated sample preparation and slow sample analysis. Selected ion flow tube mass spectrometry (SIFT-MS) analyses NDMA directly in the gas phase using soft chemical ionization, with an LOQ of 2 ng g−1. Through the novel application of the multiple headspace extraction (MHE) technique, NDMA was quantified directly and rapidly from the drug product without dissolution, at levels well below the regulatory acceptable intake of 96 ng day−1. A comparative analysis of recalled metformin using MHE-SIFT-MS and a conventional liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method showed good agreement. Use of the novel MHE-SIFT-MS approach may enable a wider screening of drug products to be conducted, since it provides around a three-fold increase in daily sample throughput.
Full article
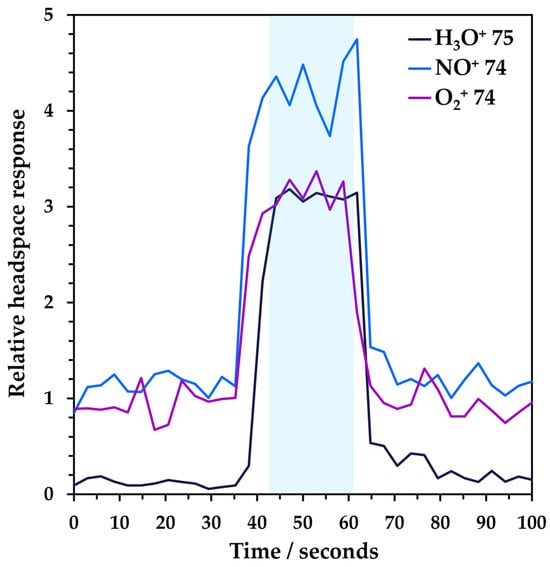
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Controlled Nickel Nanoparticles: A Review on How Parameters of Synthesis Can Modulate Their Features and Properties
by
Felipe Anchieta e Silva, Vera Maria Martins Salim and Thenner Silva Rodrigues
AppliedChem 2024, 4(1), 86-106; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem4010007 - 13 Mar 2024
Abstract
Nickel nanoparticles have wide-ranging applications in diverse fields, including electronics, catalysis, and biomedicine. The unique properties of these nanoparticles depend on their physical and chemical attributes. Consequently, there is a growing interest in understanding the performance relationships through a nuanced comprehension of their
[...] Read more.
Nickel nanoparticles have wide-ranging applications in diverse fields, including electronics, catalysis, and biomedicine. The unique properties of these nanoparticles depend on their physical and chemical attributes. Consequently, there is a growing interest in understanding the performance relationships through a nuanced comprehension of their controlled synthesis. This review explores the advancements related to precisely defined nickel nanoparticles, with a specific focus on unraveling the connections between performance and their physical/chemical characteristics. The emphasis is on elucidating how manipulating synthetic parameters, such as precursor concentration, reductant agent properties, temperature, time, and the presence of stabilizing agents, can provide additional avenues for refining the performance in terms of size and morphology. Through the analysis of each variable, we illustrate the methodology for synthesizing well-controlled nickel nanoparticles, showcasing the ability to exert precision over their composition, size, and surface morphology.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Latest Perspectives and Reviews in AppliedChem)
►▼
Show Figures
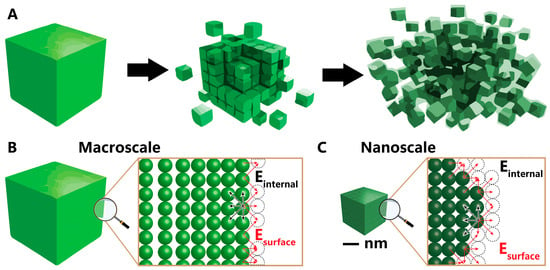
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Synergizing Immune Balance: Curcumin Gold Nanoparticles and Ultrasound Irradiation for Macrophage Down-Regulation
by
Bruna Henrique Teixeira, Karina de Oliveira Gonçalves, Daniel Perez Vieira and Lilia Coronato Courrol
AppliedChem 2024, 4(1), 70-85; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem4010006 - 06 Mar 2024
Abstract
The multifaceted health benefits of curcumin (Curcuma longa), attributed to its antioxidant, antitumor, and anti-inflammatory activities, have drawn significant scientific attention. Curcumin shows promise as a potential modulator of macrophage polarization, offering a natural strategy for managing inflammation and promoting tissue repair. However,
[...] Read more.
The multifaceted health benefits of curcumin (Curcuma longa), attributed to its antioxidant, antitumor, and anti-inflammatory activities, have drawn significant scientific attention. Curcumin shows promise as a potential modulator of macrophage polarization, offering a natural strategy for managing inflammation and promoting tissue repair. However, a limiting factor for this beneficial molecule is its limited bioavailability due to its low solubility in water. This study aimed to quantify the effect of curcumin gold nanoparticle (CurAuNP)-mediated ultrasound irradiation on THP-1-derived macrophages as potential therapeutic targets. The photoreduction method was applied to synthesize the gold nanoparticles with curcumin as a ligand (CurAu). The effect of adding polyethylene glycol in the synthesis process was studied (CurAuPEG). CurAuNP characterization included UV/Vis, Zeta potential, transmission electron microscopy, and FTIR. The amount of singlet oxygen released by curcumin and CurAuNPs was quantified by observing 1.3-diphenylisobenzofuran quenching upon ultrasound irradiation (1 MHz and 1 W/cm2). The results indicated that ultrasound therapy for 4 min with CurAuNPs significantly enhanced singlet oxygen generation and reduced macrophage viability compared to curcumin alone. The increased sonoluminescence and curcumin delivery facilitated by CurAuNPs led to greater curcumin activation. Consequently, CurAuNPs could offer promising therapeutic options for modulating macrophage polarization in pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory stages.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Nanomaterial Synthesis and Processing for Advanced Applications)
►▼
Show Figures
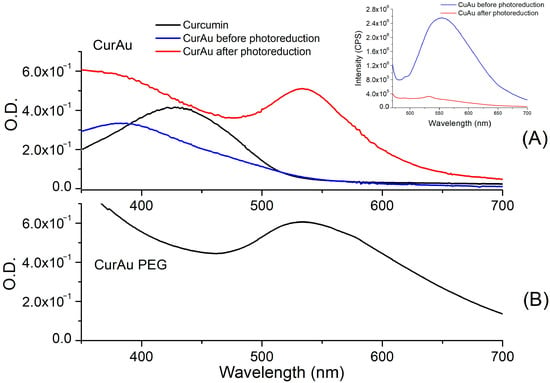
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Green Extraction of Oleoresin from Pink Pepper Fruits: Effect of Experimental Conditions and Characterization
by
Ana Flávia A. de Mello, Jaqueline Hoscheid, Djéssica T. Raspe, Natália Stevanato and Camila da Silva
AppliedChem 2024, 4(1), 56-69; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem4010005 - 28 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This work evaluated the green extraction of oleoresin from pink pepper fruits (ORPPF) using ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) and ethanol as a solvent. The effects of temperature, ultrasound power intensity, sample to solvent ratio and time on the global extraction yield (Y
[...] Read more.
This work evaluated the green extraction of oleoresin from pink pepper fruits (ORPPF) using ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) and ethanol as a solvent. The effects of temperature, ultrasound power intensity, sample to solvent ratio and time on the global extraction yield (YGE) and phenolic compounds yield (YPC) were evaluated. The oleoresin samples were characterized and its antimicrobial activity determined, and the obtained results were compared to conventional extraction in Soxhlet. From the results it was found that the application of the highest levels of the independent variables favored the extraction process. The maximum values of YGE and YPC were 28.60 wt% and 6.37 mg GAE per g fruit, respectively, obtained at 60 °C, 100% of ultrasound power (165 W), 1:20 g mL−1 (sample:solvent) and 45 min. Under maximized conditions, the ORPPF obtained by UAE showed a content of phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity inferior to soxhlet–ethanol extraction. However, the time and solvent consumption were reduced. Oleic and linoleic acids predominated in the fatty acid composition of ORPPF, in addition to sesquiterpenes and gallic and syringic acids. The ORPPF presented weak antibacterial activity, with minimum inhibitory concentration ranging from 31.25 to 125 mg mL−1.
Full article
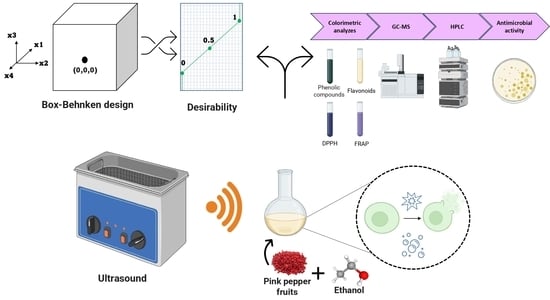
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Hydroxyalkyl Amination of Agarose Gels Improves Adsorption of Bisphenol A and Diclofenac from Water: Conceivable Prospects
by
Lennart Ljunggren, Svetlana Ivanova and Alexander E. Ivanov
AppliedChem 2024, 4(1), 42-55; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem4010004 - 24 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The hydroxyalkyl amination of agarose gels was studied as an approach to improve adsorption of polyphenols and pharmaceuticals from water. Three commercially available agarose gels, Zetarose FlashFlow4, ZetaCell-CL6B and Sepharose 4B were chemically modified using tris-(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, TRIS, and ethanolamine, EA. The adsorbed amounts
[...] Read more.
The hydroxyalkyl amination of agarose gels was studied as an approach to improve adsorption of polyphenols and pharmaceuticals from water. Three commercially available agarose gels, Zetarose FlashFlow4, ZetaCell-CL6B and Sepharose 4B were chemically modified using tris-(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, TRIS, and ethanolamine, EA. The adsorbed amounts of bisphenol A and diclofenac were significantly higher on TRIS- and EA-derivatives compared with the parent gels. Regarding bisphenol A adsorption on TRIS-ZetaCell-CL6B, a maximal adsorption capacity, Q max of 16 μmol/mL gel and an equilibrium dissociation constant KL of 2.7 × 10−4 mol/L were observed. Filtration of diclofenac-contaminated water through TRIS-Zetarose FlashFlow 4 resulted in a 10-fold reduction of the pollutant concentration within 64 column volumes of the effluent. The moderate binding affinity of polyphenols to TRIS- and EA-adsorbents facilitates efficient polyphenol desorption and column regeneration. The effects of TRIS- and EA-substituents in agarose gels, can be harnessed for the development of environmental adsorbents, as well as for the preparative separation of polyphenols and pharmaceuticals. We consider the physical shapes and textures of the prospective adsorbents with a particular focus on spongy macroporous cryogels. These innovative materials hold promise for future applications in liquid and air filtration.
Full article
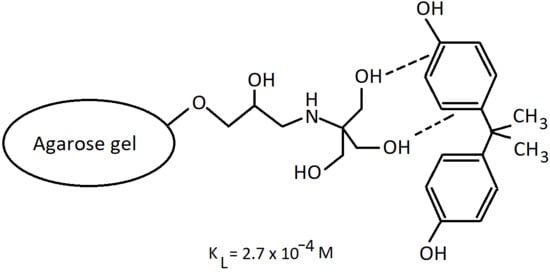
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Synthesis of Thiophene-Fused Siloles through Rhodium-Catalyzed Trans-Bis-Silylation
by
Akinobu Naka, Maho Inoue, Haruna Kawabe and Hisayoshi Kobayashi
AppliedChem 2024, 4(1), 29-41; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem4010003 - 02 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Rhodium-catalyzed reactions of 3-ethynyl-2-pentamethyldisilanylthiophene derivatives (1a–1c) have been reported. At 110 °C, compounds 1a–1c reacted in the presence of a rhodium complex catalyst, yielding thiophene-fused siloles (2a–2c) through intramolecular trans-bis-silylation. To understand
[...] Read more.
Rhodium-catalyzed reactions of 3-ethynyl-2-pentamethyldisilanylthiophene derivatives (1a–1c) have been reported. At 110 °C, compounds 1a–1c reacted in the presence of a rhodium complex catalyst, yielding thiophene-fused siloles (2a–2c) through intramolecular trans-bis-silylation. To understand the production of 2a from 1a, the mechanism was investigated using density functional theory (DFT) calculations.
Full article
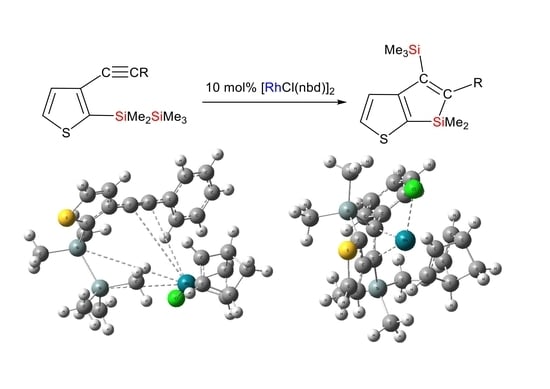
Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
The Medicinal Moroccan Plant Cladanthus arabicus as a Prominent Source of Sesquiterpenes Cladantholide and Sintenin
by
Latifa Bouissane and Christian Bailly
AppliedChem 2024, 4(1), 15-28; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem4010002 - 25 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The yellow-flowering plant Cladanthus arabicus (L.) Cass., commonly called Arabian Cladanthus or palm springs daisy, is typical of the West Mediterranean region and is particularly abundant in Morocco. The plant is used in traditional Moroccan medicine for the treatment of diabetes and other
[...] Read more.
The yellow-flowering plant Cladanthus arabicus (L.) Cass., commonly called Arabian Cladanthus or palm springs daisy, is typical of the West Mediterranean region and is particularly abundant in Morocco. The plant is used in traditional Moroccan medicine for the treatment of diabetes and other ailments. Over the past 20 years, this abundant wild plant has been neglected from a phytochemical viewpoint. For the first time, the present review provides a survey of the pharmacological properties reported from extracts of C. arabicus and from essential oils derived from the aerial parts, mainly antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties. The main bioactive natural products are discussed, with a focus on two rare sesquiterpenes of major interest, which are abundant in the stems and leaves: the 6,12-guaianolide cladantholide and the germacranolide sintenin. These sesquiterpene lactones and their analogues are presented to highlight their properties, extraction or total synthesis, and their therapeutic benefits. They both represent convenient biosourced precursors for the synthesis of derivatives. Sintenin may be used as a starting material for the design of hemi-synthetic germacradienolide-type costunolide or parthenolide derivatives. The 6,12-guaianolide scaffold of cladantholide offers opportunities to design novel arglabin derivatives. The therapeutic potential of the neglected and under-utilized plant Cladanthus arabicus and its original phytochemicals shall be explored further.
Full article
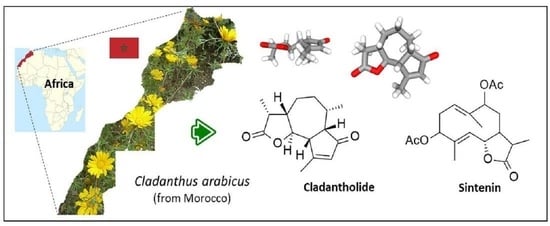
Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Interaction Parameters for the Formation of Mixed Micelles and Partitioning of Solutes in Them: A Review
by
Nozomu Suzuki
AppliedChem 2024, 4(1), 1-14; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem4010001 - 10 Jan 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
When two or more surfactants are mixed, the critical micelle concentration and solubilization capability are changed, and a careful selection of the combination promotes the micelle formation and enhances the solubilizing capability. Thus, understanding the mechanism behind the phenomena is essential for controlling
[...] Read more.
When two or more surfactants are mixed, the critical micelle concentration and solubilization capability are changed, and a careful selection of the combination promotes the micelle formation and enhances the solubilizing capability. Thus, understanding the mechanism behind the phenomena is essential for controlling the physical properties of the mixed micelle. The interaction parameters β and B that describe the formation of mixed micelles and their partitioning of solutes, respectively, were proposed by Treiner four decades ago. In this work, data on the formation and partitioning in binary surfactant systems were collected. Although the data on the parameters β and B for polar solutes and theoretical development are still insufficient, the directions of research to acquire an in-depth understanding of the formation and partitioning of the mixed micelle are proposed.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Aroma Compounds of Carrier Oils
by
Tyler Marshall, Noura S. Dosoky, Prabodh Satyal and William N. Setzer
AppliedChem 2023, 3(4), 546-580; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem3040034 - 08 Dec 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Carrier oils are used with essential oils to dilute and enhance skin penetration. They are composed of fatty acids, triglycerides, monoterpenes, and sesquiterpenes and are added to reduce potency and odor. Carrier oils have pharmaceutical applications and reduce cytotoxicity. Solvent extraction is a
[...] Read more.
Carrier oils are used with essential oils to dilute and enhance skin penetration. They are composed of fatty acids, triglycerides, monoterpenes, and sesquiterpenes and are added to reduce potency and odor. Carrier oils have pharmaceutical applications and reduce cytotoxicity. Solvent extraction is a common practice in the production of industrial-scale carrier oils, but harmful to the environment, so new eco-friendly methods are being researched. This review documents the available characteristics of various carrier oils and identifies knowledge gaps for future studies.
Full article
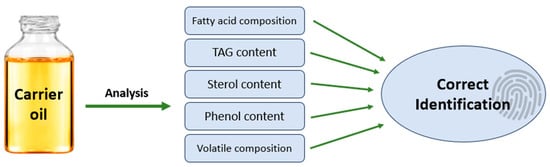
Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperReview
Light and Shadow in Near-Infrared Spectroscopy: A Powerful Tool for Cannabis sativa L. Analysis
by
María del Carmen Díaz-Liñán, Verónica Sánchez de Medina, Carlos Ferreiro-Vera and María Teresa García-Valverde
AppliedChem 2023, 3(4), 526-545; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem3040033 - 29 Nov 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Cannabis sativa L. is an ancient cultivar that has found applications in various fields, e.g., medicine, due to its beneficial effects. However, due to its psychotropic effects, the regulation of this cultivar has increased throughout the decades. In this context, the need for
[...] Read more.
Cannabis sativa L. is an ancient cultivar that has found applications in various fields, e.g., medicine, due to its beneficial effects. However, due to its psychotropic effects, the regulation of this cultivar has increased throughout the decades. In this context, the need for rapid and reliable analytical methods to ensure the quality control of Cannabis cultivars has become of extreme importance. NIRS has arisen as a powerful tool in this field due to its multiple advantages, e.g., non-destructive, rapid, and cost-effective. In this article, the chemometric techniques commonly employed in NIRS method development are described, along with their application for the analysis of Cannabis samples. Regarding qualitative methods, different mathematical treatments and classification models are explained. As for quantitative methods, the representative linear and non-linear modelling techniques applied for the development of prediction equations are described, alongside their application in the Cannabis field. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time this type of review is written, since there are several articles which address cannabinoid determination, but the main purpose of this review is to enhance the potential of NIRS over the traditional techniques employed for the analysis of Cannabis samples.
Full article
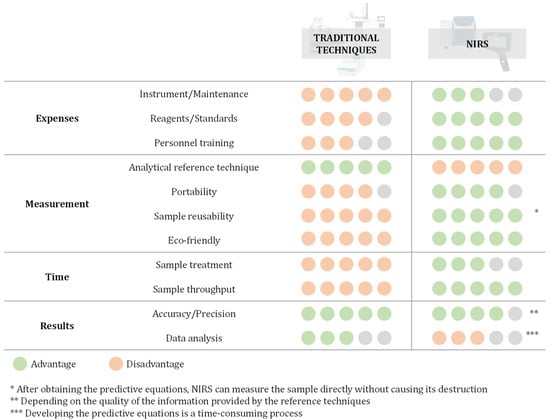
Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
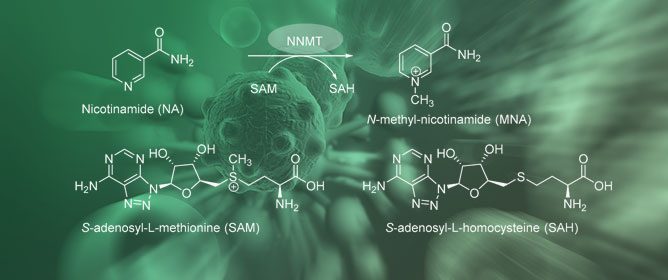
Tetrahydroisoquinoline-Triazole Derivatives: Novel Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase Inhibitors
by
Alison T. Ung and Matthew Payne
AppliedChem 2023, 3(4), 509-525; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem3040032 - 21 Nov 2023
Abstract
Through the Lilly Open Innovation Drug Discovery program (OIDD), we discovered five cationic bis(aryltriazol-4-yl)methyl)-6,7-dimethoxytetrahydroisoquinolinium derivatives that effectively inhibit human nicotinamide N-methyltransferase. Compounds 4a, 4c, and 4f demonstrated activity against hNNMT in enzymatic-based testing, with IC50 values of 3.177 μM, 7.9 μM,
[...] Read more.
Through the Lilly Open Innovation Drug Discovery program (OIDD), we discovered five cationic bis(aryltriazol-4-yl)methyl)-6,7-dimethoxytetrahydroisoquinolinium derivatives that effectively inhibit human nicotinamide N-methyltransferase. Compounds 4a, 4c, and 4f demonstrated activity against hNNMT in enzymatic-based testing, with IC50 values of 3.177 μM, 7.9 μM, and 4.477 μM, respectively. In cell-based testing, 4c and 4f inhibited the enzyme in HEK293 cells with an IC50 value of 2.81 μM and 1.97 μM. Compound 4m inhibited hNNMT in the enzymatic-based assay by 98% at a concentration of 10 μM, with IC50 of 1.011 μM in the cell-based assay. Through structure-activity relationship analysis, we found that the active compounds had electron-withdrawing substituents at the 4-position of the phenyl-triazole, while compounds containing bulky and electron-donating groups at the same position did not display any activity. The results of docking studies using AutoDock 4.2 showed that all active compounds had similar binding patterns at the NNMT active site. They occupied the nicotinamide binding site and about two-thirds of the S-adenosyl-L-methionine site. However, the SAR and docking results of 4g contradicted the compound’s inactivity. Nevertheless, the molecular docking studies provided insight into how the ligands interact with the protein and explained the activity of our compounds.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in AppliedChem)
►▼
Show Figures
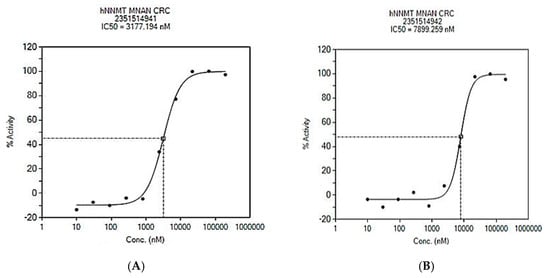
Figure 1
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
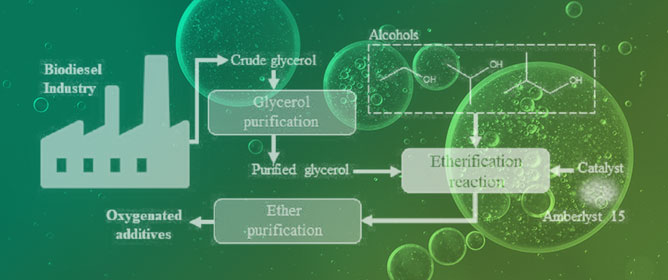
Experimental and Simulation Studies for Purification and Etherification of Glycerol from the Biodiesel Industry
by
Silvia S. O. Silva, Matheus R. Nascimento, Ricardo J. P. Lima, Francisco Murilo Tavares Luna and Célio Loureiro Cavalcante Júnior
AppliedChem 2023, 3(4), 492-508; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem3040031 - 03 Nov 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In this study, a purification route was applied to crude glycerol and its valorization via etherification was evaluated. Crude glycerol samples were obtained through transesterification reactions of soybean oil with methanol using potassium hydroxide as catalyst. A set of separation steps (acidification, neutralization,
[...] Read more.
In this study, a purification route was applied to crude glycerol and its valorization via etherification was evaluated. Crude glycerol samples were obtained through transesterification reactions of soybean oil with methanol using potassium hydroxide as catalyst. A set of separation steps (acidification, neutralization, salt precipitation, evaporation and removal of contaminants using ion-exchange resins) was performed for purification of crude glycerol. The glycerol contents of crude samples were 46% wt., and for purified samples they were above 98% wt. The etherification reactions were carried out with purified samples and different alcohols (ethanol, isopropanol and 3-methyl-1-butanol) placed into a batch reactor, using a small amount of Amberlyst 15 as a catalyst, with autogenous pressure and solvent-free conditions. The glycerol conversion, selectivity and yield to ethers were evaluated. A glycerol conversion of up to 97% wt. was obtained when using ethanol. For isopropanol, the glycerol conversion rate was 85% (97.1% of monoether and 2.8% of diether). However, the selectivity to ethers for 3-methyl-1-butanol was negligible (<3% wt.). A process simulation for the purification and etherification steps integrated with a biodiesel production process was assessed in terms of productivity and energy consumption, considering different scenarios of glycerol/alcohol molar ratios. Finally, main impacts on the overall energy consumption were evaluated for the purification processes (glycerol and ethers).
Full article
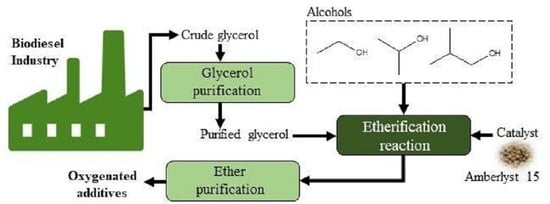
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of the Effects of Nano-SiO2 Microemulsion on Decompression and Augmented Injection in the Eunan Tight Reservoir
by
Ke Wu, Mingbiao Xu, Shoucheng Wen and Xuefeng Deng
AppliedChem 2023, 3(4), 477-491; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem3040030 - 25 Oct 2023
Abstract
The residual oil saturation of the matrix near the well zone of a tight reservoir is high due to the tight reservoir’s complex conditions, such as the small pore throat radius and low permeability of the matrix and the development of microfractures, which
[...] Read more.
The residual oil saturation of the matrix near the well zone of a tight reservoir is high due to the tight reservoir’s complex conditions, such as the small pore throat radius and low permeability of the matrix and the development of microfractures, which can result in serious water channeling, even after long-term water injection development. The aim of this paper is to improve the effects of depressurization and augmented injection for tight reservoir waterflooding development by reducing the tight matrix’s residual oil saturation, increasing and maintaining its water phase permeability near the well zone using a nano-SiO2 microemulsion system with a small particle size and high interfacial activity. Therefore, four nano-microemulsion systems were evaluated and screened for their temperature resistance, salt resistance, interfacial tension, solubilization, and dilution resistance. A microemulsion system of 13% A + 4% B + 4% C + 4% n-butanol + 6% oil phase + 69% NaCl solution (10%) + 1% OP-5 + 0.5% anti-temperature agent + 0.3% nanosilica material was preferred. According to the core displacement experiment, the depressurization rate can reach 28~60% when the injection concentration of the system is 1~10% and the injection volume is 2~5 PV. The results of the on-site test show that the water injection pressure dropped to 17.5 MPa, which was lower than the reservoir fracture re-opening pressure. The pressure reduction rate was approximately 20%. The validity period of the depressurization and augmented injection has reached 23 months to date.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in AppliedChem)
►▼
Show Figures
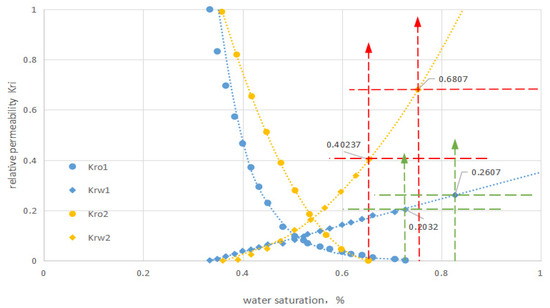
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
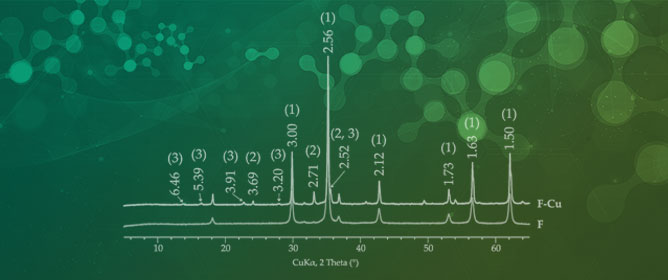
ZnFe2O4/Zeolite Nanocomposites for Sorption Extraction of Cu2+ from Aqueous Medium
by
Elena Tomina, Lyudmila Novikova, Alexandra Kotova, Anna Meshcheryakova, Victoria Krupskaya, Ivan Morozov, Tatiana Koroleva, Ekaterina Tyupina, Nikolai Perov and Yuliya Alekhina
AppliedChem 2023, 3(4), 452-476; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem3040029 - 30 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
In order to enhance the efficiency of heavy metal ion extraction from aqueous medium, new nanocomposite magnetic sorbents were synthesized on the base of natural zeolite (Zt) and nanoparticles of ZnFe2O4 (F). The composition, structure and physical–chemical properties of new
[...] Read more.
In order to enhance the efficiency of heavy metal ion extraction from aqueous medium, new nanocomposite magnetic sorbents were synthesized on the base of natural zeolite (Zt) and nanoparticles of ZnFe2O4 (F). The composition, structure and physical–chemical properties of new composites with 2% (Zt-2F), 8% (Zt-8F) and 16% (Zt-16F) of zinc ferrite were characterized by XRD, BET adsorption–desorption of nitrogen, SEM with elemental mapping, TEM and magnetometry. The sorption capacity of materials was assessed towards Cu2+ ions in aqueous solutions, for which kinetic and equilibrium features of sorption were established. The maximal sorption capacity (amax, mg/g) of the studied materials increased in the order: Zt (19.4) < Zt-2F (27.3) < Zt-8F (30.2) < Zt-16F (32.8) < ZnFe2O4 (161.3). The kinetics of the sorption process followed a pseudo-second order kinetic model. The sorption equilibrium at zinc ferrite was successfully described by the Langmuir model, while the Freundlich model better fitted the sorption equilibrium on zeolite and composites. The efficiency of Cu2+ ion extraction from 320 mg/dm3 aqueous solution was 63% for composite Zt-16F and 100% for a sample of ZnFe2O4. It was established that the proposed composite sorbents provide the operation of several cycles without regeneration, they can be easily recycled with 0.1 N HCl solution and are capable of magnetic separation. The advantages of new composites and the proposed method of synthesis allow recommending these materials as effective sorbents of heavy metals from wastewater.
Full article
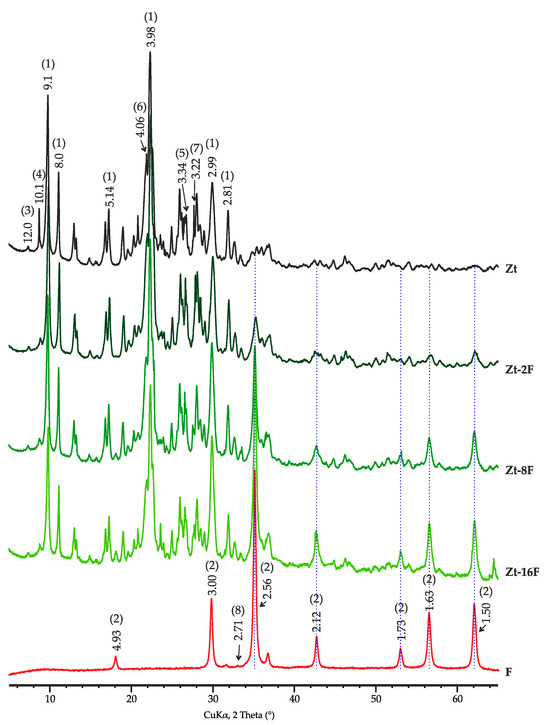
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Carotenoids Extraction from Orange Peels Using a Thymol-Based Hydrophobic Eutectic Solvent
by
Konstantinos Terlidis, Vassilis Athanasiadis, Theodoros Chatzimitakos, Eleni Bozinou and Stavros I. Lalas
AppliedChem 2023, 3(4), 437-451; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem3040028 - 25 Sep 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The food industry produces substantial amounts of waste, which can cause a lot of environmental issues. However, such waste is also a valuable source of bioactive substances that can potentially be used either by the food industry or other types of industries, in
[...] Read more.
The food industry produces substantial amounts of waste, which can cause a lot of environmental issues. However, such waste is also a valuable source of bioactive substances that can potentially be used either by the food industry or other types of industries, in the production of medicines, nutraceuticals, cosmetics, etc. The present study proposes a novel approach to extract such bioactive compounds from orange peel waste using hydrophobic eutectic solvents synthesized with thymol and fatty acids (hexanoic and octanoic acid). A response surface methodology was employed to optimize the extraction conditions and achieve maximum recovery of carotenoids. The optimal hydrophobic eutectic solvent consisted of thymol and hexanoic acid at a molar ratio of 2:1, and the optimum extraction was achieved using a solvent-to-solid ratio of 12:1 and a temperature of 20 °C for 78 min; this resulted in a recovery of 259.45 μg of total carotenoids per g of dry matter, which is a significantly higher recovery compared to common organic solvents. Based on the above, it is demonstrated that hydrophobic eutectic solvents is a promising solvent that can be used to extract bioactive compounds from orange peel waste.
Full article
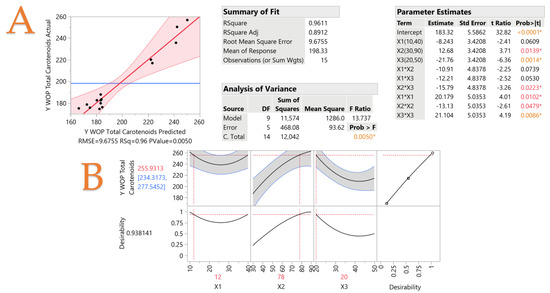
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Ability of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy to Discriminate Plant Protein Mixtures: A Preliminary Study
by
Buddhi Dayananda, Priyam Chahwala and Daniel Cozzolino
AppliedChem 2023, 3(3), 428-436; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem3030027 - 01 Sep 2023
Cited by 1
Abstract
The aim of this paper was to evaluate the effect of two different matrices (e.g., starch base flour vs. protein base flour) on the ability of near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy to classify binary mixtures of chickpea (protein), corn and tapioca (starch) flours. Binary mixtures
[...] Read more.
The aim of this paper was to evaluate the effect of two different matrices (e.g., starch base flour vs. protein base flour) on the ability of near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy to classify binary mixtures of chickpea (protein), corn and tapioca (starch) flours. Binary mixtures were made by mixing different proportions of chickpea plus corn, chickpea plus tapioca, and corn plus tapioca flour. Spectra were collected using NIR spectroscopy and the data analyzed using techniques such as principal component analysis (PCA) and partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA). The results showed an effect of the matrix on the PLS-DA classification results, in both classification rates and PLS loadings. The different combinations of flours/mixtures showed changes in absorbance values around 4752 cm−1 that are associated with starch and protein. Nevertheless, the use of NIR spectroscopic might provide a valuable initial screening and identification of the potential contamination of flours along the supply and value chains, enabling more costly methods to be used more productively on suspect samples.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in AppliedChem)
►▼
Show Figures
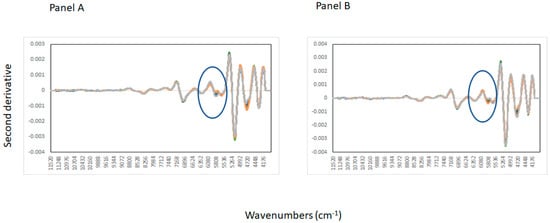
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Cuticular Hydrocarbon Profiling of Australian Gonipterini Weevils
by
Joel B. Johnson
AppliedChem 2023, 3(3), 414-427; https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem3030026 - 17 Aug 2023
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Cuticular hydrocarbon (CHC) profiling shows promise as a chemotaxonomic tool for identifying and discriminating between closely related insect species. However, there have been limited studies using CHC profiling to differentiate between weevil species (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). This proof-of-concept study investigated the use of CHC
[...] Read more.
Cuticular hydrocarbon (CHC) profiling shows promise as a chemotaxonomic tool for identifying and discriminating between closely related insect species. However, there have been limited studies using CHC profiling to differentiate between weevil species (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). This proof-of-concept study investigated the use of CHC and volatile profiling to discriminate between five weevil species from three genera in the Gonipterini tribe. A total of 56 CHCs and 41 other volatile compounds were found across the five species, with 83 of the compounds being identified through their mass fragmentation patterns. The number of CHCs from each species ranged from 20 to 43, while the proportion of CHCs unique to each species varied between 0% and 19%. The most abundant CHCs were nonacosane, 7-methylheptacosane, heptacosane, and hexacosane. Principal component analysis of the centred log-ratio transformed data revealed broad differences in CHC profiles between the two Oxyops species, with Bryachus squamicollis demonstrating the greatest divergence from the other Gonipterini species. The results suggest that CHC analysis could be used to support established taxonomic methods, including morphological features and genetic sequencing results.
Full article
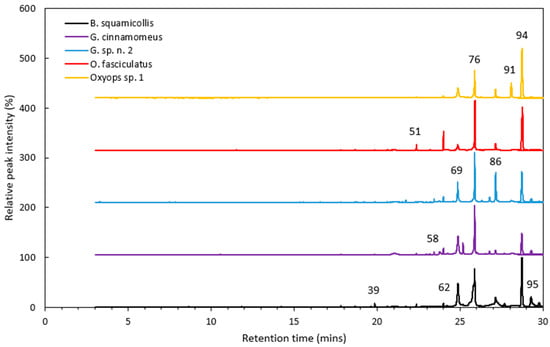
Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
AppliedChem, ChemEngineering, Energies, Membranes, Processes, Recycling, Separations, Water
Capacitive Deionization Technology for Water Treatment
Topic Editors: Shenxu Bao, Xin ZhangDeadline: 30 September 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
AppliedChem
Spectroscopy in Food Science and Engineering
Guest Editors: Alessandra Biancolillo, Martina FoschiDeadline: 31 May 2024
Special Issue in
AppliedChem
Nanomaterial Synthesis and Processing for Advanced Applications
Guest Editors: Gnanaprakasam Janani, Uk SimDeadline: 30 June 2024
Special Issue in
AppliedChem
Latest Perspectives and Reviews in AppliedChemGuest Editor: Jason LoveDeadline: 31 August 2024