-
 TLR2 and TLR9 Blockade Using Specific Intrabodies Inhibits Inflammation-Mediated Pancreatic Cancer Cell Growth
TLR2 and TLR9 Blockade Using Specific Intrabodies Inhibits Inflammation-Mediated Pancreatic Cancer Cell Growth -
 Performance Characteristics and Limitations of the Available Assays for the Detection and Quantitation of Monoclonal Free Light Chains and New Emerging Methodologie
Performance Characteristics and Limitations of the Available Assays for the Detection and Quantitation of Monoclonal Free Light Chains and New Emerging Methodologie -
 Diversity in the HLA-I Recognition of HLA-F Monoclonal Antibodies: HLA-F or HLA-Ib Monospecific, HLA-E or HLA-G Bispecific Antibodies with or without HLA-Ia Reactivity
Diversity in the HLA-I Recognition of HLA-F Monoclonal Antibodies: HLA-F or HLA-Ib Monospecific, HLA-E or HLA-G Bispecific Antibodies with or without HLA-Ia Reactivity -
 Antiphospholipid Antibodies Associated with Native Arteriovenous Fistula Complications in Hemodialysis Patients: A Comprehensive Review of the Literature
Antiphospholipid Antibodies Associated with Native Arteriovenous Fistula Complications in Hemodialysis Patients: A Comprehensive Review of the Literature
Journal Description
Antibodies
Antibodies
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on immunoglobulins, published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Embase, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q1 (Drug Discovery)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 17.7 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 4.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2023).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
Impact Factor:
4.7 (2022);
5-Year Impact Factor:
4.9 (2022)
Latest Articles
Cross-Reactivity of N6AMT1 Antibodies with Aurora Kinase A: An Example of Antibody-Specific Non-Specificity
Antibodies 2024, 13(2), 33; https://doi.org/10.3390/antib13020033 - 22 Apr 2024
Abstract
►
Show Figures
Primary antibodies are one of the main tools used in molecular biology research. However, the often-occurring cross-reactivity of primary antibodies complicates accurate data analysis. Our results show that three commercial polyclonal antibodies raised against N-6 adenine-specific DNA methyltransferase 1 (N6AMT1) strongly cross-react with
[...] Read more.
Primary antibodies are one of the main tools used in molecular biology research. However, the often-occurring cross-reactivity of primary antibodies complicates accurate data analysis. Our results show that three commercial polyclonal antibodies raised against N-6 adenine-specific DNA methyltransferase 1 (N6AMT1) strongly cross-react with endogenous and recombinant mitosis-associated protein Aurora kinase A (AURKA). The cross-reactivity was verified through immunofluorescence, immunoblot, and immunoprecipitation assays combined with mass spectrometry. N6AMT1 and AURKA are evolutionarily conserved proteins that are vital for cellular processes. Both proteins share the motif ENNPEE, which is unique to only these two proteins. We suggest that N6AMT1 antibodies recognise this motif in N6AMT1 and AURKA proteins and exhibit an example of “specific” non-specificity. This serves as an example of the importance of controls and critical data interpretation in molecular biology research.
Full article
Open AccessReview
A Narrative Review of the State of the Art of CCR4-Based Therapies in Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphomas: Focus on Mogamulizumab and Future Treatments
by
Corrado Zengarini, Alba Guglielmo, Martina Mussi, Giovanna Motta, Claudio Agostinelli, Elena Sabattini, Bianca Maria Piraccini and Alessandro Pileri
Antibodies 2024, 13(2), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/antib13020032 - 22 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
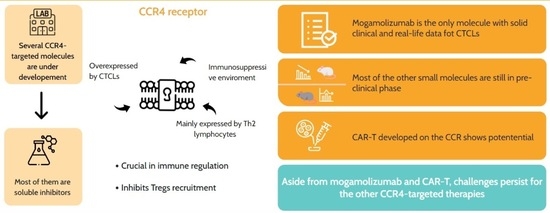
The CCR4 receptor is a pivotal target in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) therapy due to its role in impairing immune responses against malignant T-cells and expression profiles. Monoclonal antibodies like mogamulizumab effectively bind to CCR4, reducing tumour burden and enhancing patient outcomes by
[...] Read more.
The CCR4 receptor is a pivotal target in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) therapy due to its role in impairing immune responses against malignant T-cells and expression profiles. Monoclonal antibodies like mogamulizumab effectively bind to CCR4, reducing tumour burden and enhancing patient outcomes by inhibiting the receptor’s interaction with ligands, thereby hindering malignant T-cell migration and survival. Combining CCR4 antibodies with chemotherapy, radiation, and other drugs is being explored for synergistic effects. Additionally, small-molecular inhibitors, old pharmacological agents interacting with CCR4, and CAR-T therapies are under investigation. Challenges include drug resistance, off-target effects, and patient selection, addressed through ongoing trials refining protocols and identifying biomarkers. Despite advancements, real-life data for most of the emerging treatments are needed to temper expectations. In conclusion, CCR4-targeted therapies show promise for CTCL management, but challenges persist. Continued research aims to optimise treatments, enhance outcomes, and transform CTCL management. This review aims to elucidate the biological rationale and the several agents under various stages of development and clinical evaluation with the actual known data.
Full article
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Fcγ-Receptor-Independent Controlled Activation of CD40 Canonical Signaling by Novel Therapeutic Antibodies for Cancer Therapy
by
Karsten Beckmann, Carmen Reitinger, Xianglei Yan, Anna Carle, Eva Blümle, Nicole Jurkschat, Claudia Paulmann, Sandra Prassl, Linda V. Kazandjian, Karin Loré, Falk Nimmerjahn and Stephan Fischer
Antibodies 2024, 13(2), 31; https://doi.org/10.3390/antib13020031 - 18 Apr 2024
Abstract
The activation of CD40-mediated signaling in antigen-presenting cells is a promising therapeutic strategy to promote immune responses against tumors. Most agonistic anti-CD40 antibodies currently in development require the Fcγ-receptor (FcγR)-mediated crosslinking of CD40 molecules for a meaningful activation of CD40 signaling but have
[...] Read more.
The activation of CD40-mediated signaling in antigen-presenting cells is a promising therapeutic strategy to promote immune responses against tumors. Most agonistic anti-CD40 antibodies currently in development require the Fcγ-receptor (FcγR)-mediated crosslinking of CD40 molecules for a meaningful activation of CD40 signaling but have limitations due to dose-limiting toxicities. Here we describe the identification of CD40 antibodies which strongly stimulate antigen-presenting cells in an entirely FcγR-independent manner. These Fc-silenced anti-CD40 antibodies induce an efficient upregulation of costimulatory receptors and cytokine release by dendritic cells. Finally, the most active identified anti-CD40 antibody shows activity in humanized mice. More importantly, there are no signs of obvious toxicities. These studies thus demonstrate the potent activation of antigen-presenting cells with anti-CD40 antibodies lacking FcγR-binding activity and open the possibility for an efficacious and safe combination therapy for cancer patients.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Antibody-Based Therapeutics)
►▼
Show Figures
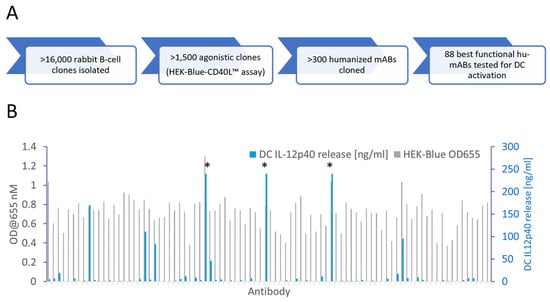
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Enhanced Characterization of Lysine-Linked Antibody Drug Conjugates Enabled by Middle-Down Mass Spectrometry and Higher-Energy Collisional Dissociation-Triggered Electron-Transfer/Higher-Energy Collisional Dissociation and Ultraviolet Photodissociation
by
Eleanor Watts, Aarti Bashyal, Sean D. Dunham, Christopher M. Crittenden and Jennifer S. Brodbelt
Antibodies 2024, 13(2), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/antib13020030 - 17 Apr 2024
Abstract
As the development of new biotherapeutics advances, increasingly sophisticated tandem mass spectrometry methods are needed to characterize the most complex molecules, including antibody drug conjugates (ADCs). Lysine-linked ADCs, such as trastuzumab-emtansine (T-DM1), are among the most heterogeneous biotherapeutics. Here, we implement a workflow
[...] Read more.
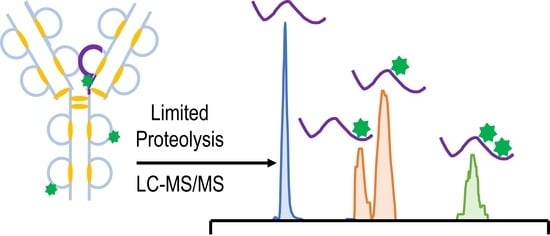
As the development of new biotherapeutics advances, increasingly sophisticated tandem mass spectrometry methods are needed to characterize the most complex molecules, including antibody drug conjugates (ADCs). Lysine-linked ADCs, such as trastuzumab-emtansine (T-DM1), are among the most heterogeneous biotherapeutics. Here, we implement a workflow that combines limited proteolysis with HCD-triggered EThcD and UVPD mass spectrometry for the characterization of the resulting middle-down large-sized peptides of T-DM1. Fifty-three payload-containing peptides were identified, ranging in mass from 1.8 to 16.9 kDa, and leading to the unambiguous identification of 46 out of 92 possible conjugation sites. In addition, seven peptides were identified containing multiple payloads. The characterization of these types of heterogeneous peptides represents an important step in unraveling the combinatorial nature of lysine-conjugated ADCs.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Antibody-Based Therapeutics)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Efficient Expression of Functionally Active Aflibercept with Designed N-glycans
by
Tahereh Keshvari, Stanislav Melnik, Lin Sun, Ali Niazi, Farzaneh Aram, Ali Moghadam, Benjamin Kogelmann, Gordana Wozniak-Knopp, Somanath Kallolimath, Amin Ramezani and Herta Steinkellner
Antibodies 2024, 13(2), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/antib13020029 - 07 Apr 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Aflibercept is a therapeutic recombinant fusion protein comprising extracellular domains of human vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFRs) and IgG1-Fc. It is a highly glycosylated protein with five N-glycosylation sites that might impact it structurally and/or functionally. Aflibercept is produced in mammalian cells
[...] Read more.
Aflibercept is a therapeutic recombinant fusion protein comprising extracellular domains of human vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFRs) and IgG1-Fc. It is a highly glycosylated protein with five N-glycosylation sites that might impact it structurally and/or functionally. Aflibercept is produced in mammalian cells and exhibits large glycan heterogeneity, which hampers glycan-associated investigations. Here, we report the expression of aflibercept in a plant-based system with targeted N-glycosylation profiles. Nicotiana benthamiana-based glycoengineering resulted in the production of aflibercept variants carrying designed carbohydrates, namely, N-glycans with terminal GlcNAc and sialic acid residues, herein referred to as AFLIGnGn and AFLISia, respectively. Both variants were transiently expressed in unusually high amounts (2 g/kg fresh leaf material) in leaves and properly assembled to dimers. Mass spectrometric site-specific glycosylation analyses of purified aflibercept showed the presence of two to four glycoforms in a consistent manner. We also demonstrate incomplete occupancy of some glycosites. Both AFLIGnGn and AFLISia displayed similar binding potency to VEGF165, with a tendency of lower binding to variants with increased sialylation. Collectively, we show the expression of functionally active aflibercept in significant amounts with controlled glycosylation. The results provide the basis for further studies in order to generate optimized products in the best-case scenario.
Full article
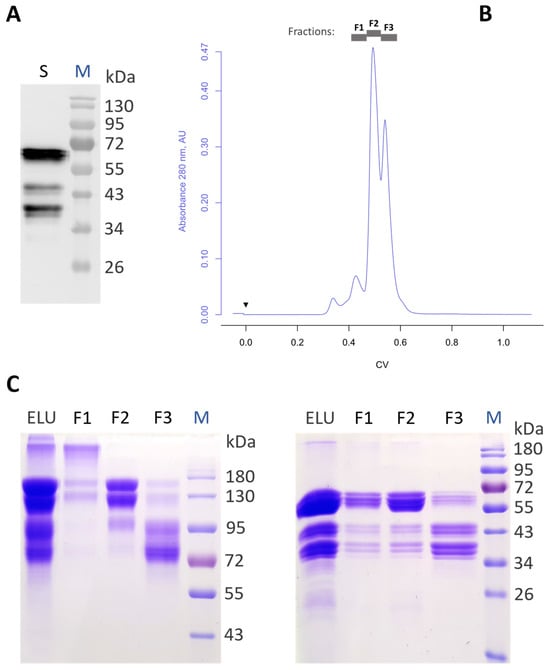
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Beyond bNAbs: Uses, Risks, and Opportunities for Therapeutic Application of Non-Neutralising Antibodies in Viral Infection
by
Kahlio Mader and Lynn B. Dustin
Antibodies 2024, 13(2), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/antib13020028 - 03 Apr 2024
Abstract
The vast majority of antibodies generated against a virus will be non-neutralising. However, this does not denote an absence of protective capacity. Yet, within the field, there is typically a large focus on antibodies capable of directly blocking infection (neutralising antibodies, NAbs) of
[...] Read more.
The vast majority of antibodies generated against a virus will be non-neutralising. However, this does not denote an absence of protective capacity. Yet, within the field, there is typically a large focus on antibodies capable of directly blocking infection (neutralising antibodies, NAbs) of either specific viral strains or multiple viral strains (broadly-neutralising antibodies, bNAbs). More recently, a focus on non-neutralising antibodies (nNAbs), or neutralisation-independent effects of NAbs, has emerged. These can have additive effects on protection or, in some cases, be a major correlate of protection. As their name suggests, nNAbs do not directly neutralise infection but instead, through their Fc domains, may mediate interaction with other immune effectors to induce clearance of viral particles or virally infected cells. nNAbs may also interrupt viral replication within infected cells. Developing technologies of antibody modification and functionalisation may lead to innovative biologics that harness the activities of nNAbs for antiviral prophylaxis and therapeutics. In this review, we discuss specific examples of nNAb actions in viral infections where they have known importance. We also discuss the potential detrimental effects of such responses. Finally, we explore new technologies for nNAb functionalisation to increase efficacy or introduce favourable characteristics for their therapeutic applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Review Collection on Humoral Immunity)
►▼
Show Figures
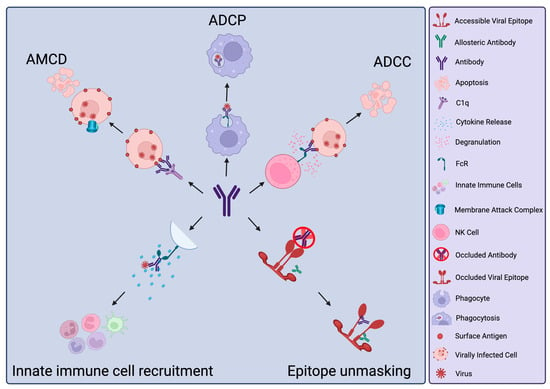
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Factors Governing B Cell Recognition of Autoantigen and Function in Type 1 Diabetes
by
Lindsay E. Bass and Rachel H. Bonami
Antibodies 2024, 13(2), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/antib13020027 - 01 Apr 2024
Abstract
Islet autoantibodies predict type 1 diabetes (T1D) but can be transient in murine and human T1D and are not thought to be directly pathogenic. Rather, these autoantibodies signal B cell activity as antigen-presenting cells (APCs) that present islet autoantigen to diabetogenic T cells
[...] Read more.
Islet autoantibodies predict type 1 diabetes (T1D) but can be transient in murine and human T1D and are not thought to be directly pathogenic. Rather, these autoantibodies signal B cell activity as antigen-presenting cells (APCs) that present islet autoantigen to diabetogenic T cells to promote T1D pathogenesis. Disrupting B cell APC function prevents T1D in mouse models and has shown promise in clinical trials. Autoantigen-specific B cells thus hold potential as sophisticated T1D biomarkers and therapeutic targets. B cell receptor (BCR) somatic hypermutation is a mechanism by which B cells increase affinity for islet autoantigen. High-affinity B and T cell responses are selected in protective immune responses, but immune tolerance mechanisms are known to censor highly autoreactive clones in autoimmunity, including T1D. Thus, different selection rules often apply to autoimmune disease settings (as opposed to protective host immunity), where different autoantigen affinity ceilings are tolerated based on variations in host genetics and environment. This review will explore what is currently known regarding B cell signaling, selection, and interaction with T cells to promote T1D pathogenesis.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Autoimmune and Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases: Potential Biomarkers, Antibodies Response and New Therapies)
Open AccessCommunication
Case Series: Efficacy of Polyclonal Intravenous Immunoglobulin for Refractory Clostridioides difficile Infection
by
Sophie A. Ragan, Caitlin Doyle, Neha Datta, Heather Abdic, Mark H. Wilcox, Ros Montgomery, Shanika A. Crusz, Yashwant R. Mahida and Tanya M. Monaghan
Antibodies 2024, 13(2), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/antib13020026 - 01 Apr 2024
Abstract
Background: Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) for Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) no longer features in treatment guidelines. However, IVIg is still used by some clinicians for severe or recurrent CDI (rCDI) cases. The main objective of this study was to investigate the efficacy of IVIg
[...] Read more.
Background: Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) for Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) no longer features in treatment guidelines. However, IVIg is still used by some clinicians for severe or recurrent CDI (rCDI) cases. The main objective of this study was to investigate the efficacy of IVIg and to identify possible predictors of disease resolution post IVIg administration for patients with CDI. Methods: This retrospective observational cohort study of patients ≥2 years old hospitalised with severe, relapsing, or rCDI treated with IVIg therapy was performed in a large UK tertiary hospital between April 2018 and March 2023. Scanned electronic notes from patient admissions and clinical reporting systems were used to collect relevant data. Results: In total, 20/978 patients diagnosed with CDI over the 5-year study were treated with IVIg. Twelve (60%) had hospital-onset CDI. Eleven of the twenty patients (55%) responded to treatment, with a mean of 8.6 (SD 10.7) days to disease resolution. Sixteen (80%) patients were treated for severe CDI and four (20%) for rCDI (n = 3) and relapsing CDI (n = 1). There were no statistically significant differences in possible independent predictors of disease resolution post IVIg administration between groups. There was an average of 6.2 (4.9) days to IVIg administration after diagnosis with no difference between responders and non-responders (p = 0.88) and no further significant difference in additional indicators. Four (36%) of the responders were immunosuppressed compared to just one (11%) of the non-responders (p = 0.15). Six of the responders (two with recurrent and four with severe CDI) improved rapidly within 2 days, and three of these were immunosuppressed. Conclusion: We observed disease resolution post IVIg therapy in over 50% of patients with refractory CDI. Our data also support a potential enhanced effect of IVIg in immunosuppressed individuals. Thus, the role of IVIg for CDI treatment, particularly in the immunosuppressed, warrants future case–control studies coupled to mechanistic investigations to improve care for this ongoing significant healthcare-associated infection.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Antibody-Based Therapeutics)
►▼
Show Figures
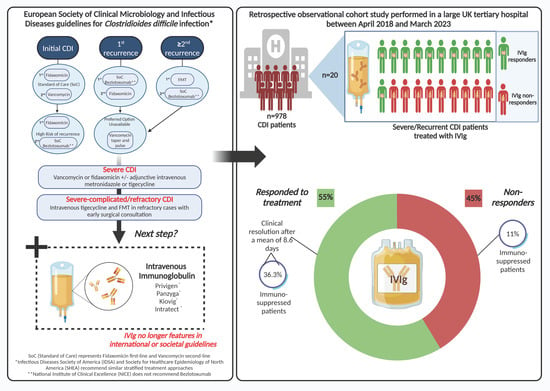
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
vNARs as Neutralizing Intracellular Therapeutic Agents: Glioblastoma as a Target
by
Alejandro Manzanares-Guzmán, Pavel H. Lugo-Fabres and Tanya A. Camacho-Villegas
Antibodies 2024, 13(1), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/antib13010025 - 18 Mar 2024
Abstract
Glioblastoma is the most prevalent and fatal form of primary brain tumors. New targeted therapeutic strategies for this type of tumor are imperative given the dire prognosis for glioblastoma patients and the poor results of current multimodal therapy. Previously reported drawbacks of antibody-based
[...] Read more.
Glioblastoma is the most prevalent and fatal form of primary brain tumors. New targeted therapeutic strategies for this type of tumor are imperative given the dire prognosis for glioblastoma patients and the poor results of current multimodal therapy. Previously reported drawbacks of antibody-based therapeutics include the inability to translocate across the blood–brain barrier and reach intracellular targets due to their molecular weight. These disadvantages translate into poor target neutralization and cancer maintenance. Unlike conventional antibodies, vNARs can permeate tissues and recognize conformational or cryptic epitopes due to their stability, CDR3 amino acid sequence, and smaller molecular weight. Thus, vNARs represent a potential antibody format to use as intrabodies or soluble immunocarriers. This review comprehensively summarizes key intracellular pathways in glioblastoma cells that induce proliferation, progression, and cancer survival to determine a new potential targeted glioblastoma therapy based on previously reported vNARs. The results seek to support the next application of vNARs as single-domain antibody drug-conjugated therapies, which could overcome the disadvantages of conventional monoclonal antibodies and provide an innovative approach for glioblastoma treatment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Antibody-Based Therapeutics)
►▼
Show Figures
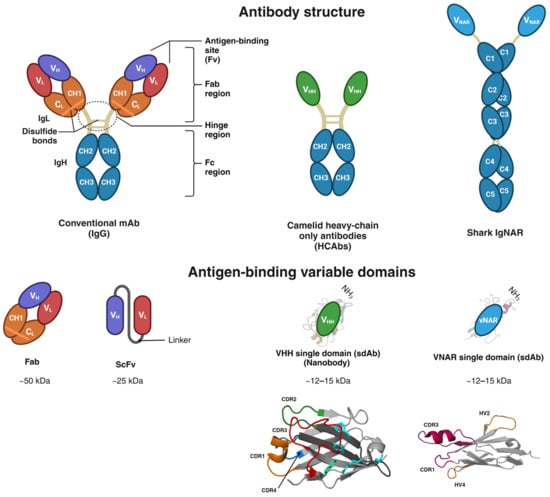
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Anti-CD99 Antibody Therapy Triggers Macrophage-Dependent Ewing Cell Death In Vitro and Myeloid Cell Recruitment In Vivo
by
Allison F. O’Neill, Evelyn M. Nguyen, Evelyn D. Maldonado, Matthew R. Chang, Jiusong Sun, Quan Zhu and Wayne A. Marasco
Antibodies 2024, 13(1), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/antib13010024 - 18 Mar 2024
Abstract
Background: Ewing sarcoma is a rare tumor of the bone or soft tissues characterized by diffuse membranous staining for CD99. As this tumor remains incurable in the metastatic, relapsed, and refractory settings, we explored the downstream immune implications of targeting CD99. Methods: We
[...] Read more.
Background: Ewing sarcoma is a rare tumor of the bone or soft tissues characterized by diffuse membranous staining for CD99. As this tumor remains incurable in the metastatic, relapsed, and refractory settings, we explored the downstream immune implications of targeting CD99. Methods: We discovered a human anti-CD99 antibody (NOA2) by phagemid panning and investigated NOA2 immune cell-mediated cytotoxicity in vitro and in vivo focusing on the myeloid cell compartment, given that M2 macrophages are present in human tumors and associated with a poor prognosis. Results: NOA2 is capable of inducing immune effector cell-mediated Ewing death in vitro via engagement of macrophages. Mice with metastatic Ewing tumors, treated with NOA2, experience tumor growth arrest and an associated increase in intratumoral macrophages. Further, incubation of macrophages and Ewing cells with NOA2, in conjunction with anti-PILRα antibody blockade in vitro, results in the reactivation of previously dormant macrophages possibly due to interrupted binding of Ewing CD99 to macrophage PILRα. Conclusions: These studies are the first to demonstrate the role of human immune effector cells in anti-CD99-mediated Ewing tumor death. We propose that the engagement of CD99 by NOA2 results in the recruitment of intratumoral macrophages. In addition, interruption of the CD99:PILRα checkpoint axis may be a relevant therapeutic approach to activate tumor-associated macrophages.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Topic Anti-Tumor Immune Responses 2.0)
►▼
Show Figures
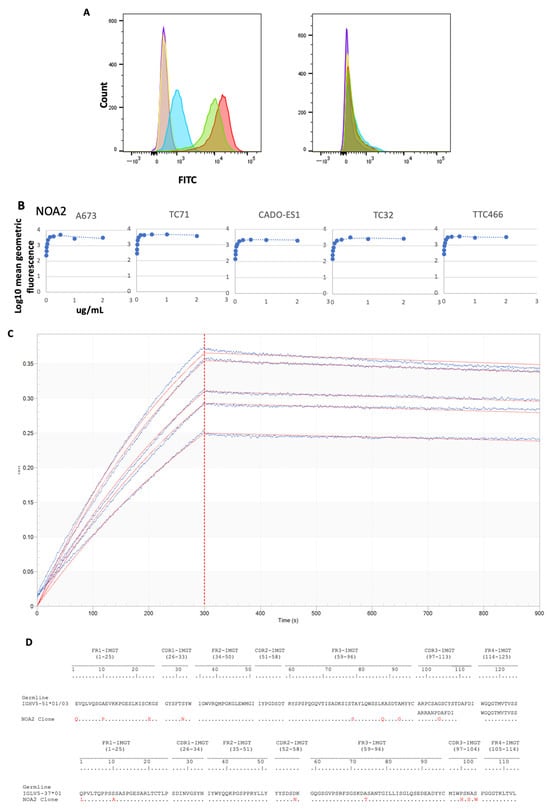
Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
New, Old, and Shared Antibody Specificities in Autoimmune Diseases
by
Loredana Frasca, Anna Mennella and Raffaella Palazzo
Antibodies 2024, 13(1), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/antib13010023 - 13 Mar 2024
Abstract
Autoantibodies represent a primary characteristic of many systemic autoimmune diseases [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New, Old, and Shared Antibody Specificities in Autoimmune Diseases)
Open AccessSystematic Review
Vitamin D Status in Patients with Primary Antiphospholipid Syndrome (PAPS): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
by
Md Asiful Islam, Saleh Ahmed, Shabiha Sultana, Sayeda Sadia Alam, Tareq Hossan, Wesam Gouda, Faisal Alsaqabi, Rosline Hassan and Przemysław J. Kotyla
Antibodies 2024, 13(1), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/antib13010022 - 13 Mar 2024
Abstract
Primary antiphospholipid syndrome (PAPS) is a systemic autoimmune disorder, characterised by consistently high levels of antiphospholipid antibodies, thrombosis, and/or pregnancy morbidity. Due to various suspected causes, deficient or insufficient levels of vitamin D in the serum have been reported in patients with PAPS;
[...] Read more.
Primary antiphospholipid syndrome (PAPS) is a systemic autoimmune disorder, characterised by consistently high levels of antiphospholipid antibodies, thrombosis, and/or pregnancy morbidity. Due to various suspected causes, deficient or insufficient levels of vitamin D in the serum have been reported in patients with PAPS; however, the reports have been sporadic and inconclusive. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to comprehensively evaluate the serum vitamin D levels in patients with PAPS compared to controls. A protocol was registered in PROSPERO (Registration No. CRD42019132128) and a systematic literature search was conducted through Google Scholar, PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, and ScienceDirect databases without restricting language and year. Pooled prevalence, mean difference (MD), and odds ratio (OR) along with 95% confidence intervals (CI) were determined by using a random effects model. Study quality was assessed by the Joana Brigg’s Institute (JBI) protocol and publication bias was evaluated by a trim and fill funnel plot, Begg’s, and Egger’s tests. The pooled prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency was found to be 32.2% [95% CI: 16.3–48.2] and 61.5% [95% CI: 40.2–82.8], respectively. Serum levels of vitamin D were considerably lower in the PAPS patients compared to controls (MD: −5.75, 95% CI: −9.73 to −1.77; p = 0.005). Multiple sensitivity analyses showed that the results remained statistically significant, demonstrating the robustness of this meta-analysis. No significant publication bias was detected in determining the MD of serum vitamin D levels in PAPS and controls. In conclusion, PAPS patients had greater rates of vitamin D deficiency or insufficiency, higher frequency of thrombosis, and lower serum vitamin D levels than healthy individuals.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antiphospholipid Antibodies)
►▼
Show Figures
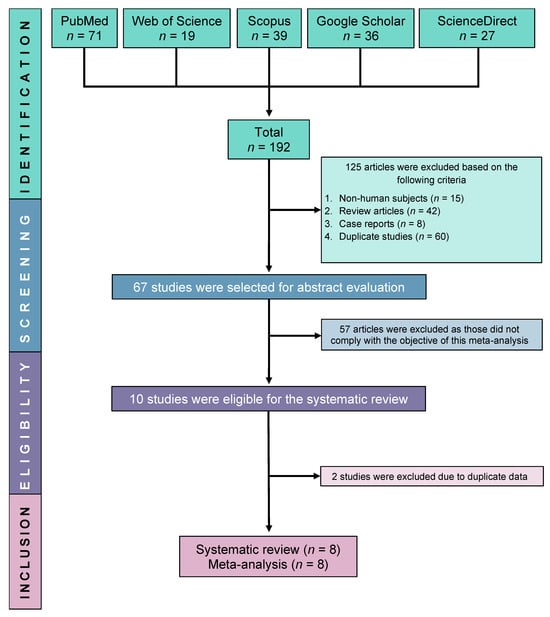
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Diagnosis and Management of Catastrophic Antiphospholipid Syndrome and the Potential Impact of the 2023 ACR/EULAR Antiphospholipid Syndrome Classification Criteria
by
Lucas Jacobs, Nader Wauters, Yahya Lablad, Johann Morelle and Maxime Taghavi
Antibodies 2024, 13(1), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/antib13010021 - 12 Mar 2024
Abstract
Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome (CAPS) is a rare and life-threatening condition characterized by the persistence of antiphospholipid antibodies and occurrence of multiple vascular occlusive events. CAPS currently remains a diagnostic challenge and requires urgent treatment. The diagnosis of CAPS is made difficult by classification
[...] Read more.
Catastrophic antiphospholipid syndrome (CAPS) is a rare and life-threatening condition characterized by the persistence of antiphospholipid antibodies and occurrence of multiple vascular occlusive events. CAPS currently remains a diagnostic challenge and requires urgent treatment. The diagnosis of CAPS is made difficult by classification criteria used as diagnostic criteria in clinical practice, knowledge derived from retrospective data and case reports, confounding clinical and biological features, and its rapid onset and mortality. The absence of prospective studies of CAPS limits the strength of evidence for guideline treatment protocols. This comprehensive review summarizes the current understanding of the disease, and discusses how the 2023 ACR/EULAR Antiphospholipid Syndrome Classification Criteria impact the definition and therapeutic management of CAPS, which is considered the most severe form of APS. The correct integration of 2023 ACR/EULAR APS classification criteria is poised to facilitate CAPS diagnosis, particularly in critical situations, offering a promising avenue for improved outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Antiphospholipid Antibodies)
►▼
Show Figures
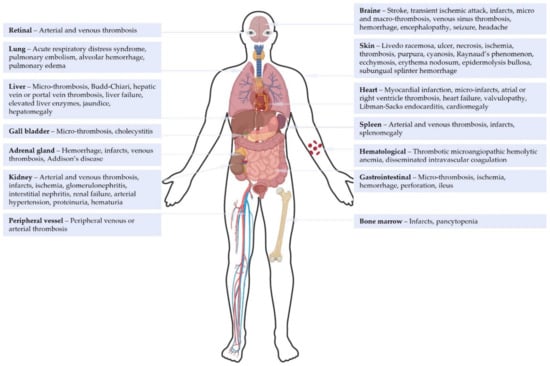
Figure 1
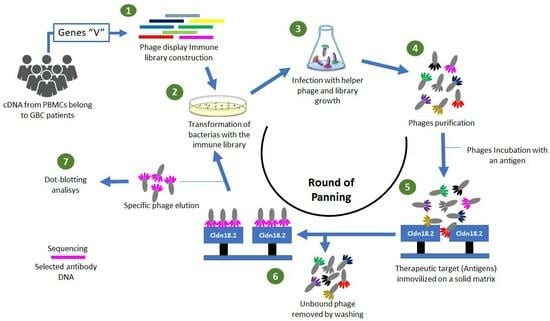
Open AccessArticle
Construction of a Human Immune Library from Gallbladder Cancer Patients for the Single-Chain Fragment Variable (scFv) Antibody Selection against Claudin 18.2 via Phage Display
by
Brian Effer, Daniel Ulloa, Camila Dappolonnio, Francisca Muñoz, Isabel Iturrieta-González, Loraine Cotes, Claudio Rojas and Pamela Leal
Antibodies 2024, 13(1), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/antib13010020 - 12 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Gallbladder cancer (GBC) is a very aggressive malignant neoplasm of the biliary tract with a poor prognosis. There are no specific therapies for the treatment of GBC or early diagnosis tools; for this reason, the development of strategies and technologies that facilitate or
[...] Read more.
Gallbladder cancer (GBC) is a very aggressive malignant neoplasm of the biliary tract with a poor prognosis. There are no specific therapies for the treatment of GBC or early diagnosis tools; for this reason, the development of strategies and technologies that facilitate or allow an early diagnosis of GBC continues to be decisive. Phage display is a robust technique used for the production of monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) involving (1) the generation of gene libraries, (2) the screening and selection of isoforms related to an immobilized antigen, and (3) the in vitro maturation of the affinity of the antibody for the antigen. This research aimed to construct a human immune library from PBMCs of GBC patients and the isolation of scFv-phage clones with specificity against the larger extracellular loop belonging to claudin 18.2, which is an important biomarker overexpressed in GBC as well as gastric cancer. The immune-library-denominated GALLBLA1 was constructed from seven GBC patients and has a diversity of 6.12 × 1010 pfu mL−1. After three rounds of panning, we were able to identify clones with specificity against claudin 18.2. GALLBLA1 can contribute to the selection, isolation, and recombinant production of new human mAbs candidates for the treatment of gastrointestinal cancers.
Full article
Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Performance Characteristics and Limitations of the Available Assays for the Detection and Quantitation of Monoclonal Free Light Chains and New Emerging Methodologies
by
Hannah V. Giles and Kamaraj Karunanithi
Antibodies 2024, 13(1), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/antib13010019 - 11 Mar 2024
Abstract
Light chain measurements form an essential component of the testing strategy for the detection and monitoring of patients with suspected and/or proven plasma cell disorders. Urine-based electrophoretic assays remain at the centre of the international guidelines for response assessment but the supplementary role
[...] Read more.
Light chain measurements form an essential component of the testing strategy for the detection and monitoring of patients with suspected and/or proven plasma cell disorders. Urine-based electrophoretic assays remain at the centre of the international guidelines for response assessment but the supplementary role of serum-free light chain (FLC) assays in response assessment and the detection of disease progression due to their increased sensitivity has been increasingly recognised since their introduction in 2001. Serum FLC assays have also been shown to be prognostic across the spectrum of plasma cell disorders and are now incorporated into risk stratification scores for patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), smouldering multiple myeloma, and light chain amyloidosis (AL amyloidosis), as well as being incorporated into the criteria for defining symptomatic multiple myeloma. There are now multiple different commercially available serum FLC assays available with differing performance characteristics, which are discussed in this review, along with the implications of these for patient monitoring. Finally, newer methodologies for the identification and characterisation of monoclonal FLC, including modifications to electrophoretic techniques, mass spectrometry-based assays and Amylite, are also described along with the relevant published data available regarding the performance of each assay.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Antibody-Based Diagnostics)
►▼
Show Figures
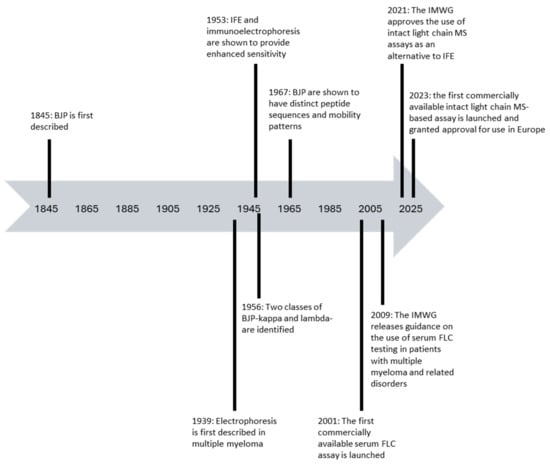
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Episomal Vectors for Stable Production of Recombinant Proteins and Engineered Antibodies
by
Ian Fallahee and Daniel Hawiger
Antibodies 2024, 13(1), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/antib13010018 - 11 Mar 2024
Abstract
There is tremendous interest in the production of recombinant proteins, particularly bispecific antibodies and antibody–drug conjugates for research and therapeutic use. Here, we demonstrate a highly versatile plasmid system that allows the rapid generation of stable Expi293 cell pools by episomal retention of
[...] Read more.
There is tremendous interest in the production of recombinant proteins, particularly bispecific antibodies and antibody–drug conjugates for research and therapeutic use. Here, we demonstrate a highly versatile plasmid system that allows the rapid generation of stable Expi293 cell pools by episomal retention of transfected DNA. By linking protein expression to puromycin resistance through an attenuated internal ribosome entry site, we achieve stable cell pools producing proteins of interest. In addition, split intein–split puromycin-mediated selection of two separate protein expression cassettes allows the stable production of bispecific antibody-like molecules or antibodies with distinct C-terminal heavy chain modifications, such as an antigen on one chain and a sortase tag on the other chain. We also use this novel expression system to generate stable Expi293 cell pools that secrete sortase A Δ59 variant Srt4M. Using these reagents, we prepared a site-specific drug-to-antibody ratio of 1 antibody–siRNA conjugate. We anticipate the simple, robust, and rapid stable protein expression systems described here being useful for a wide variety of applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Antibody Discovery and Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures
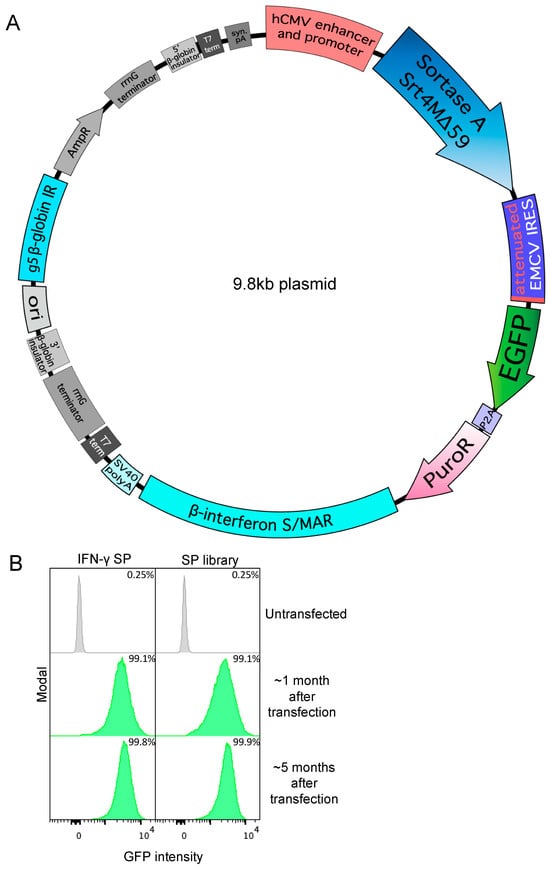
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Platform-Specific Fc N-Glycan Profiles of an Antisperm Antibody
by
Ellena Nador, Chaoshuang Xia, Philip J. Santangelo, Kevin J. Whaley, Catherine E. Costello and Deborah J. Anderson
Antibodies 2024, 13(1), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/antib13010017 - 06 Mar 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
IgG Fc N-glycosylation is necessary for effector functions and is an important component of quality control. The choice of antibody manufacturing platform has the potential to significantly influence the Fc glycans of an antibody and consequently alter their activity and clinical profile.
[...] Read more.
IgG Fc N-glycosylation is necessary for effector functions and is an important component of quality control. The choice of antibody manufacturing platform has the potential to significantly influence the Fc glycans of an antibody and consequently alter their activity and clinical profile. The Human Contraception Antibody (HCA) is an IgG1 antisperm monoclonal antibody (mAb) currently in clinical development as a novel, non-hormonal contraceptive. Part of its development is selecting a suitable expression platform to manufacture HCA for use in the female reproductive tract. Here, we compared the Fc glycosylation of HCA produced in two novel mAb manufacturing platforms, namely transgenic tobacco plants (Nicotiana benthamiana; HCA-N) and mRNA-mediated expression in human vaginal cells (HCAmRNA). The Fc N-glycan profiles of the two HCA products were determined using mass spectrometry. Major differences in site occupancy, glycan types, and glycoform distributions were revealed. To address how these differences affect Fc function, antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP) assays were performed. The level of sperm phagocytosis was significantly lower in the presence of HCA-N than HCAmRNA. This study provides evidence that the two HCA manufacturing platforms produce functionally distinct HCAs; this information could be useful for the selection of an optimal platform for HCA clinical development and for mAbs in general.
Full article
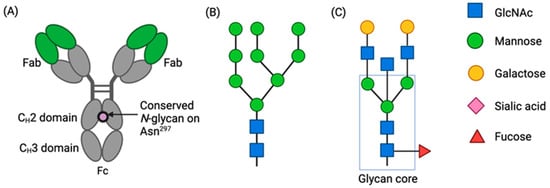
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Immunogenicity and Loss of Effectiveness of Biologic Therapy for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients Due to Anti-Drug Antibody Development
by
Tsvetelina Velikova, Metodija Sekulovski and Monika Peshevska-Sekulovska
Antibodies 2024, 13(1), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/antib13010016 - 26 Feb 2024
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Many patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) experience a loss of effectiveness to biologic therapy (i.e., anti-TNF therapy, etc.). Therefore, in addition to the adverse effects of the treatment, these patients also face failure to achieve and maintain remission. Immunogenicity, the process of
[...] Read more.
Many patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) experience a loss of effectiveness to biologic therapy (i.e., anti-TNF therapy, etc.). Therefore, in addition to the adverse effects of the treatment, these patients also face failure to achieve and maintain remission. Immunogenicity, the process of production of antibodies to biological agents, is fundamental to the evolution of loss of response to treatment in IBD patients. The presence of these antibodies in patients is linked to decreased serum drug levels and inhibited biological activity. However, immunogenicity rates exhibit significant variability across inflammatory disease states, immunoassay formats, and time periods. In this review, we aimed to elucidate the immunogenicity and immune mechanisms of antibody formation to biologics, the loss of therapy response, clinical results of biological treatment for IBD from systematic reviews and meta-analyses, as well as to summarize the most recent strategies for overcoming immunogenicity and approaches for managing treatment failure in IBD.
Full article
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Development of a Bispecific IgG1 Antibody Targeting BCMA and PDL1
by
Irene Cattaneo, Sylvie Choblet, Rut Valgardsdottir, Muriel Roth, Annamaria Massafra, Marten Beeg, Marco Gobbi, Martine Duonor-Cerutti and Josée Golay
Antibodies 2024, 13(1), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/antib13010015 - 20 Feb 2024
Abstract
We designed, produced, and purified a novel IgG1-like, bispecific antibody (bsAb) directed against B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA), expressed by multiple myeloma (MM) cells, and an immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI), PDL1, expressed in the MM microenvironment. The BCMA×PDL1 bsAb was fully characterized in vitro.
[...] Read more.
We designed, produced, and purified a novel IgG1-like, bispecific antibody (bsAb) directed against B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA), expressed by multiple myeloma (MM) cells, and an immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI), PDL1, expressed in the MM microenvironment. The BCMA×PDL1 bsAb was fully characterized in vitro. BCMA×PDL1 bound specifically and simultaneously, with nM affinity, to both native membrane-bound antigens and to the recombinant soluble antigen fragments, as shown by immunophenotyping analyses and surface plasmon resonance (SPR), respectively. The binding affinity of bsAb for PDL1 and BCMA was similar to each other, but PDL1 affinity was about 10-fold lower in the bsAb compared to parent mAb, probably due to the steric hindrance associated with the more internal anti-PDL1 Fab. The bsAb was also able to functionally block both antigen targets with IC50 in the nM range. The bsAb Fc was functional, inducing human-complement-dependent cytotoxicity as well as ADCC by NK cells in 24 h killing assays. Finally, BCMA×PDL1 was effective in 7-day killing assays with peripheral blood mononuclear cells as effectors, inducing up to 75% of target MM cell line killing at a physiologically attainable, 6 nM, concentration. These data provide the necessary basis for future optimization and in vivo testing of this novel bsAb.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Antibody-Based Therapeutics)
►▼
Show Figures
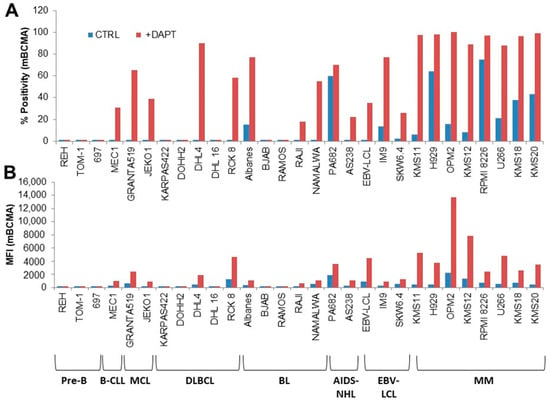
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
An Engineered Mouse Model That Generates a Diverse Repertoire of Endogenous, High-Affinity Common Light Chain Antibodies
by
Yinghui Rong, I-Ling Chen, Lance Larrabee, Manali S. Sawant, Germaine Fuh and Patrick Koenig
Antibodies 2024, 13(1), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/antib13010014 - 08 Feb 2024
Abstract
Bispecific antibodies have gained increasing popularity as therapeutics as they enable novel activities that cannot be achieved with monospecific antibodies. Some of the most popular bispecific formats are molecules in which two Fab arms with different antigen specificities are combined into one IgG-like
[...] Read more.
Bispecific antibodies have gained increasing popularity as therapeutics as they enable novel activities that cannot be achieved with monospecific antibodies. Some of the most popular bispecific formats are molecules in which two Fab arms with different antigen specificities are combined into one IgG-like molecule. One way to produce these bispecific molecules requires the discovery of antibodies against the two antigens of interest that share a common light chain. Here, we present the generation and characterization of a common light chain mouse model, in which the endogenous IGKJ cluster is replaced with a prearranged, modified murine IGKV10-96/IGKJ1 segment. We demonstrate that genetic modification does not impact B-cell development. Upon immunization with ovalbumin, the animals generate an antibody repertoire with VH gene segment usage of a similar diversity to wildtype mice, while the light chain diversity is restricted to antibodies derived from the prearranged IGKV10-96/IGKJ1 germline. We further show that the clonotype diversity of the common light chain immune repertoire matches the diversity of immune repertoire isolated from wildtype mice. Finally, the common light chain anti-ovalbumin antibodies have only slightly lower affinities than antibodies isolated from wildtype mice, demonstrating the suitability of these animals for antibody discovery for bispecific antibody generation.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Antibody Discovery and Engineering)
►▼
Show Figures
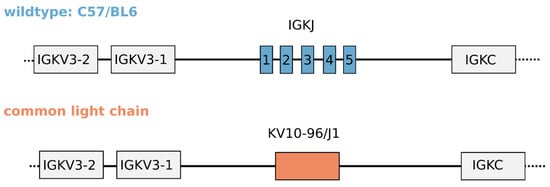
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Antibodies Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Topical Advisory Panel
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Editor’s Choice Articles
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Antibodies, Cancers, Immuno, IJMS, Vaccines
Anti-Tumor Immune Responses 2.0
Topic Editors: Massimo Zollo, Renata GrifantiniDeadline: 31 August 2024

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Antibodies
Autoimmune and Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases: Potential Biomarkers, Antibodies Response and New Therapies
Guest Editor: Marino ParoliDeadline: 30 April 2024
Special Issue in
Antibodies
Unravelling Effector Functions of B cells in Infectious Diseases and Cancer
Guest Editor: Farhat AfrinDeadline: 20 May 2024
Special Issue in
Antibodies
Antiphospholipid Antibodies
Guest Editors: Md Asiful Islam, Przemysław KotylaDeadline: 30 June 2024
Special Issue in
Antibodies
Review Collection on Humoral Immunity
Guest Editors: Jagadeesh Bayry, Linqi ZhangDeadline: 31 July 2024
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Antibodies
Computational Antibody and Antigen Design
Collection Editor: Buyong Ma








