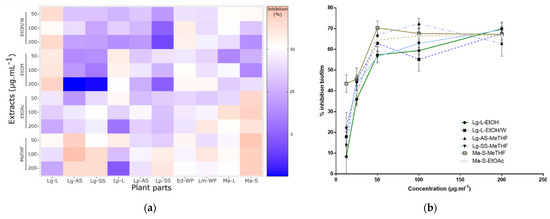
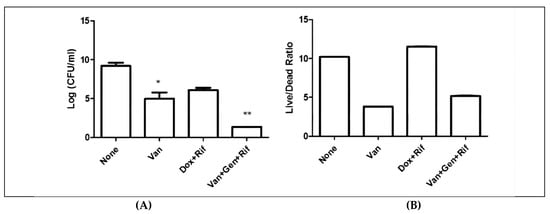
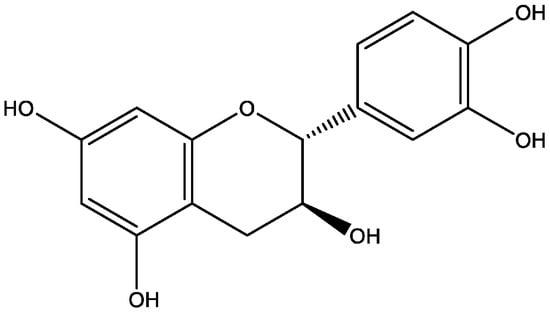
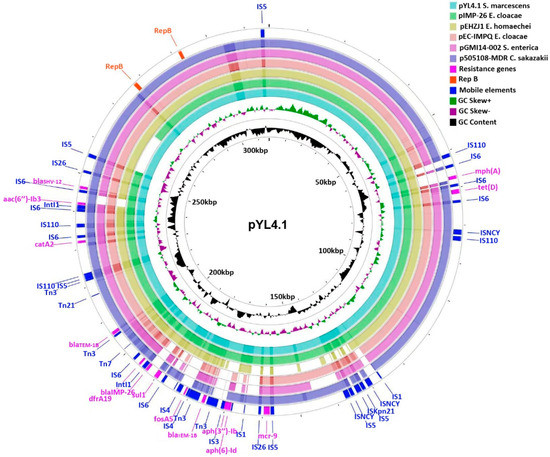
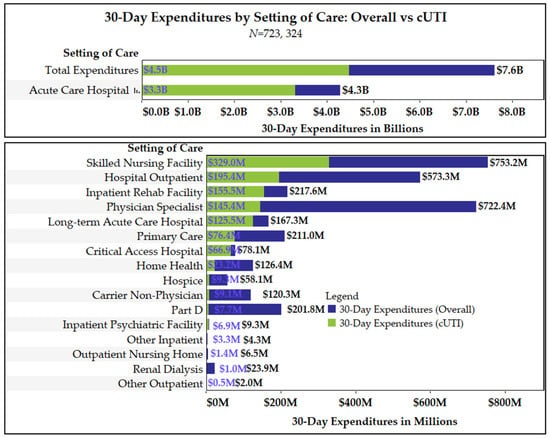
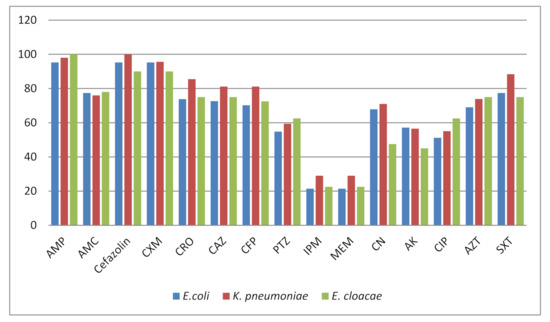
Antimicrobial Resistance and Anti-Biofilms (Closed)
A topical collection in Antibiotics (ISSN 2079-6382). This collection belongs to the section "Antibiofilm Strategies".
Viewed by 35048Editors
Interests: antimicrobial resistance; clinical microbiology; mechanisms for microbial drug resistance
Interests: biofilms; anti-biofilms technology; anti-biofilms nanomaterials
Interests: phytochemicals; probiotics; prebiotics; gut microbiota; nutrition; functional food
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: preventive veterinary medicine; veterinary biotechnology and biological products
Interests: biofilm; foodborne microorganisms; antimicrobial resistance; pathogenicity and virulence; stress response; quorum sensing; polymicrobial interaction
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: antimicrobial resistance; biofilms; viable but non-culturable (VBNC) and persistence; stress response; polymicrobial interaction
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
This Topical Collection is created in cooperation with Asia-Pacific Biofilms (www.asiapacificbiofilms.org), one of the three major international conferences in the field of biofilms along with EuroBiofilms and ASM Biofilms. We welcome advanced research articles and reviews related to antimicrobial resistance and anti-biofilms. There are three major research avenue of this Topical Collection, described below.
1. Antimicrobial resistance in microorganisms: epidemiology and molecular mechanism (led by Dr. Dingqiang Chen)
The emergence and worldwide spread of antimicrobial resistance in microorganisms is a significant threat to human health. The epidemiology of infection by resistant microbes is still not clear in many areas. Investigating the underlying mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance is important for the control of infections caused by resistant microorganisms.
This research avenue seeks manuscript submissions that can improve our understanding of the epidemiology and molecular mechanism on antimicrobial resistance. Manuscripts regarding the prevalence of resistant microbes, the emergence and evolution of resistance, and the molecular investigation of resistance mechanisms, such as genomic or proteomic analysis, are welcome.
2. New antibiofilm strategy against fungal and/or bacterial biofilms (led by Dr. Yulong Tan)
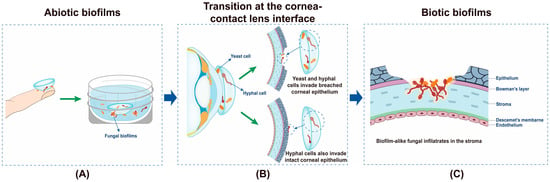
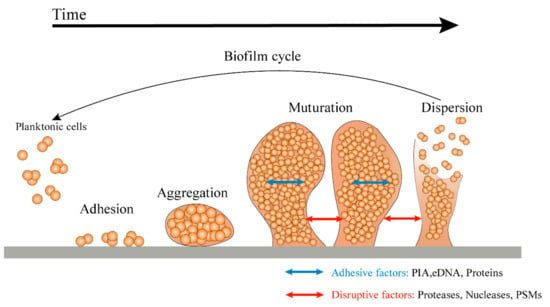
Microorganisms in nature produce biofilms to resist the pressures of the environment. The outer layer of the mature biofilm is a polysaccharide protein complex secreted by bacteria, and the inner layer is the coated bacteria. Bacterial biofilm formation is a dynamic process, which is mainly divided in four stages—initial adhesion, irreversible adhesion, aggregation, and development and abscission. Biofilms can protect microbial cells from antibiotics, chlorine, detergent, host immune defense mechanism, and other factors. The resistance of microbes to antimicrobial substances in biofilms is 10 times or even 1000 times higher than that of planktonic mode. At present, the conventional chemical or physical methods are unable to completely remove biofilms. Traditional antibiotics can kill the cells inside, but thye will cause drug resistance. In addition, the "inactive" biofilm structure can still promote the adhesion and regeneration of the biofilms of other microorganisms. Therefore, in addition to the microbial cells in thin biofilms, the biofilm matrix itself should also be a target. As a result, novel antibiofilm strategies that are able to interfere with cells inside and disassemble the biofilm matrix are needed in order to inhibit biofilm formation and/or disrupt persistent biofilms. At present, the study of biofilm formation and antibiofilm strategies has been of utmost importance in scientific research.
3. Influence of Functional Material-Based Encapsulation/Delivery on the Antimicrobial and Antivirulent Effects of Natural Compounds (led by Dr. Renyou Gan)
Many natural compounds exhibit antimicrobial and antivirulent effects. Different functional materials, such as nanoparticles (e.g., lipid-based, polymer-based, carbohydrate-based, protein-based, metal-based, and nucleic acid-based nanoparticles), hydrogels, as well as micro/nano emulsions and packaging materials, can be used to encapsulate/deliver natural compounds and further enhance their antimicrobial and antivirulent effects. Therefore, understanding the antimicrobial and antivirulent effects of these functional material-encapsulated/delivered natural compounds as well as their underlying mechanism of action can provide a scientific basis for their further applications as antibiotic alternatives.
This research avenue seeks manuscript submissions that can improve our understanding of the influence of functional material-based encapsulation/delivery on the antimicrobial and antivirulent effects of natural compounds. Manuscripts regarding the production and characteristics of these functional material-encapsulated/delivered natural compounds, their in vitro and in vivo antimicrobial and antivirulent effects, and their potential applications, such as in food and medicine, are welcome.
Dr. Ding-Qiang Chen
Dr. Yulong Tan
Dr. Ren-You Gan
Prof. Dr. Guanggang Qu
Prof. Dr. Zhenbo Xu
Dr. Junyan Liu
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Antibiotics is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2900 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.