Smart Farming in Dairy Production (Closed)
A topical collection in Animals (ISSN 2076-2615). This collection belongs to the section "Cattle".
Viewed by 60857Editors
Interests: dairy cow; nutrition and metabolism; smart farming; integrating knowledge; vitamins and minerals; precision feeding
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Worldwide dairy production has drastically evolved during the last decades; from hand milking to automatic milking system; from feeding hay and pasture to total mixed ration formulated using a specialized software according to cow requirements. Here are only few examples that allowed more than doubling yearly milk production of cows. Over the last few years, the concept of smart farming has emerged and there has been a tremendous increase of cow sensor use that, by generating large dataset, helps monitoring cow health, reproduction, productivity, and welfare. The technology can also be used to better meet cow nutrient requirements. We are nowadays aware that optimizing cow productivity can be done by integrating knowledge on precision feeding (i.e. better suit nutrient requirements at a given stage), cow health and welfare. Moreover, the impact of any recommendations at the farm level on the ecosystem should not be discarded from the integration.
We are seeking original research papers about how technology can be used to better meet nutrient requirements of dairy cows, better monitor cow health disorders related to nutrition or better monitor cow nutrient status. Moreover, topics may be related to precision feeding, smart farming, and integration of the ecosystem by studying the impact of nutrient supply and excretion in manure relating to dairy production.
Dr. Mélissa DuplessisDr. Liliana Fadul-Pacheco
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Animals is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- dairy cow
- nutrient requirements
- technology use
- precision feeding
- health
- ecosystem integration
- smart farming
Planned Papers
The below list represents only planned manuscripts. Some of these manuscripts have not been received by the Editorial Office yet. Papers submitted to MDPI journals are subject to peer-review.
1. Review
Opportunities to harness data from precision technologies to manage feed and improve feed efficiency in dairy cattle.
Cori J Siberski* and James E Koltes*
Department of Animal Science, Iowa State University
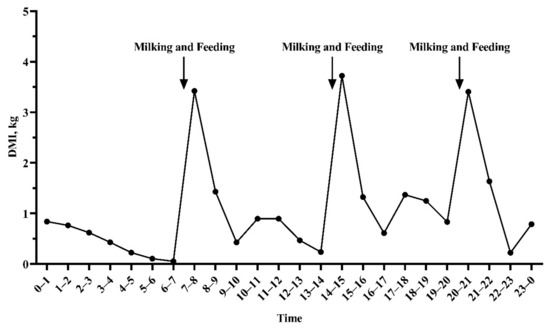
Abstract: Feed use and management plays a large role in the sustainability of the dairy industry, with economic, environmental, and social implications. Unfortunately, collection of feed intake data is limited to the research sector because of the costs associated with the technology and labor required to measure individual cow phenotypes. Improvement of feed efficiency in the industry will require routinely collected data from commercial farms. Therefore, research is needed to identify affordable and portable technologies to collect feed intake and related measurements. Interest has grown in the use of precision technologies (ex: wearable sensors, image data, global positioning systems, and milk monitoring systems) as possible indicators of feed intake, due to their practicality and increasing use in commercial farms. Additional research is needed to investigate new high-throughput phenotypes, genomics data, and prediction methods to improve the accuracy of feed intake prediction. Critical consideration needs to be given to how feed intake or efficiency is defined, changes in efficiency at different stages of life, health, management systems, and environmental factors such as feed quality and climate when developing future precision feeding tool. The ability of the dairy industry to utilize diverse data has facilitated major improvements in production efficiency. Capitalizing on precision technologies and high-throughput data could impel the next advance in precision feed management.
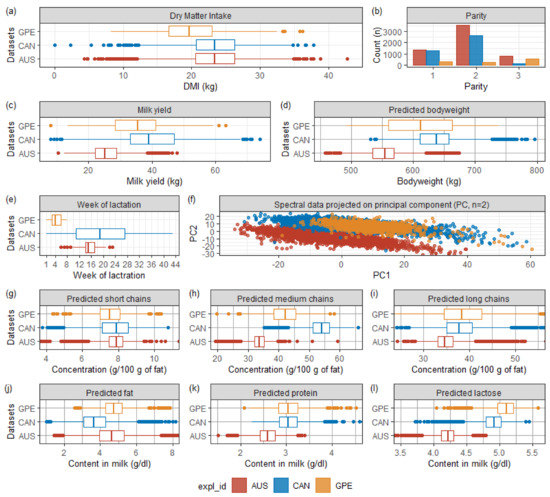
2. Prediction of dry matter intake ingested by dairy cows from lactation stage, parity, milk yield and milk mid-infrared spectrum using different machine learning techniques
TEDDE A., GRELET C., HO P.N., PRYCE J.E., GENGLER N., DEHARENG F., CONSORTIUM G.P.L.U.S.E, SOYEURT H.
3. Multiple breeds and countries predictions of mineral contents in milk from milk mid-infrared spectrometry.
Christophe O.1, Grelet C.1, Reuter V.1, Bertozzi C.2, Veselko D.3, Lecomte C.4, Höckels P.5, Werner A.6, Auer F.J.7, Gengler N.8, Dehareng F.1, Soyeurt H.8
4. The use of fatty acid profiles from milk recording samples to predict body weight change of dairy cows in early lactation in commercial dairy farms
Dettmann,*† D. Warner,* A. J. Buitenhuis,‡ M. Kargo,‡§ A. M. Hostrup Kjeldsen,§ N.H. Nielsen,# D. M. Lefebvre,* and D. E. Santschi*
*Lactanet, Sainte-Anne-de-Bellevue, QC, H9X3R4, Canada
*Lactanet, Sainte-Anne-de-Bellevue, QC, H9X3R4, Canada
†LKV Niedersachsen e.V., 26789 Leer, Germany
‡Aarhus University, Center for Quantitative Genetics and Genomics, 8830 Tjele, Denmark
§ SEGES, 8200 Aarhus N, Denmark
#RYK, 8200 Aarhus N, Denmark
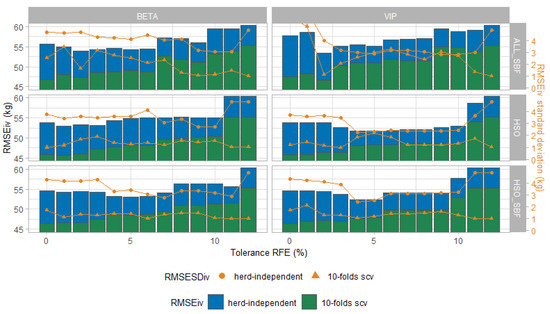
Abstract: Cows typically mobilize body reserves to maintain milk fat production during early lactation, which is reflected in the milk fatty acid (FA) profile. Milk FA can be routinely predicted by Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy. This rapid milk analysis offers therefore an opportunity to develop an early indicator for body weight change (BWC) based on the milk FA profile. The objective of this study was to validate if the milk FA profile can be used to predict BWC in early lactating cows in commercial dairy farms. Data originated from 16,847 Danish Holstein cows at 7-35 days in milk across 165 herds in Denmark between March 2015 and March 2017 with body weight (BW) records from floor scales in Lely automatic milking systems at each milking. Milk FA in monthly test-day milk samples were predicted by FT-IR. Data for BWC predictions included parity, stage of lactation, and test day data for milk production and components (fat, protein, and FA concentrations). Daily BWC (mean ± standard deviation) was −0.52 ± 2.65 g/kg of BW (first parity), −0.64 ± 2.82 g/kg of BW (second parity) and −0.82 ± 5.53 g/kg of BW (third parity). Predictions of BWC were based on a random forest model. Body weight loss was mainly explained by decreased short-chain FA (SCFA; C4:0–C10:0) and increased C18:0 FA. The root mean square error (RMSE) of prediction after cross-validation was 1.79 g/kg of BW (R2 of 0.94). Model evaluation with previously unseen BWC records resulted in reduced prediction performance (RMSE of 2.33 g/kg of BW; R2 of 0.31). An early warning system may thus be implemented for cows with a large BW loss during early lactation based on the FT-IR milk FA profiles, but model performance should be improved, ideally by using the full FT-IR milk spectra.
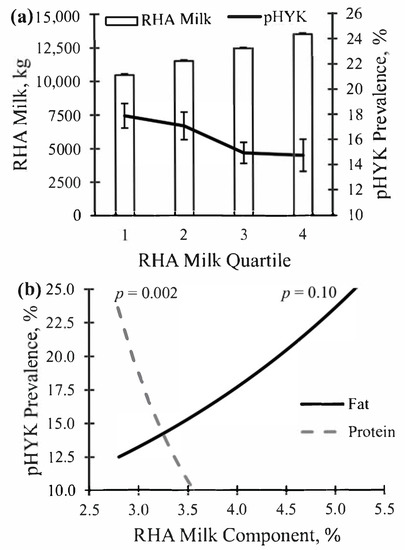
5. Hyperketonemia predictions provide an on-farm management tool with epidemiological insights.
Pralle, R., Fourdraine, R. and White, H. M.
University of Wisconsin Madison, Madison, WI, USA
6. Assessment of the relationship between postpartum hyperketonemia and mid-lactation residual feed intake in Holstein dairy cows
Martin, M. J., K. A. Weigel, and H. M. White
7. Data Science Tools for Smart Farming: Moving Academic Projects into Practice within Dairy Brain
Ferris, M.C., Wangen, S.R., Issaka, S.M. and Shortnacy, L.
University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison-WI, USA
Abstract: We describe a decision support tool – the Dairy Brain – that couples together data analytics tools with a suite of applications to integrate the cow, herd and economic data in ways that inform management, operational and animal health improving practices and controls uncertainties. Specific applications are often generated from research papers in academic journals using specialized data collection and formats. We show how to transform these into decision support tools to inform improved operation of modern-day dairy farms. The paper demonstrates a particular application for feed efficiency and outlines the design of an application programming interface to allow data from multiple sources that is gathered, cleaned and organized to be disseminated using an agricultural data hub into a working tool that uses it and machine learning to provide additional value to the stakeholders or users.
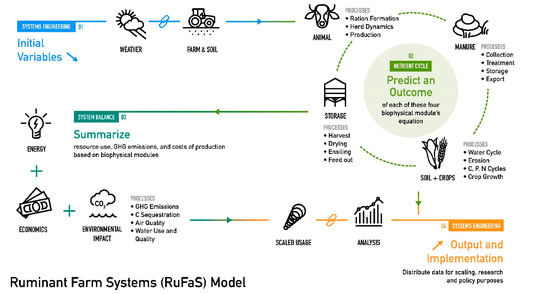
8. Connecting Precision Feed Management to Environmental Outcomes with the Ruminant Farm Systems (RuFaS) Model
Reed, Kristan F.1, Tayler L. Hansen1, Manfei Li2, Jinghui Li3, Victor E. Cabrera2
1 Department of Animal Science, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14850
2Department of Dairy Science, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison WI 53705
3Department of Animal Science, University of California -Davis, Davis CA 95616
Abstract: Feed efficiency is a primary driver of economic and environmental sustainability for dairy producers. Metrics like total feed costs, milk production, and income over feed costs connect feed efficiency to economic outcomes, but linking environmental outcomes to improved feed efficiency is more complex as it requires an integrated system approach. The Ruminant Farm Systems (RuFaS) model simulates nutrient cycling, production, and environmental impacts under various conditions and it’s modular is customizable to represent both current and future management systems. Through this flexible structure, RuFaS can assess novel management practices that improve feed efficiency such as herd-level nutritional grouping or cow-level residual feed intake and quantify their impacts on environmental outcomes like enteric methane and manure production.
9. Adoption of precision technologies by Brazilian dairy farms: the farmer’s perception
R. Silvi*, L. G. R. Pereira1†, C. A. V. Paiva †, T. R. Tomich†, M. M. Campos†, F. S. Machado†, V. T. Amorim‡, S. G. Coelho‡, L. C.S Gonçalves‡, J.R.R. Dórea+
* Universidade Estadual de Santa Cruz, Ilhéus, Bahia, Brazil, 45662-900
† Brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation – Embrapa Dairy Cattle, Juiz de Fora, Minas Gerais, Brazil, 36038-330
‡Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais, Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais, Brazil, 31270-901
+Department of Animal and Dairy Sciences, University of Wisconsin, Madison 53706, United States
Abstract: The use of precision farming technologies, such as milking robots, automated calf feeders, wearable sensors, and others, has significantly increased in dairy operations over the last few years. The growing interest for such technologies to reduce labor, maximize productivity, and increase profitability is becoming noticeable in several countries, including Brazil. Information regarding technology adoption, perception, and effectiveness in dairy farms could shed light on challenges that need to be addressed by scientific research and extension programs. In this context, we created and applied a survey to: i) characterize Brazilian dairy farms that adopt precision technologies; ii) identify the main technologies used; and iii) investigate the motivation to invest in precision farming technologies. An online survey was distributed to 372 Brazilian farms between 2019 to 2020. The South of Brazil was the region with the larger adoption of precision technologies. The standard Brazilian farm using precision farm technologies has free-stalls or compost bedded pack systems, midline piped milking machines as milking parlor, and Holstein as the main breed. Among the technologies adopted by Brazilian producers, the most frequent were: automatic weighing systems (36%), milking parlor separation gate (17%), and cow activity meters (10%). Producers scored a list of technologies on usefulness using a 5-point scale (from 1 = not useful to 5 = useful). Producers indicated (mean ± SD) automatic weighing, milk flow detection systems (4.03 ± 1.23), automatic mastitis detectors (3.98 ± 1.22), and cow activity meters (3.53 ± 1.33) to be the most useful. Producers were asked to score (from 1 = not important to 5 = important) the reasons to purchase a precision dairy farming technology from a predetermined list of technologies. Producers indicated that the availability of technical support (4.48 ± 0.95), total investment cost (4.46 ± 0.93), and user-friendly interface (4.32 ± 0.91) are the most important factors when deciding whether to implement a technology. On the other hand, producers indicated that investment in other areas (22%), the uncertainty of return on investment (20.4%), and the lack of integration between the technologies and the main management software used in the farm are the most important factors when deciding to do not invest in precision technologies.
Keywords: cattle, sensor, livestock, smart farm, survey